- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记2.5.2 DNA Replication
DNA Replication
- The replication of DNA is semi-conservative and depends on complementary base pairing
- Semi-conservative means that one strand of the 'parent' DNA is kept in the 'daughter' molecule
- This is called the template strand
- The other half is determined by the code on the template strand and is built up from free nucleotides in the nuclear space around the chromosomes
- This takes place in the nucleus
- Nucleotides are added one by one to the new strand according to the rules of complimentary base-pairing
- If an adenine is the next exposed base on the original strand, a thymine nucleotide is added and vice versa
- If a cytosine is the next exposed base on the original strand, a guanine nucleotide is added and vice versa
Hydrogen bonds can only form between the template strand and the new strand if the correct bases are paired up
- Therefore, the new DNA molecule has kept half of the parent DNA and then used this to create a new, daughter strand
Exam Tip
Make sure you don’t confuse ‘parent cell’ with ‘parent organism’. A parent cell is any cell in the body that divides into two cells and the terminology is used to refer to the ‘original’ cell that the DNA came from before it was split and replicated semi-conservatively.
Enzymes Involved in Replication
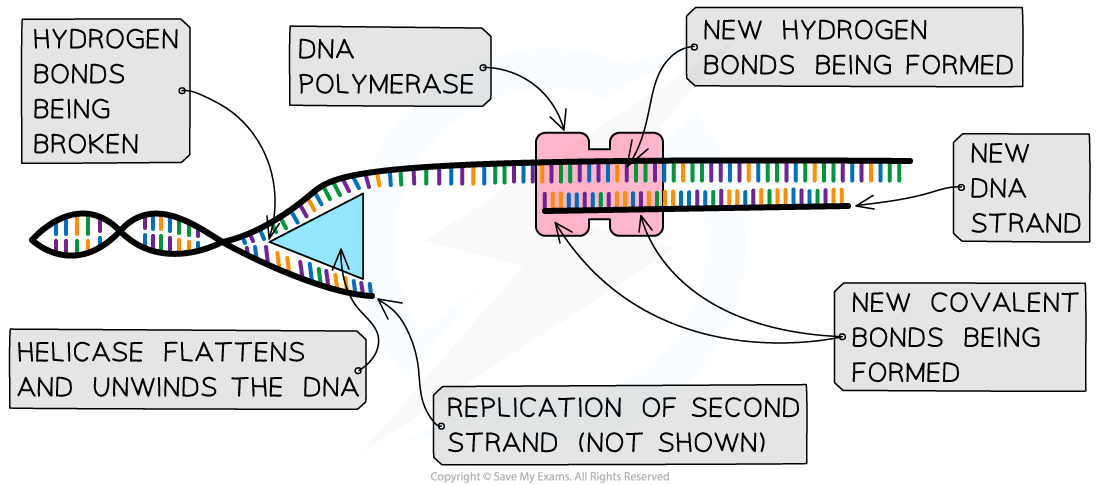
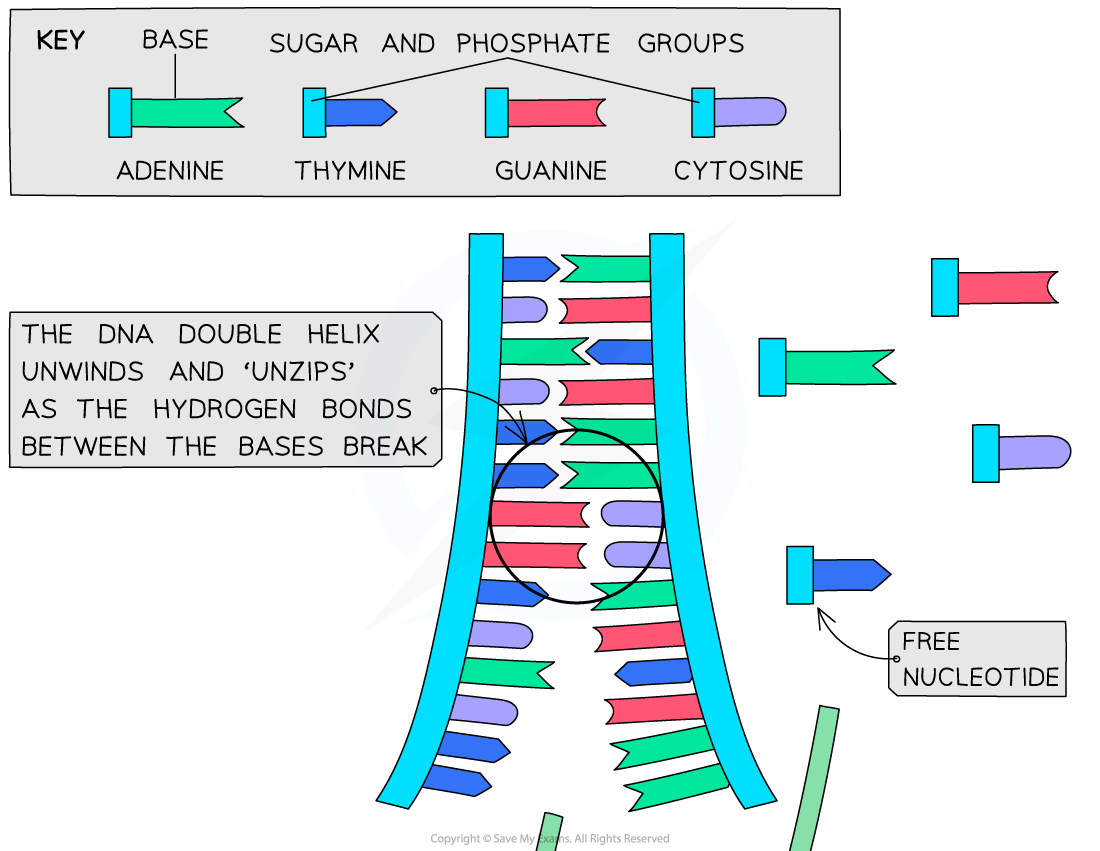
- Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the two strands by breaking hydrogen bonds
- DNA replication occurs in preparation for mitosis, when DNA must be doubled before the parent cell can divide to produce two genetically identical daughter cells
- The enzyme helicase first unwinds the DNA, by flattening out its helical structure
- Analogy - think about untwisting a rope ladder
Helicase then causes the hydrogen bonds to break between pairs of bases, exposing bases on either strand
- Analogy - unzipping a zipper
Each of these single polynucleotide DNA strands acts as a template for the formation of a new strand made from free nucleotides that are attracted to the exposed DNA bases by base pairing
Helicase and DNA polymerase work together to replicate each strand of DNA
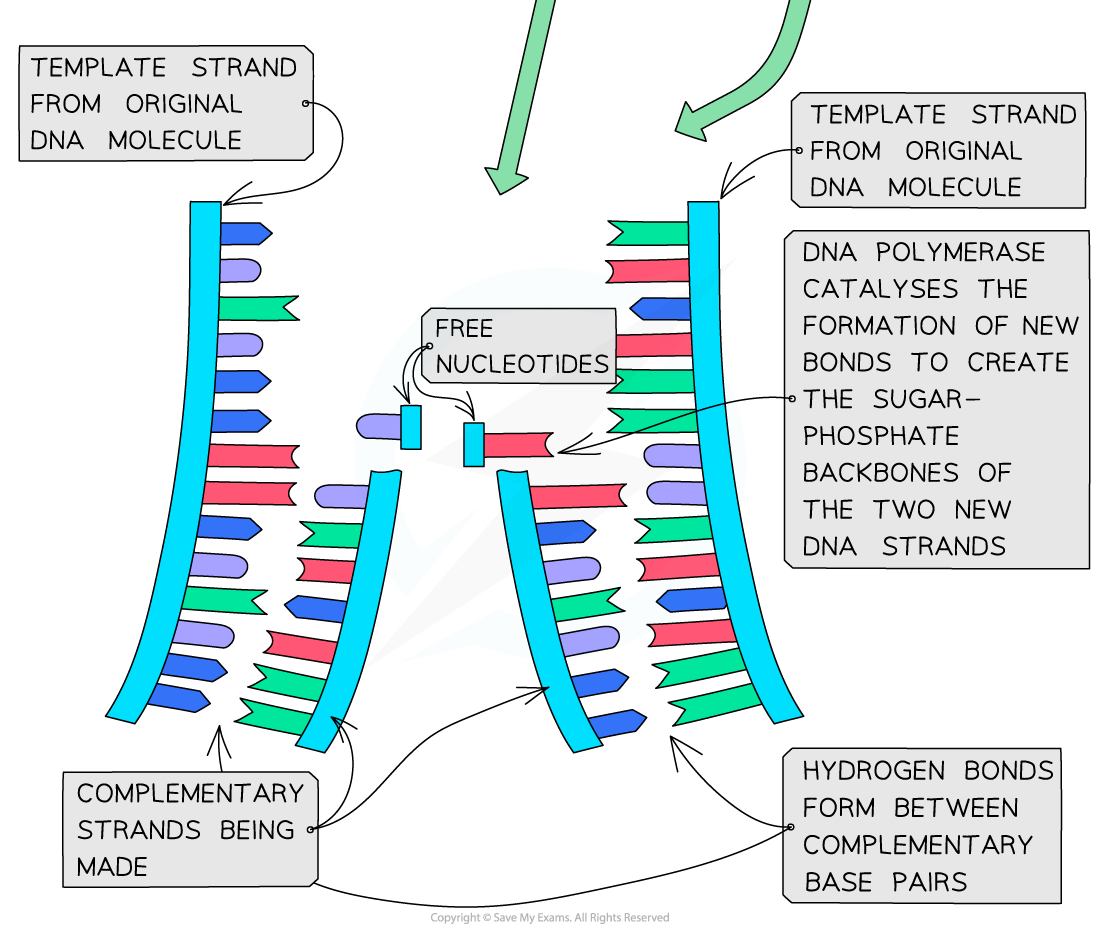
- DNA polymerase links nucleotides together to form a new strand, using the pre-existing strand as a template
- Following the action of helicase, the template strand is exposed and new nucleotides are joined together by DNA polymerase, which catalyses condensation reactions, to form a new strand
- The original strand and the new strand join together through hydrogen bonding between base pairs to form the new DNA molecule
- This method of replicating DNA is known as semi-conservative replication because half of the original DNA molecule is kept (conserved) in each of the two new DNA molecules
- The enzyme DNA polymerase synthesises new DNA strands from the two template strands
- It does this by catalysing condensation reactions between the deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups of adjacent nucleotides within the new strands, creating the sugar-phosphate backbone of the new DNA strands
- DNA polymerase always works in the same direction along a strand of DNA, the 5' to 3' direction
- Adding the 5' terminal of the new nucleotide to the 3' terminal of the strand being built
- Hydrogen bonds then form between the complementary base pairs of the template and new DNA strands
- The copying accuracy of DNA polymerase is very high
- Very few copying errors are made in DNA replication
The combined actions of helicase and DNA polymerase create new complementary DNA strands
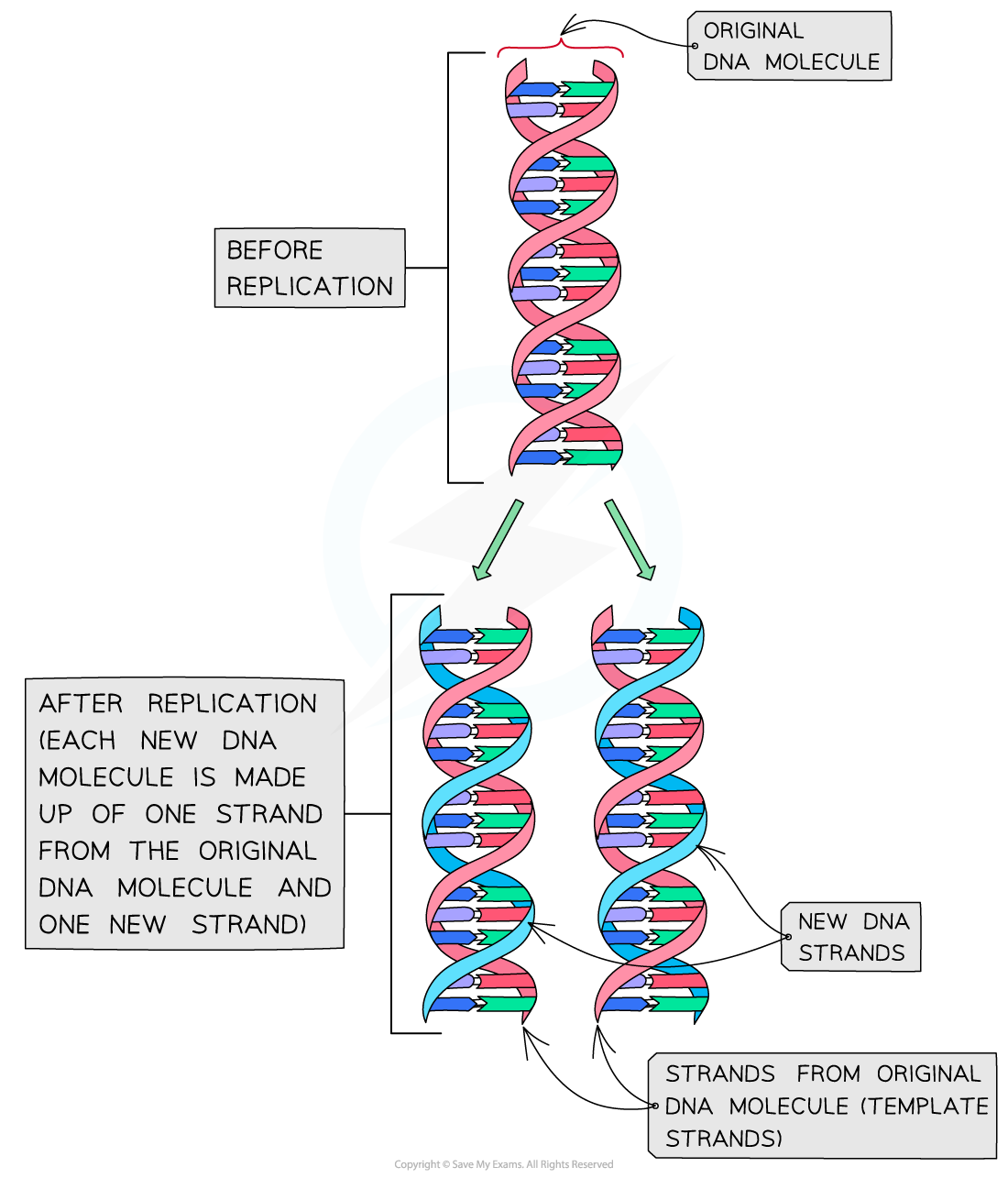
Semi-Conservation Replication
- DNA polymerase links nucleotides together to form a new strand, using the pre-existing strand as a template
- Before a (parent) cell divides, it needs to copy the DNA contained within it
- This is so that the two new (daughter) cells produced will both receive the full copies of the parental DNA
The DNA is copied via a process known as semi-conservative replication (half the DNA is kept)
- The process is called so because in each new DNA molecule produced, one of the polynucleotide DNA strands (half of the new DNA molecule) is from the original DNA molecule being copied
- The other polynucleotide DNA strand (the other half of the new DNA molecule) has to be newly created by the cell
Semi-conservative replication of DNA
The importance of keeping one original DNA strand
- It ensures there is genetic continuity between generations of cells
- In other words, it ensures that the new cells produced during cell division inherit all their genes from their parent cells
This is important because cells in our body are replaced regularly and therefore we need the new cells to be able to do the same role as the old ones
- Replication of DNA and cell division also occurs during growth
Crick and Watson proposed semi-conservative replication
- As part of their discovery of the double-helix structure of DNA, Crick and Watson made a hypothesis about how DNA copies during cell growth
- They proposed a semi-conservative model, but had not provided the evidence
- This was provided by two later scientists, Meselson and Stahl, in another award-winning piece of research
- Analysis of Meselson and Stahl’s results gave the necessary support for Crick & Watsons' hypothesis of semi-conservative replication of DNA
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









