- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记3.2.1 Meiosis
Meiosis
- There are two processes by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell can divide. These are:
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
Mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells and is the type of cell division used for growth, repair of damaged tissues, replacement of cells and asexual reproduction
- Meiosis gives rise to cells that are genetically different from each other and is the type of cell division used to produce gametes (sex cells)
- During meiosis, the nucleus of the original 'parent' cell undergoes two rounds of division. These are:
- Meiosis I
- Meiosis II
Meiosis I
- The nucleus of the original 'parent' cell is diploid (2n) i.e. it contains two sets of chromosomes
- Before meiosis I, these chromosomes replicate
- During meiosis I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes are split up, to produce two haploid (n) nuclei
- At this point, each chromosome still consists of two chromatids
Note that the chromosome number halves (from 2n to n) in the first division of meiosis (meiosis I), not the second division (meiosis II)
Meiosis II
- During meiosis II, the chromatids that make up each chromosome separate to produce four haploid (n) nuclei
- At this point, each chromosome now consists of a single chromatid
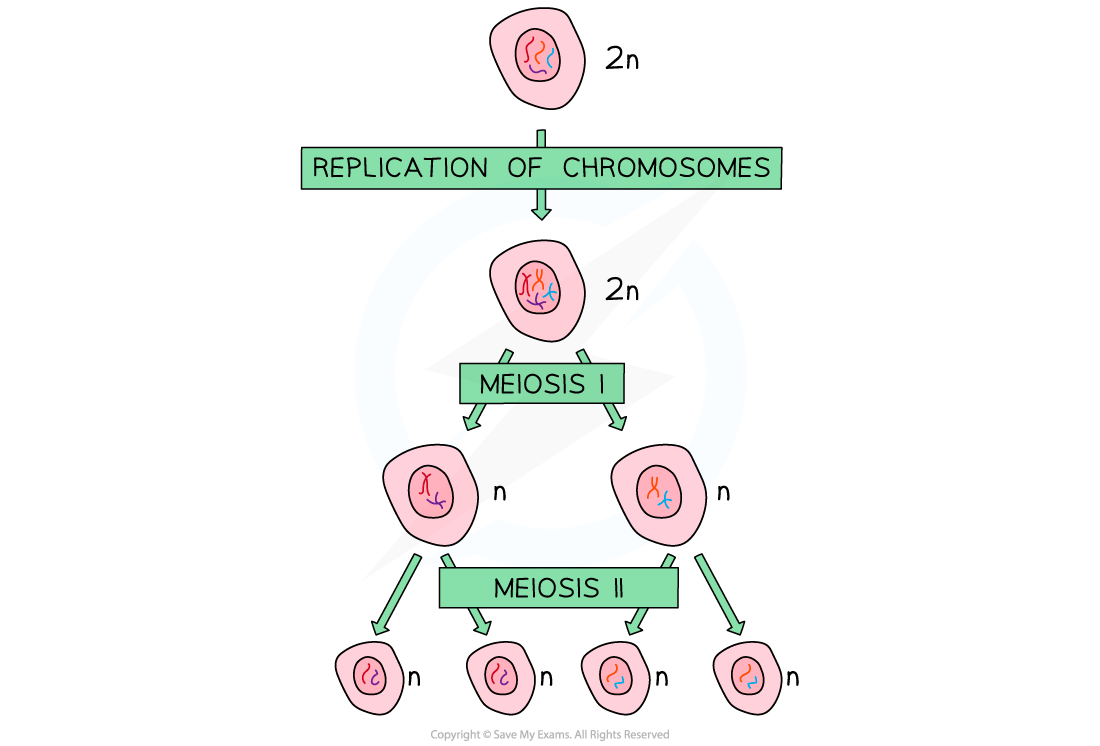
One diploid nucleus divides by meiosis to produce four haploid nuclei
Discovery of Meiosis
NOS: Making careful observations; meiosis was discovered by microscope examinations of dividing germ-line cells
- In the 19th century, microscopes were developed that could be used to view certain internal cell structures
- Around this time, it was also discovered that certain dyes could be used to stain (and observe) the cell nucleus
- The use of these dyes eventually led to the discovery of thread-like structures inside dividing nuclei
- These were name chromosomes
In the 1880s, a group of German biologists used these new developments to make detailed observations of dividing nuclei
- Their careful observations led to the discovery of the process of meiosis and a basic understanding of how it occurs
One key observation was made by viewing the chromosomes in specific cells in an organism known as the horse threadworm (Parascaris equorum)
- It was observed that the nuclei of their egg and sperm cells contained two chromosomes, whereas the nuclei of a fertilised egg contained four chromosomes
- This suggested that the chromosome number had been doubled by the process of fertilisation
- This led to the hypothesis that, at some point in every generation, a special type of nuclear division must occur that halves the chromosome number
The specific sequence of events in meiosis was finally discovered by carefully observing cells from the ovaries of European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) between 0 and 28 days old
- This was possible because in females of this species, certain cells in the ovaries start undergoing meiosis from birth and the process continues slowly over a period of many days
The initial discovery of meiosis (as well as the following series of discoveries that revealed to scientists how it occurs) was made possible through careful scientific observations
- Such careful observations are needed in order to validate the claims and discoveries that scientists make, as scientific evidence is required. Careful observations can enable scientists to collect evidence that allows theories to be developed
- The use of apparatus, dyes, sensors, amongst many other scientific tools, allows scientists to make these precise and accurate observations
- The methods used to make such observations must be able to be repeated so that the results can be confirmed by other scientists if necessary
Sexual Life Cycle
The life cycles of organisms can be sexual or asexual (some organisms are capable of both)
- In an asexual life cycle, the offspring are genetically identical to the parent (they have exactly the same chromosomes)
- In a sexual life cycle, the offspring are genetically distinct from each other and from each of the parents (their chromosomes are different, causing them to be genetically distinct)
The halving of the chromosome number during meiosis is very important for a sexual life cycle as it allows for the fusion of gametes
- Sexual reproduction is a process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote (fertilised egg cell) and the production of offspring that are genetically distinct from each other
- This fusion of gamete nuclei is known as fertilisation
- Fertilisation doubles the number of chromosomes each time it occurs
- This is why it is essential that the chromosome number is also halved at some stage in organisms with a sexual life cycle, otherwise the chromosome number would keep doubling every generation
- This halving of the chromosome number occurs during meiosis
- In animals, this halving occurs during the creation of gametes
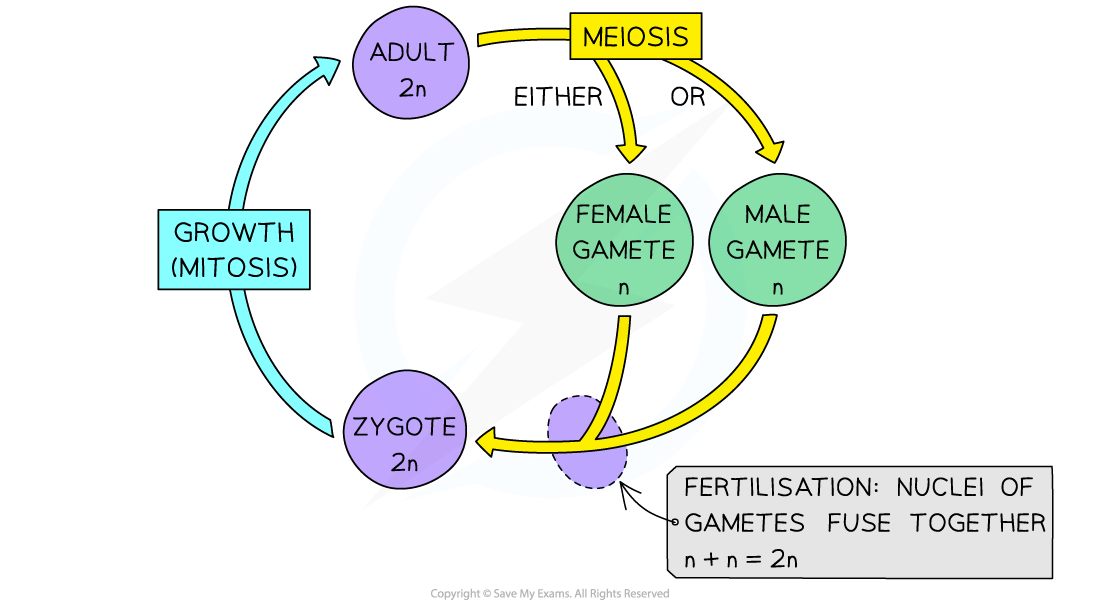
Sexual life cycle
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









