- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记2.6.2 Translation
Translation
- Translation is the synthesis of polypeptides on ribosomes
- This stage of protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell
- After leaving the nucleus, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome
- A ribosome is a complex structure that is made of a large and small subunit
- Ribosomes are themselves made of proteins and RNA (called ribosomal RNA or rRNA)
There are binding sites on the subunits for the various other molecules involved in translation
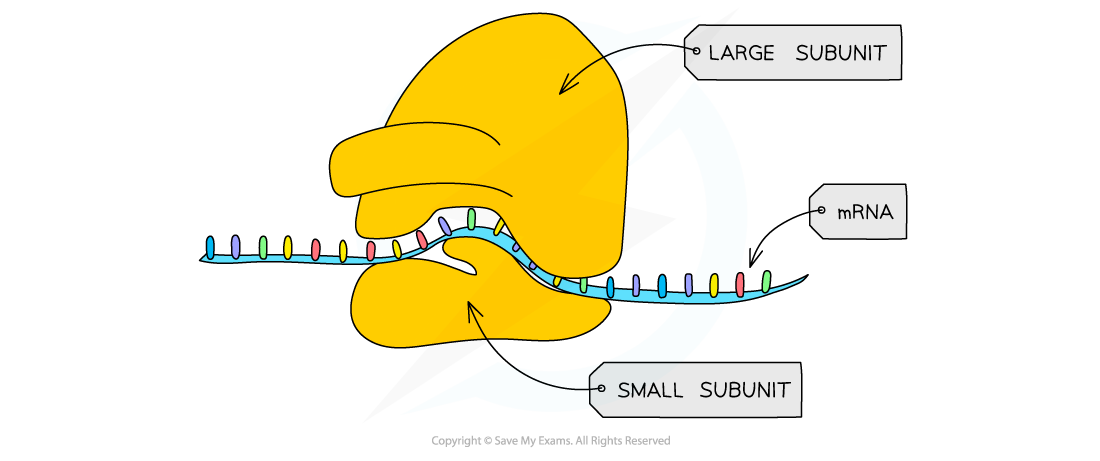
A ribosome is built of large and small subunits, ribosomal RNA and an area on the surface that catalyses the formation of peptide bonds in a newly-synthesised protein
Exam Tip
Make sure you learn both stages of protein synthesis fully. Don’t forget WHERE these reactions take place – transcription occurs in the nucleus but translation occurs in the cytoplasm!
Genetic Code & mRNA
- The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is determined by mRNA according to the genetic code
- mRNA varies in length, depending on the length of the gene, but is around 2,000 nucleotides long, on average (in mammals)
- Only certain genes are transcribed in a particular cell, depending on the function of that cell
- The gene for rhodopsin (a light-sensitive protein in the eye) is transcribed to mRNA in retina cells, but not transcribed in other body cells where rhodopsin is not required; that would be a waste of cellular energy
Exam Tip
Most RNA exists as mRNA but don't forget the other types; transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Codons
- Codons of three bases on mRNA correspond to one amino acid in a polypeptide
- The four nucleotide bases in mRNA are not enough to code for 20 separate amino acids
- Pairs of nucleotides would only give 16 combinations (42 = 16), which is still not enough
- Triplets of nucleotides would yield 64 combinations (43 = 64), which is more than enough
- Different triplets code for the same amino acid, giving some protection against mutation
- A triplet is a sequence of three DNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid
- A codon is a sequence of three mRNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid
- A codon is transcribed from the triplet and is complementary to it
An anticodon is a sequence of three transfer RNA (tRNA) bases that are complementary to a codon
- The transfer RNA carries the appropriate amino acid to the ribosome
- The amino acid can then be condensed onto the growing polypeptide chain
Certain codons carry the command to stop translation when the polypeptide chain is complete ('Stop codons')
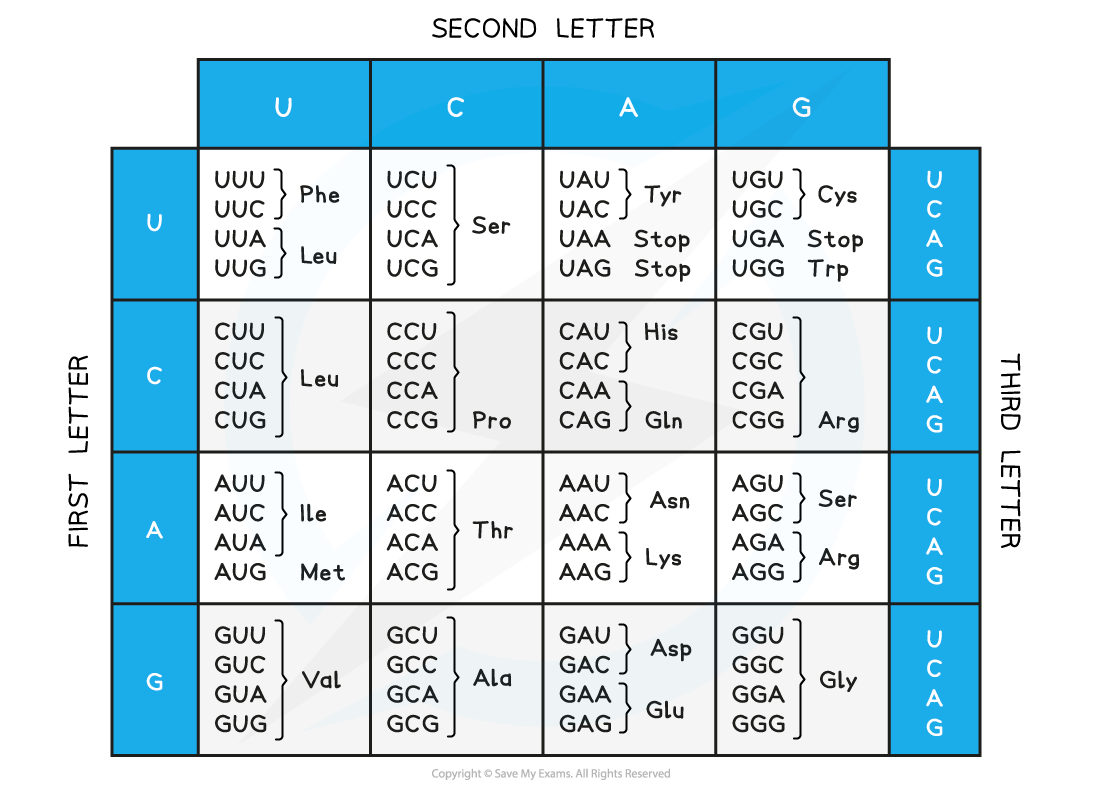
mRNA Codons and Amino Acids Table
Worked Example
Use the rules of base-pairing and the mRNA Codons and Amino Acids Table (above) to deduce the amino acid sequence coded for by the following DNA sense strand sequenceTTC GAG CAT TAC GCC
Step 1: Work out the antisense sequence using A-T and C-G base pairing rules
AAG CTC GTA ATG CGG
Step 2: Work out the mRNA codons, complementary to the antisense strand
UUC GAG CAU UAC GCC
Step 3: Use the mRNA Codons and Amino Acids Table (above) to work out the first amino acid
First base in codon = U, second base = U, third base = C
So we're looking in the top-left box of the table; this amino acid is Phe
Step 4: Repeat for the remaining 4 codons
GAG = Glu
CAU = His
UAC = Tyr
GCC = Ala
Answer: The final sequence of amino acids is Phe-Glu-His-Tyr-Ala
Codons & Anticodons
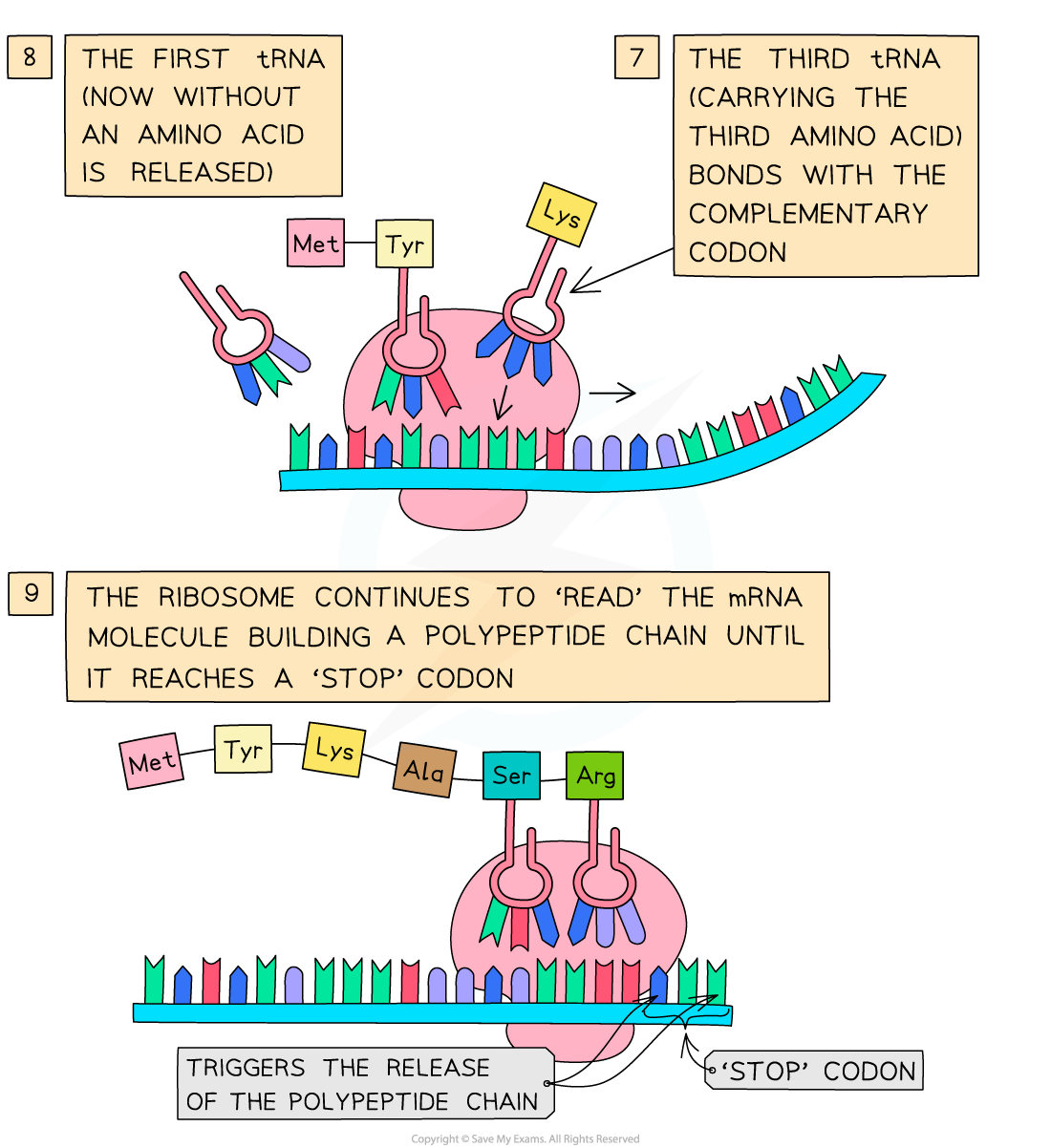
- Translation depends on complementary base pairing between codons on mRNA and anticodons on tRNA
- In the cytoplasm, there are free molecules of tRNA (transfer RNA)
- The tRNA molecules bind with their specific amino acids (also in the cytoplasm) and bring them to the mRNA molecule on the ribosome
- The triplet of bases (anticodon) on each tRNA molecule pairs with a complementary triplet (codon) on the mRNA molecule
- Two tRNA molecules fit onto the ribosome at any one time, bringing the amino acid they are each carrying side by side
- A peptide bond is then formed (by condensation) between the two amino acids
- The formation of a peptide bond between amino acids is an anabolic reaction
- It requires energy, in the form of ATP
- The ATP needed for translation is provided by the mitochondria within the cell
This process continues until a ‘stop’ codon on the mRNA molecule is reached – this acts as a signal for translation to stop and at this point the amino acid chain coded for by the mRNA molecule is complete
- This amino acid chain then diffuses away from the ribosome and forms the final polypeptide
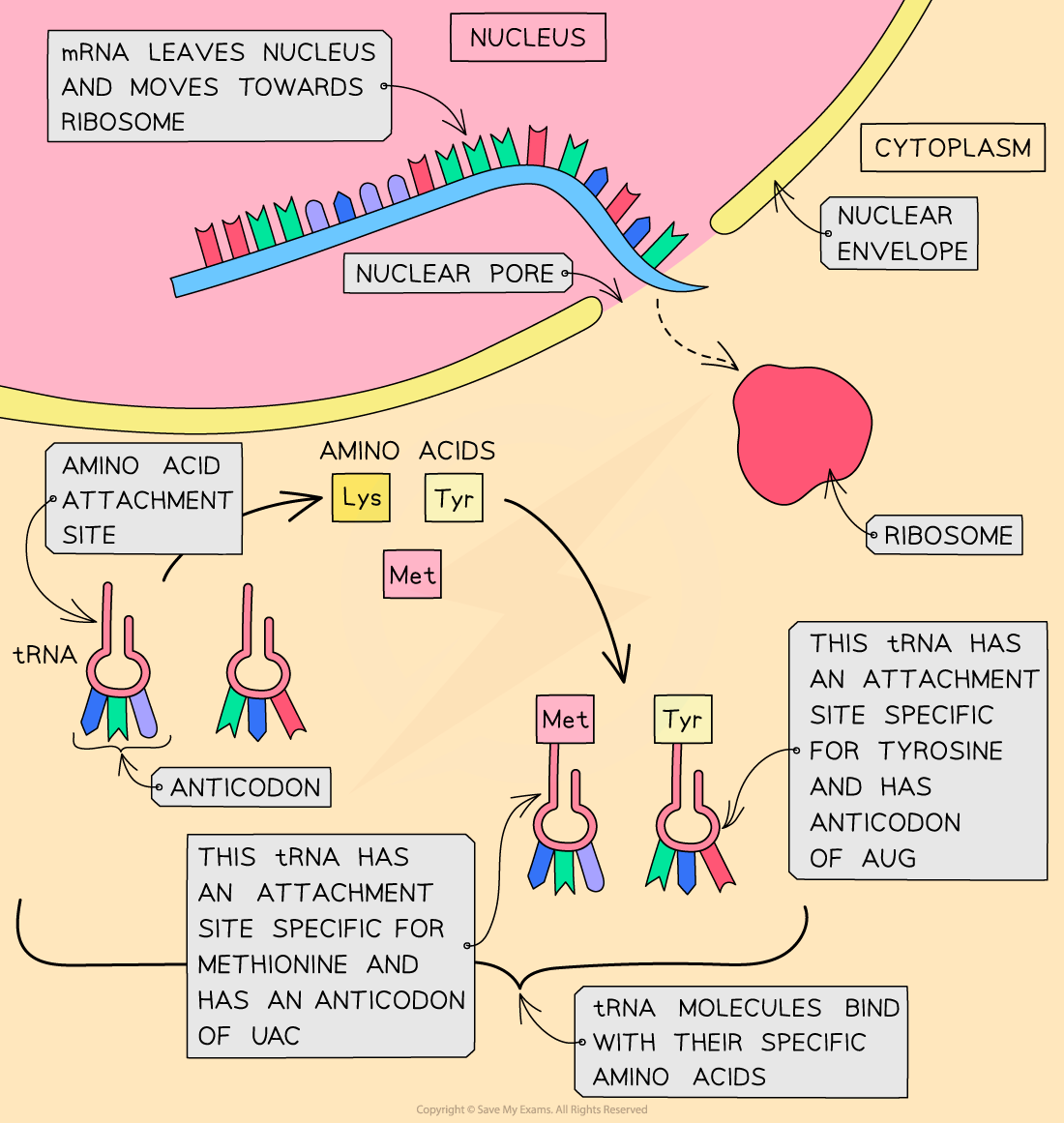
The translation stage of protein synthesis – tRNA molecules bind with their specific amino acids
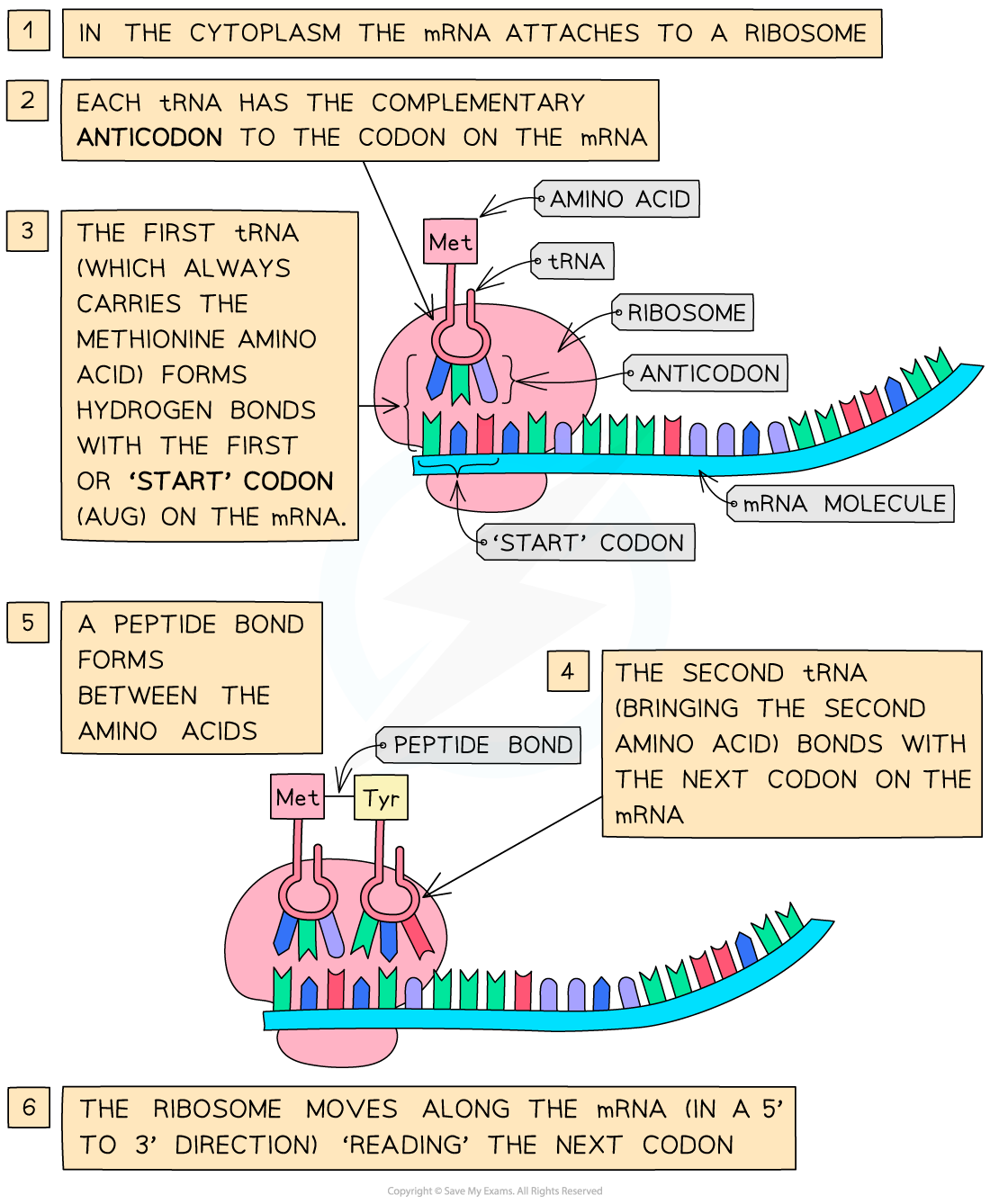
The translation stage of protein synthesis – an amino acid chain is formed
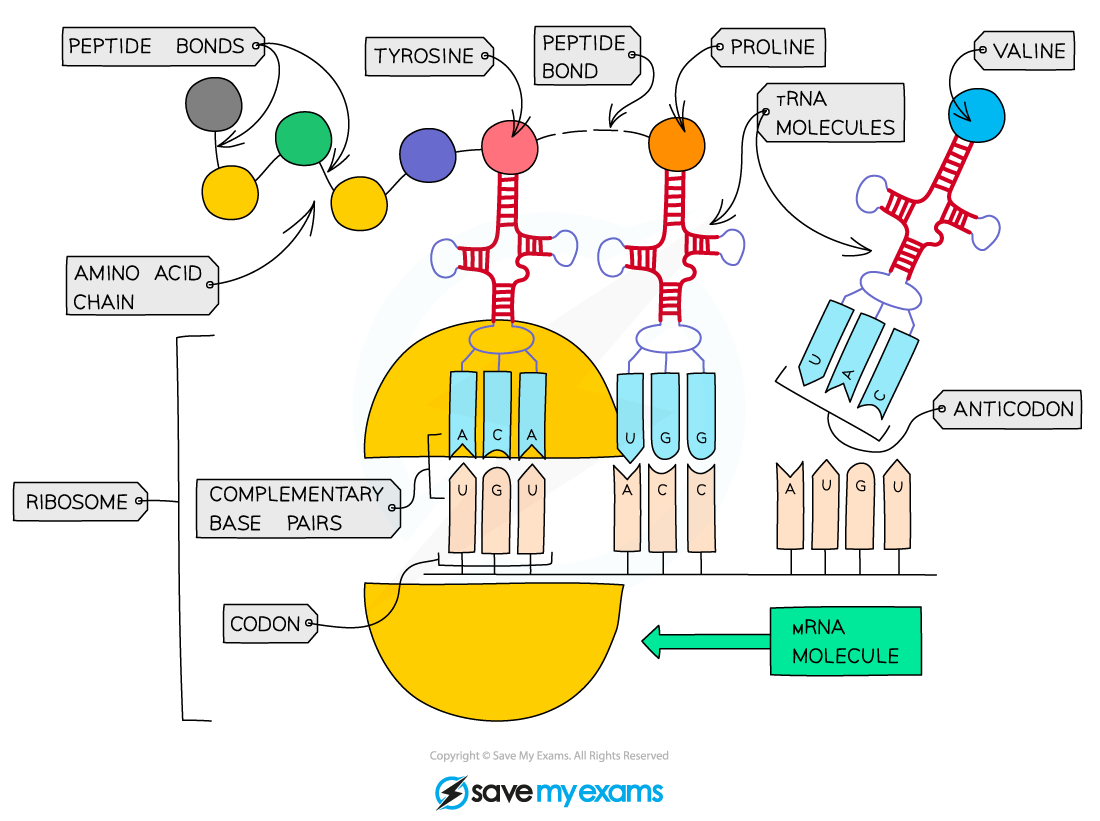
An polypeptide forms as peptide bonds are added in sequence
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1