- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记2.3.2 Protein Structure & Function
Protein structure
- A protein may consist of a single polypeptide or more than one polypeptide linked together
- Some proteins exist as a single polypeptide chain (of amino acids)
- Other proteins are made up of two or more polypeptide chains joined together
- Single polypeptide chain proteins include lysozyme, an enzyme present in mucus secretions and tears, that kills bacteria as part of our primary defences against pathogens
- Proteins with two polypeptide chains include
- insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels
- integrins, a group of membrane proteins that span a phospholipid bilayer and act as a receptor
- integrins' two polypeptide chains each have a hydrophobic section that sits in the membrane bilayer
Proteins with three polypeptide chains include collagen, the main structural protein in skin, tendons, ligaments and the walls of blood vessels
- Proteins with four polypeptide chains include haemoglobin, which binds oxygen in red blood cells and delivers it from the lungs to respiring tissues
- Each polypeptide chain in a multi-polypeptide protein is referred to as a subunit of the protein
3D Structure of Proteins
The amino acid sequence determines the three-dimensional conformation of a protein
- Proteins perform their diverse roles because of their 3-D shape and structure
- This is known as the protein's conformation
- The precise sequence of amino acids determines how the protein folds and aligns itself as the individual amino acids are being added at the ribosome
- Amino acids are always added in the same sequence so a protein can start to form its shape even before it is fully formed
- Bonds form between parts of amino acids that can cause a bridge to form between one part of the chain and another
- this creates loops, sheets, helices and folds
Many of the bonds that hold the protein's shape form between the various R groups of individual amino acids
- If an amino acid is not present in its usual place in the chain due to mutation, this can drastically alter the protein's 3-D shape, and affect its function
Haemoglobin is a globular protein (forms a globe-shaped protein)
- Some of haemoglobin's outer parts are hydrophilic to be in contact with water whilst its inner parts are made up of amino acids with hydrophobic R groups
Collagen is a fibrous protein (forms a rope-like protein for tensile strength)
- It has a repeating sequence of amino acids to create a helical structure
- The chain of amino acids remains in an elongated conformation to give fibrous strength
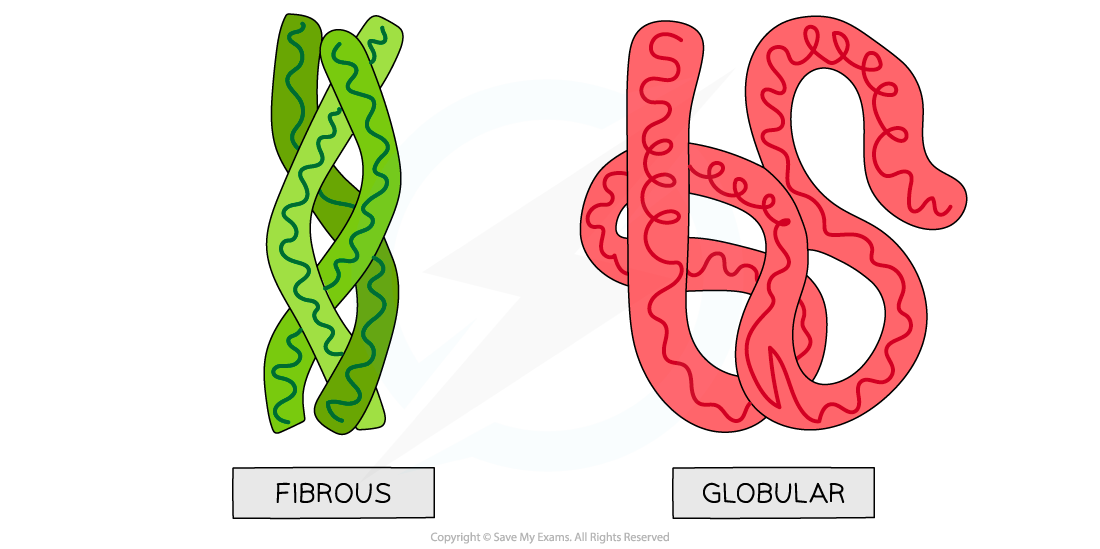
Globular and fibrous protein models illustrating the roughly spherical shape of globular proteins and the long, stranded shape of fibrous proteins
Denaturation: Proteins
- Denaturation is the irreversible change of protein conformation caused by temperature and pH extremes
- The bonds that form between different R groups are relatively weak (compared to the peptide bonds that hold the amino acids in sequence)
- These bonds can be broken easily, which can cause the conformation of the protein to change
- The altered protein shape may affect its function, physical state and general usefulness in its original role
- This is called denaturation
- Heat and extremes of pH are the most common causes of denaturation
- Both cause breaking of the weak bonds between R groups
A certain pH is considered as an optimum for a particular protein, because at that pH, the protein's 3-D structure is not denatured
- Denaturation is almost always irreversible
- The protein cannot be re-formed in its original conformation by reversing the change in conditions
- However, small denaturations and renaturations are possible in certain proteins to respond to small fluctuations in pH eg. haemoglobin
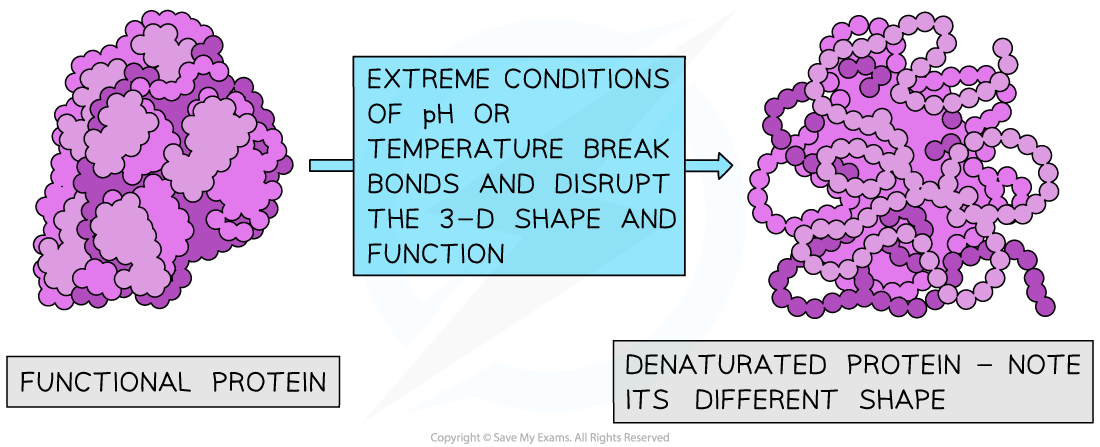
The effect of heat and pH on the shape and function of a globular protein
Denaturation in action
- Denaturation can be seen most easily by looking at the changes in an egg white as the egg is fried or poached
- Egg white is mainly the protein albumin
- The hydrophobic amino acids in albumin are at the centre of the molecule in its normal state, so albumin is soluble
- Heating causes the hydrophobic amino acids to appear at the edges, where they cause the protein to become insoluble
- A harder, solid layer forms, which is the cooked white
- Similar events occur in the proteins of the egg yolk as it cooks
- Denaturation also occurs in the stomach, where the low pH (pH2) causes proteins in the diet to become denatured on their way to being fully hydrolysed further down the digestive system
- The stomach enzyme pepsin, a protein-digesting enzyme has an optimum pH of 2 for this reason
- Certain extremophiles have evolved to have proteins that are stable even at extreme pH or temperature
- eg. Thermus aquaticus, a bacteria that lives in hot springs at 80°C
- This temperature would denature most other proteins
Denaturation of enzymes can be used as part of experiments to measure enzyme activity
- For example, an experiment to establish the optimum pH or temperature of an enzyme eg. pepsin or lipase
Many drugs are proteins that cannot be taken by mouth, because the protein will be denatured by stomach acid
- These drugs should be delivered in another way eg. by direct injection into the blood
Exam Tip
Remember to avoid confusing the bonds that hold a protein's shape together with the peptide bonds that attach each amino acid in sequence. Picture the peptide bonds holding the amino acids in a straight chain, then the other bonds holding the chain in its folded, 3-D structure.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









