- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记2.6.5 Skills: Interpreting Sequences
Determination of mRNA Base Sequence
- The rules of base pairing and the table of mRNA codons are needed to be able to convert between DNA sequences, mRNA base sequences and amino acid sequences
- A triplet is a sequence of three DNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid
- A codon is a sequence of three mRNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid
- A codon is transcribed from the triplet and is complementary to it
- When comparing the genetic code to amino acid sequences, mRNA codons are often used
- The four bases found in RNA molecules (adenine, uracil, cytosine and guanine) have the ability to form 64 different codons
- Multiple mRNA codons can encode the same amino acid
- This means that a change in the genetic code doesn’t necessarily result in a change in the amino acid sequence
- For example, UGU and UGC both code for the amino acid, cysteine
Some send important signals to the transcription machinery
- The START codon initiates the process of transcription and ensures it starts in the right location (this is always the amino acid methionine in eukaryotic cells, coded for by the codon AUG)
- STOP codons cause transcription to terminate and do not code for an amino acid e.g. UAA
The genetic code is non-overlapping
- Each base is only read once in the codon it is part of
The rules of base pairing
- This means that a change in the genetic code doesn’t necessarily result in a change in the amino acid sequence
- In DNA,
- Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G)
In RNA, Thymine (T) is replaced by Uracil (U)
- This means that the base Adenine (A) in DNA is transcribed to Uracil (U) in the mRNA strand
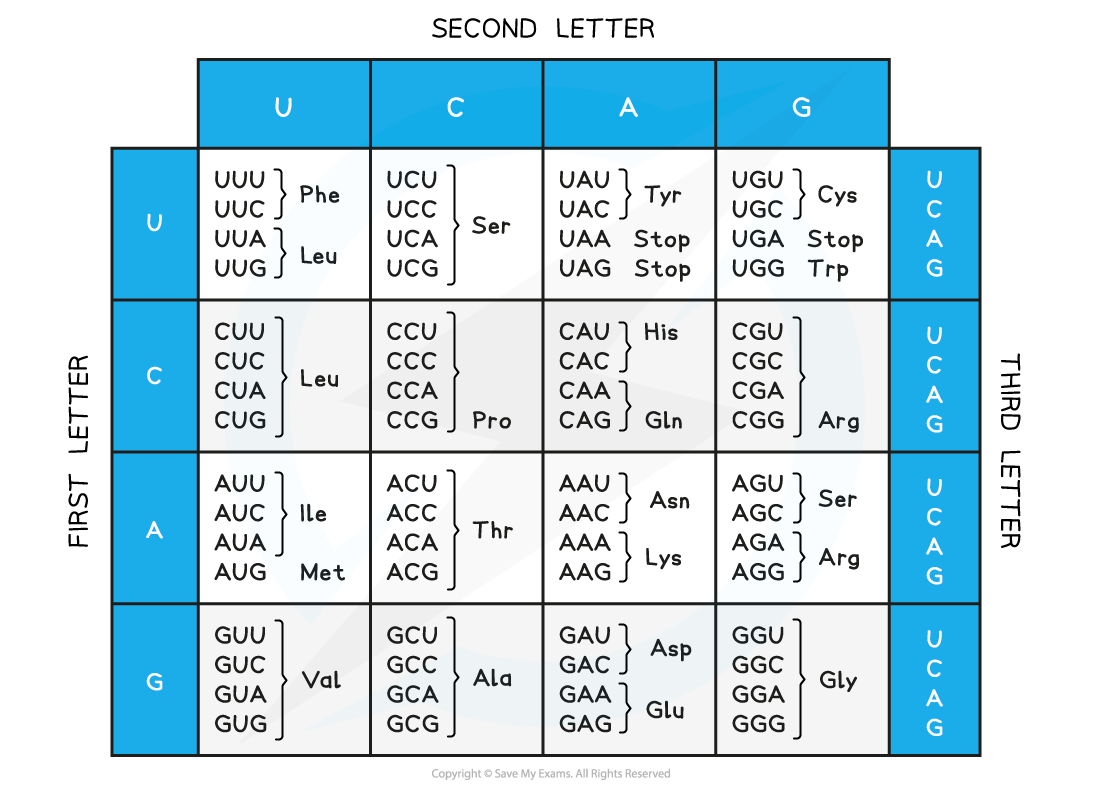
The mRNA Codons and Amino Acids table
- The first three bases of an mRNA strand form the first codon
- The first base of the codon is read from the first column of the table
- The second base of the codon is read from the top row of the table
- The third base of the codon is read from the final column of the table
mRNA Codons and Amino Acids Table
Intrepreting the Genetic Code
- Use a table of the genetic code to deduce which codon(s) corresponds to which amino acid
- The 20 amino acids are all coded for in the Table of mRNA Codons
- Some amino acids are only coded for by one codon eg. methionine (Met), coded by AUG
- Other amino acids have several codons that code for them eg. arginine (Arg), coded by CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA and AGG
Worked Example
Use the table of mRNA Codons and Amino Acids to identify the mRNA codons that code for the following amino acids:
- Histidine (His)
- Tryptophan (Trp)
- Glycine (Gly)
- Leucine (Leu)
Step 1: Look up His in the table
Codon CAU (no others)
Step 2: Look up Trp in the table
Codon UGG (no others)
Step 3: Look up Gly in the table
Codons GGU, GGC, GGA and GGG
Step 4: Look up Leu in the table
Codons CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG, UUA, UUG
Deducing the Sequences
- Use a table of mRNA codons and their corresponding amino acids to deduce the sequence of amino acids coded by a short mRNA strand of a known base sequence
Worked Example
Deduce the amino acid sequence coded for by the mRNA sequenceAUGACUGGGCCUCCCCAAUAUUAG
Step 1: split the mRNA sequence into triplets
AUG ACU GGG CCU CCC CAA UAU UAG
Step 2: look up the first triplet in the mRNA Codons and Amino Acids Table:
AUG = Met
Step 3: repeat for the remaining triplets
ACU = Thr
GGG = Gly
CCU = Pro
CCC = Pro
CAA = Gln
UAU = Tyr
UAG = Stop
Step 4 : link the amino acids together
Met-Thr-Gly-Pro-Pro-Gln-Tyr
Exam Tip
In an exam, you may be asked to predict the effect of specific mutations in the genetic code. Remember that the genetic code allows more than one amino acid to be coded for by triplets and is non-overlapping!You will not be required to memorise specific codons and the amino acids that they code for.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1