- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记1.4.2 Phases of Mitosis
Phases of Mitosis
- Mitosis is the process of nuclear division by which two genetically identical daughter nuclei are produced that are also genetically identical to the parent cell nucleus (they have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell)
- Significance of mitosis: mitosis occurs whenever the production of genetically identical nuclei are required in eukaryotic cells
- E.g. during embryonic development, growth, tissue repair and asexual reproduction
Embryonic development and growth of multicellular organisms
Unicellular zygotes divide by mitosis in order to grow in sizeAfter a certain amount of growth, they then differentiate into embryos
Growth of multicellular organisms occurs as the number of new cells increases due to mitosis
- This growth may occur across the whole body of the organism or be confined to certain regions, such as in the meristems (growing points) of plants
Replacement of cells & repair of tissues
- Damaged tissues can be repaired by mitosis followed by cell division
- As cells are constantly dying they need to be continually replaced by genetically identical cells
- In humans, for example, cell replacement occurs particularly rapidly in the skin and the lining of the gut
- Some animals can regenerate body parts, for example, zebrafish can regenerate fins and axolotls regenerate legs and their tail amongst other parts
Asexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction is the production of new individuals of a species by a single parent organism – the offspring are genetically identical to the parent
- For unicellular organisms such as Amoeba, cell division results in the reproduction of a genetically identical offspring
- For multicellular organisms, new individuals grow from the parent organism (by cell division) and then detach (‘bud off’) from the parent in different ways
- This type of reproduction can be observed in different plant, fungi and animal species
- Some examples of these are budding in Hydra and yeast and runners from strawberries
Phases of Mitosis
- Although mitosis is, in reality, one continuous process, it can be divided into four main stages or phases
- These stages are:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
Most organisms contain many chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells (eg. humans have 46) but the diagrams below show mitosis of an animal cell with only four chromosomes, for simplicity
- The different colours of the chromosomes are just to show that half are from the female parent and half from the male parent
Prophase
- Chromosomes condense and are now visible when stained
- The chromosomes consist of two identical chromatids called sister chromatids (each containing one DNA molecule) that are joined together at the centromere
- The two centrosomes (replicated in the G2 phase just before prophase) move towards opposite poles (opposite ends of the nucleus)
- Spindle fibres (protein microtubules) begin to emerge from the centrosomes (consists of two centrioles in animal cells)
- The nuclear envelope (nuclear membrane) breaks down into small vesicles
- The nucleolus disappears
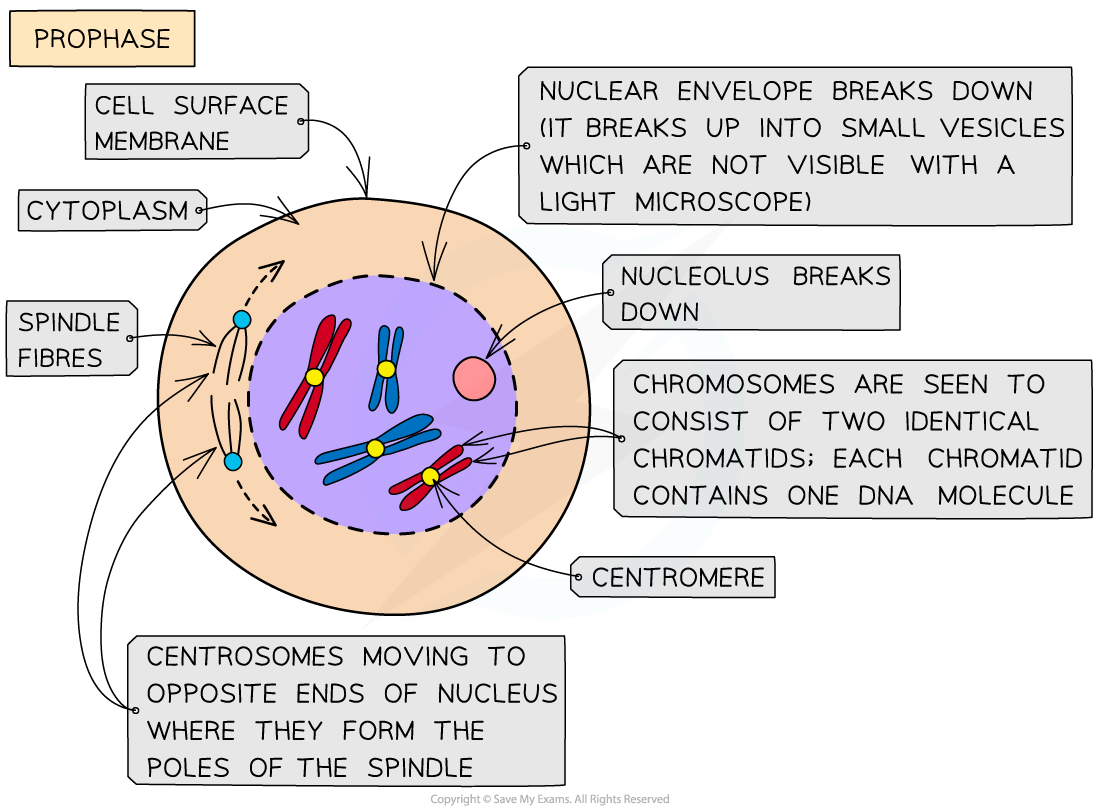
Prophase
Metaphase
- Centrosomes reach opposite poles
- Spindle fibres (protein microtubules) continue to extend from centrosomes
- Chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle (also known as the metaphase plate) so they are equidistant to the two centrosome poles
- Spindle fibres (protein microtubules) reach the chromosomes and attach to the centromeres
- This attachment involves specific proteins called kinetochores
Each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fibre originating from opposite poles
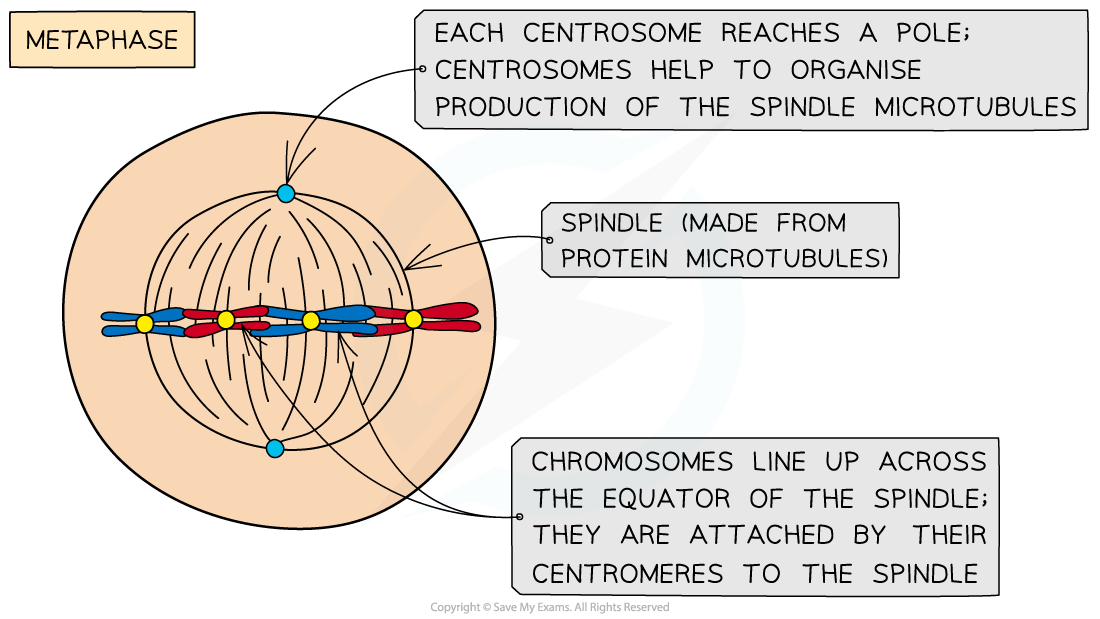
Metaphase
Anaphase
- The sister chromatids separate at the centromere (the centromere divides in two)
- Spindle fibres (protein microtubules) begin to shorten
- The separated sister chromatids (now called chromosomes) are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle fibres (protein microtubules)
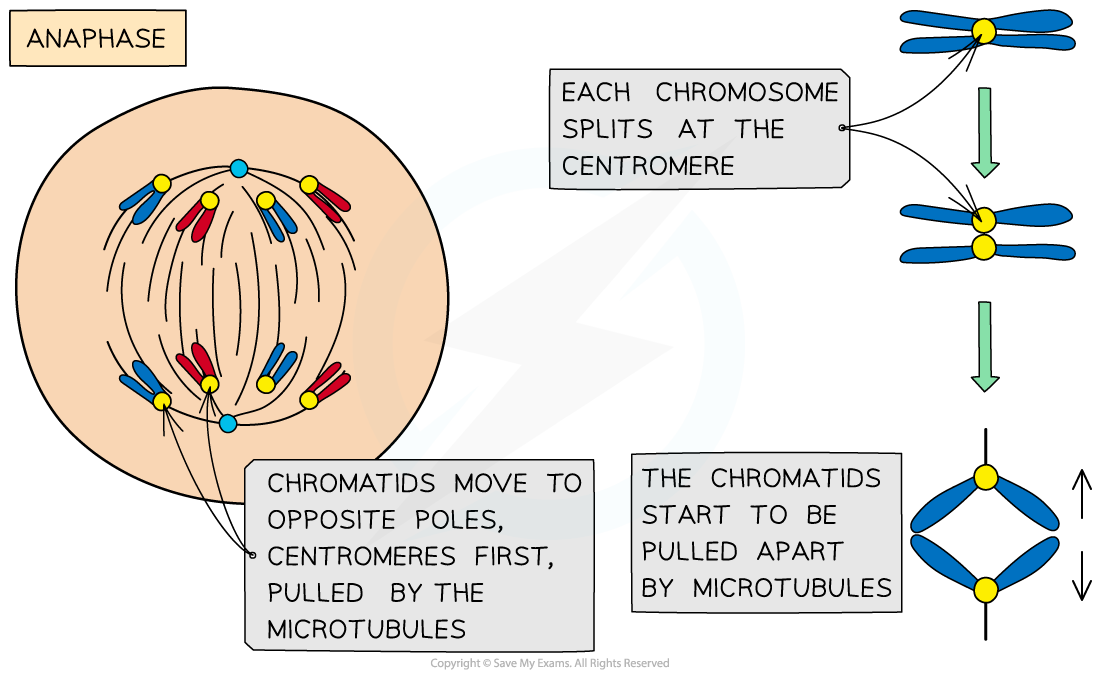 Anaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
- Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense
- Nuclear envelopes (nuclear membranes) begin to reform around each set of chromosomes
- The spindle fibres break down
- New nucleoli form within each nucleus
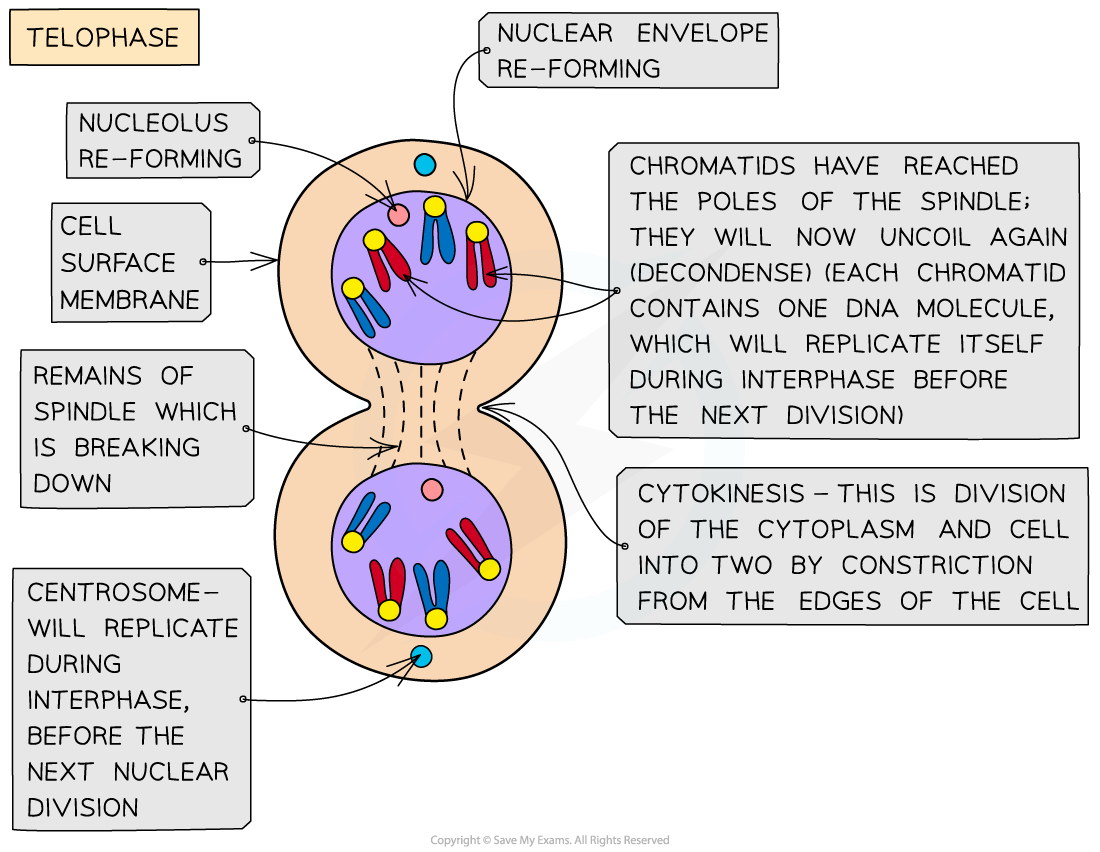
Telophase
Exam Tip
Make sure you learn the four stages of mitosis and what is happening to the DNA molecules (one chromatid contains one DNA molecule) at each stage – learn ‘PMAT’ (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) to help you remember the order of the stages!After interphase but before the parent cell undergoes mitosis, the human parent cell nucleus actually contains 92 DNA molecules! This is because during interphase (S phase), the 46 DNA molecules in the parent cell have replicated to form sister chromatids. As human cells have a diploid number of 46 this replication results in 92 molecules. This ensures the two daughter cells will be diploid (have 46 chromosomes each) when mitosis occurs.Remember to read the questions carefully as only human diploid cells have 46 chromosomes so if the question refers to another organism, its diploid number will be different.
Chromosomes Condense
Condensation of chromosomes
- DNA molecules are very long molecules (human DNA can be more than 50,000 µm) that need to fit within much smaller nuclei (human nuclei average less than 5 µm)
- Prior to mitosis, the DNA molecules are loosely coiled (around histones in eukaryotic cells) to form a complex called chromatin
- During prophase, the chromatin gets condensed by supercoiling to form chromosomes
- Condensation occurs by the repeated coiling of the DNA molecule (supercoiling)
- This supercoiling is aided in eukaryotic cells by the presence of histone proteins and enzymes
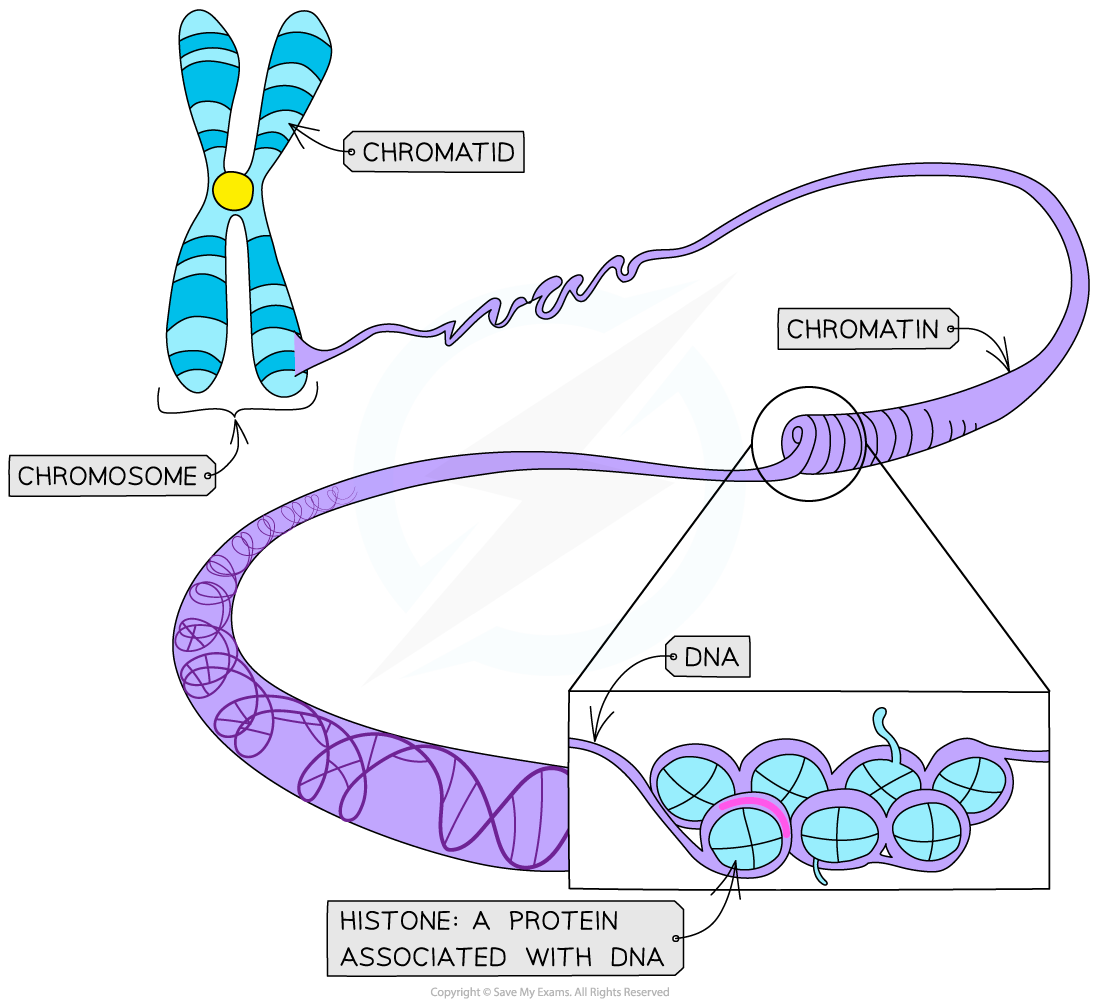
DNA is coiled around histone proteins to make chromatin
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









