- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记2.1.1 Molecules
Molecular Biology
The substances of life
- There are 118 elements in the Periodic Table
- Only the first 92 elements occur in Nature ; the rest are artificially-synthesised in laboratories and are very unstable
- Only around 21 elements are required for life
- The rest have no role in sustaining life (some are poisonous eg. arsenic)
- Some elements can be used in medicine eg. titanium for skeletal implants, thanks to its inertness, lightness and strength
There are 4 ubiquitous elements in biological systems (this means they are found everywhere)
- These 4 make up over 96% of living matter
- Oxygen - 65% of body mass (humans)
- Carbon - 18%
- Hydrogen - 10%
- Nitrogen - 3%
Other trace elements found in organic compounds are: bromine, calcium, chlorine, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, magnesium, manganese, molybdenum, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, silicon and sodium
- There are other trace elements found in certain phyla only e.g. strontium in certain corals (Cnidaria)
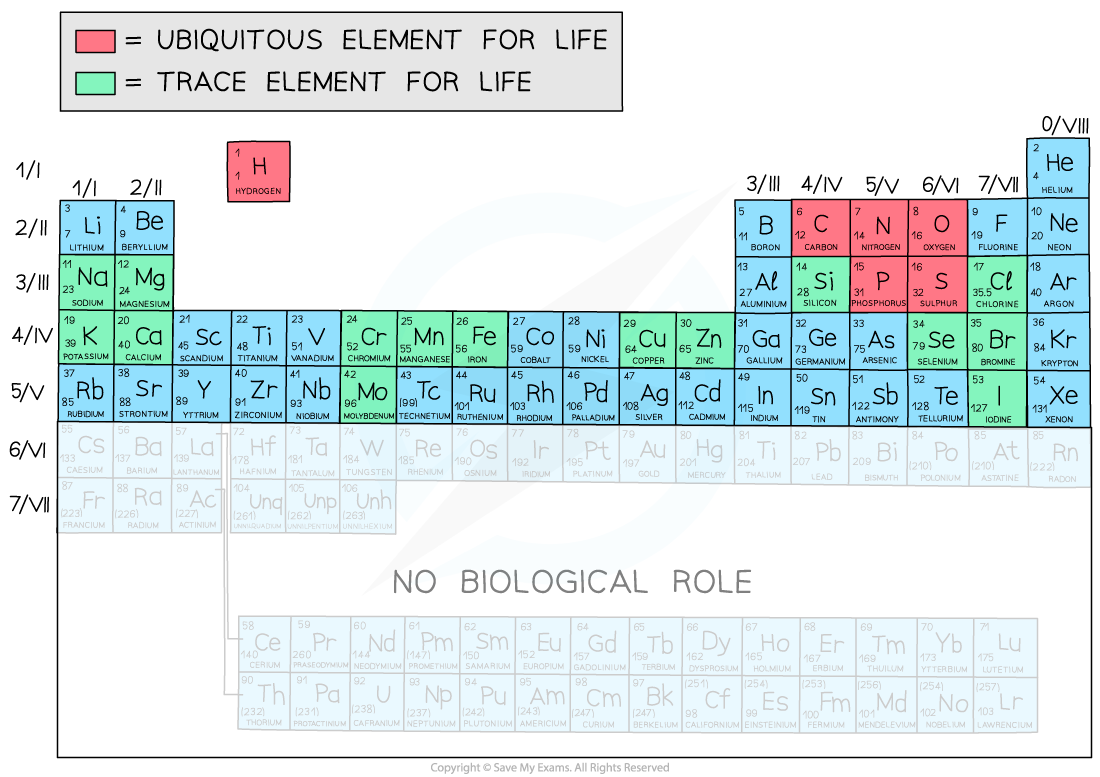
The elements of the Periodic Table that form parts of biological molecules
Elements in biology exist mainly in compounds
- Such compounds are mainly covalent compounds
- Electrons are shared between atoms to generate strong bonds within compounds
- For example, elemental carbon only exists as graphite and diamond, which are of no direct use to organisms
- Carbon forms millions of different covalently-bonded compounds, mainly with hydrogen and oxygen
- Oxygen is absorbed in elemental form but is quickly converted to its compounds during transportation and respiration
Some are ionic eg. sodium chloride
- Some elements form prosthetic groups with larger organic molecules eg. magnesium in chlorophyll, iron in haemoglobin
All of Biology can be explained at a molecular level
- The molecules in cells, and the elements that go to form them, are the basis of all events that occur in Nature
- Everything that is observed has a molecular explanation
- Imagine an all-powerful 'zoom lens' that could look into any level of detail of life
- Such a lens could start at its most zoomed-out, looking at our biosphere, the Earth
- We assume that alien life does not exist because we haven't found evidence for it yet
We see habitats, populations, communities and individual organisms coming into view in that order, as we zoom in
- As we zoom in on one organism, we enter its body and see increasing levels of detail, right down to the molecular level
- The zoom model helps understand the important interfaces between chemistry, biology and physics
- We could zoom in further, to look at sub-atomic particles, although that begins to enter into the realms of physics!
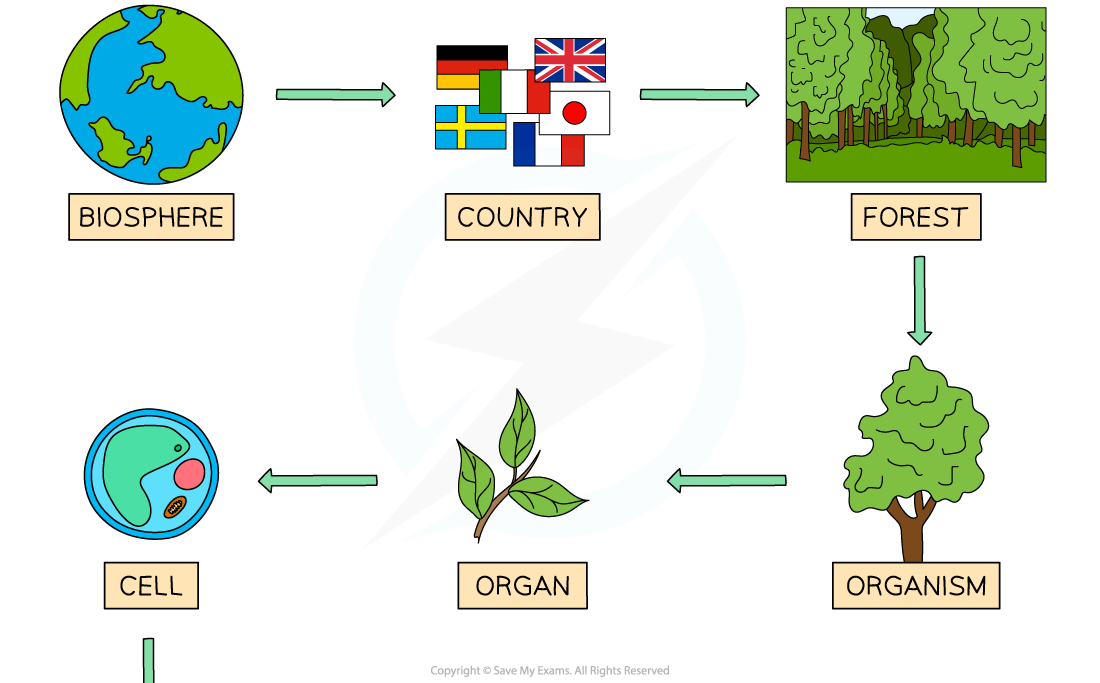
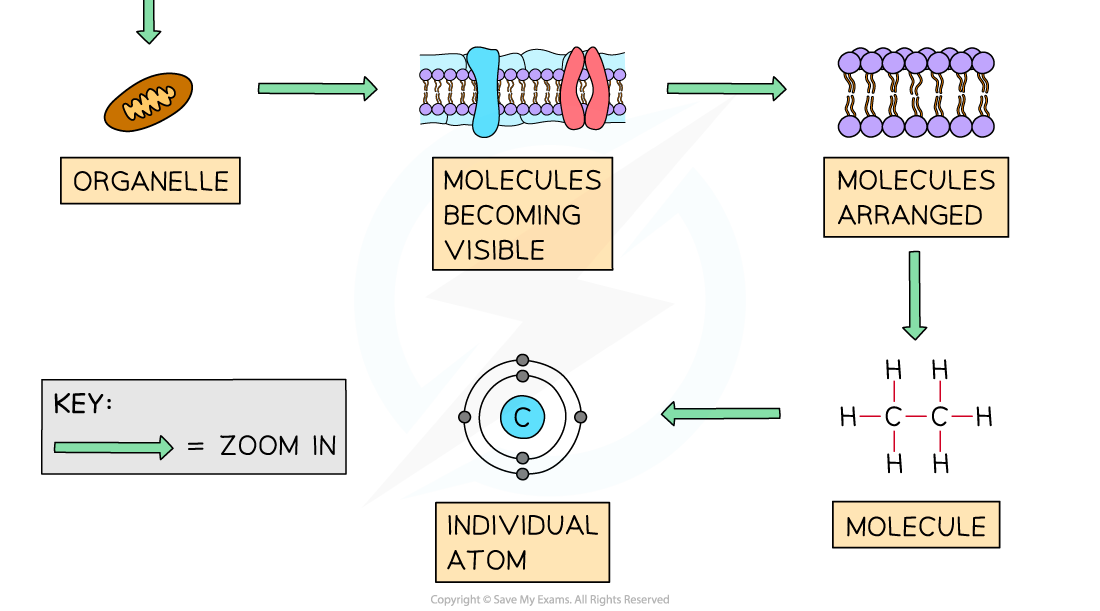
We can zoom into any part of the biosphere to identify all of Biology at a molecular (and atomic) level
Exam Tip
Please note that you do not need to know the specific details of the Periodic Table, it is provided here for context to support your understanding of important biological compounds
Synthesis of Organic Molecules
NOS: Falsification of theories; the artificial synthesis of urea helped to falsify vitalism
- When scientists do not have all the necessary information to understand or explain a biological process/phenomenon they use their knowledge and expertise to propose a theory
- Other scientists or researchers will often test theories through experiments and gathering data. Sometimes this can lead to an existing theory being disproved or replaced
- In the early 1800s, the theory of vitalism stated that a living force, a mysterious non-molecular entity, was necessary for the synthesis of all organic molecules
- This theory advocated that all biological molecules were exclusive to living beings and could not be found in other branches of science
- Frederick Wöhler, a German physician, was the first to synthesise a biological molecule, urea, from inorganic compounds
- Urea was thought to be synthesised only in living organisms
Wöhler heated ammonium cyanate and produced urea, a well-known organic constituent of blood and urine
- Urea had been thought to be found only in living organisms
The formation of urea from ammonium cyanate helped to disprove the theory of vitalism, which has been completely falsified by subsequent findings
- All of the observations of biology now have a molecular explanation, and that is now universally accepted
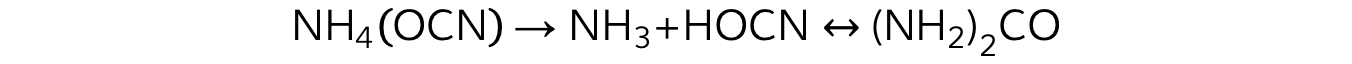
A balanced chemical equation showing the formation of urea

Chemical Structure of Urea
Carbon
- Carbon's unique chemistry makes it the ideal basis of living systems
- The structure and bonding possibilities of carbon can be detailed as follows:
-
- Four electrons in its outer (second) shell
- Each atom can form four strong covalent bonds using these 4 electrons and therefore forms very stable, large molecules
-
- Bonds to other carbon atoms, or other atoms such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur and the halogens
- Forms long-chain and cyclic compounds that are stable, this allows a very high number of possible organic compounds to exist
- Produce a tetrahedral structure, due to the four bonds, which allows the formation of varied carbon compounds which have different 3-D shapes and hence, different biological properties
- Double and triple bonds can form with an adjacent carbon atom, allowing unsaturated compounds to form
- Can form part of (and join onto) many different functional groups that give organic compounds their individual properties
- Alcohol groups
- Hydroxyl groups
- Ketone groups
- Aldehyde groups
- Carbonyl groups
- Amino groups
- Sulfhydryl groups
- Phosphate groups
Carbon Compounds
- The key molecules that are required to build structures that enable organisms to function are:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Nucleic Acids
- Water
All of these except water contain carbon
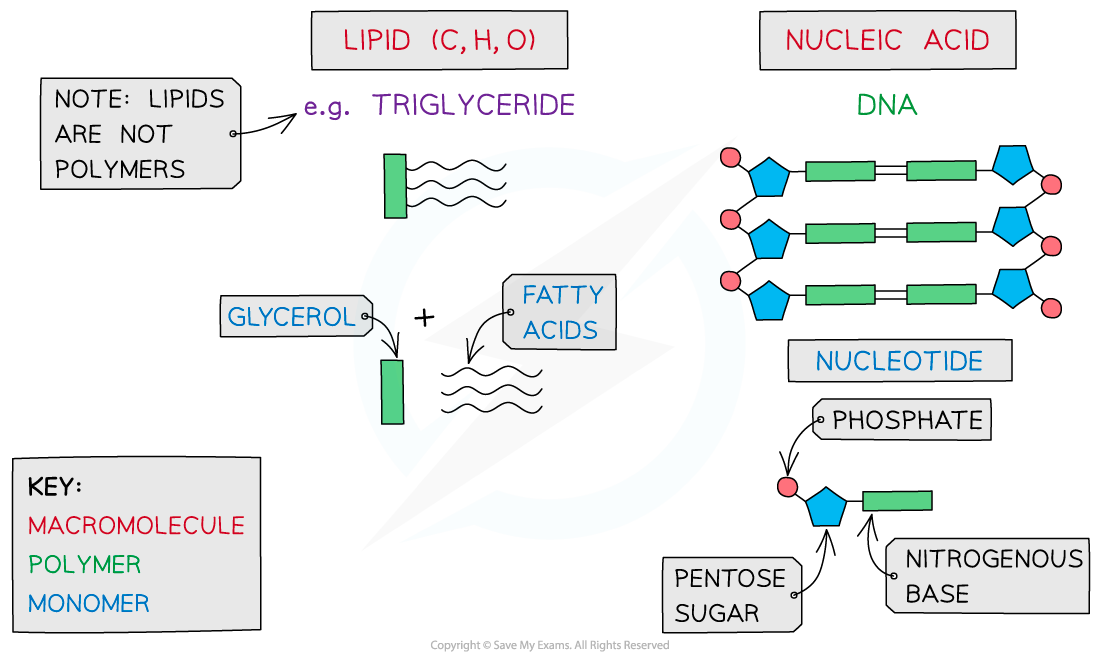
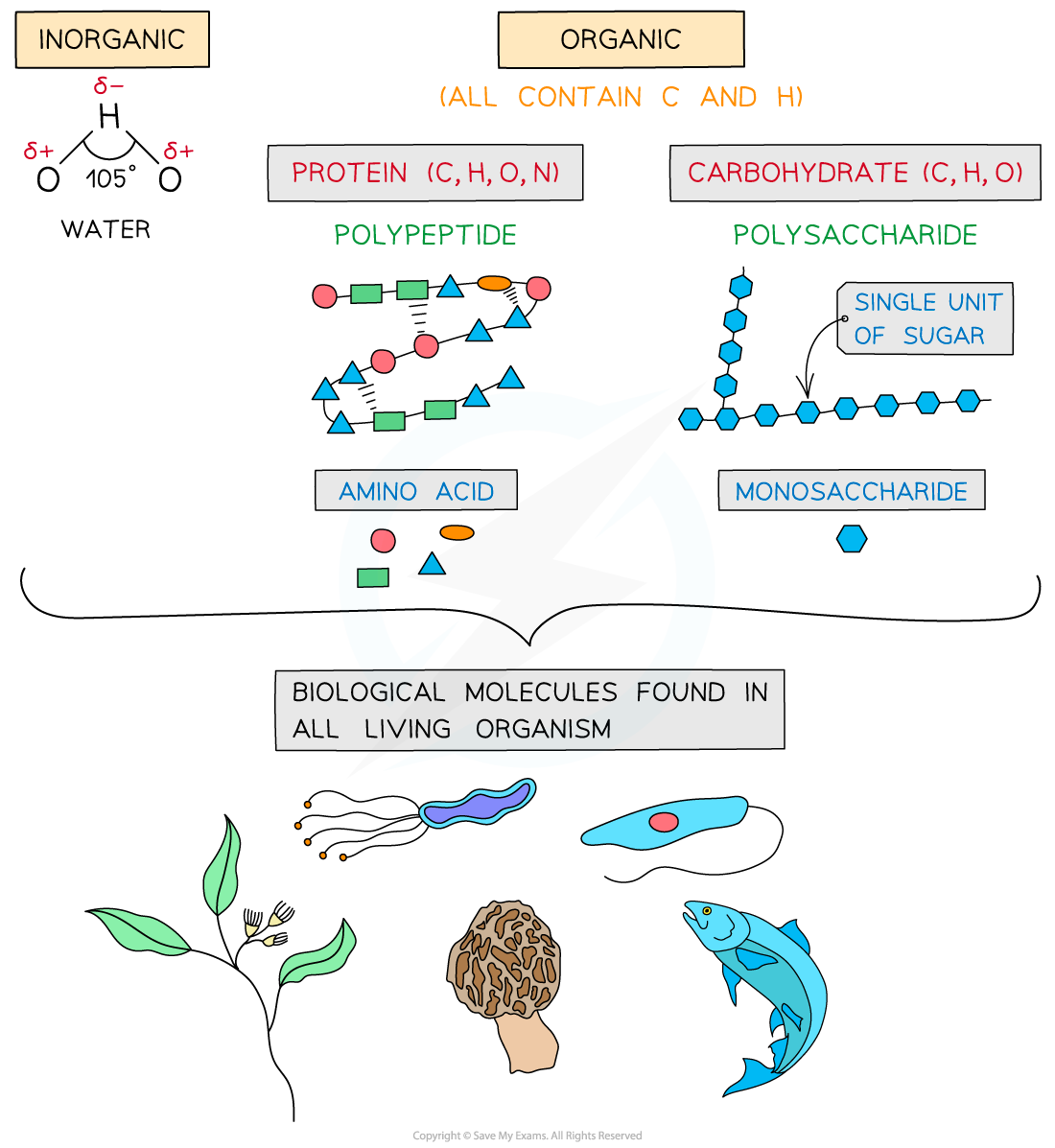
The key biological molecules for living organisms
- Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids contain the elements carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) making them organic compounds
- Carbon atoms are key to organic compounds because:
- Each carbon atom can form four covalent bonds – this makes the compounds very stable (as covalent bonds are so strong they require a large input of energy to break them)
- Carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur
- Carbon atoms can bond to form straight chains, branched chains or rings
Carbon compounds can form small single subunits (monomers) that bond with many repeating subunits to form large molecules (polymers) by a process called polymerisation
- Macromolecules are very large molecules that contain 1000 or more atoms therefore having a high molecular mass
- Polymers can be macromolecules, however not all macromolecules are polymers as the subunits of polymers have to be the same repeating units
Exam Tip
When discussing monomers and polymers, you should be able to give the definition and also name specific examples eg. nucleic acids – the monomer is a nucleotide.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









