- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记1.3.7 Skills: Estimation of Osmolarity
Practical 2: Estimation of Osmolarity
NOS: Experimental design; accurate quantitative measurements in osmosis experiments are essential
- Planning is an essential part of experimental biology, it will help ensure that valid conclusions can be made
- Preliminary (meaning "to come before") research must be completed to ensure the experiment design considers:
- The results that will be collected
- Quantitative data allows more valid conclusions to be made
- Qualitative data (descriptive) can be useful to support the conclusions
How measurements will be made so they are as precise and as accurate as possible
- The choice of apparatus and techniques should be based on the science surrounding the issue being investigated
How many repeats will be undertaken to ensure the data collected is reliable
- The variables that will be tested and need to be controlled
Once the preliminary research has been completed then preliminary studies can be conducted to further aid the experimental design
- The results that will be collected
- These studies are very important for:
- Identifying additional variables that affect the experiment
- Finding the best way to control these variables
- Deciding on the quantities and volumes of substances that are needed so that you do not run out of reactants/reagents
Any experiment conducted without preliminary research or studies is likely to be invalid as the other variables that affect the results in the experiment will not have been identified and controlled
Practical 2: Estimation of osmolarity in tissues by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
- The osmolarity of a solution measures the number of solute particles (that can form bonds with water) per 1 L of solvent
- Osmolarity is expressed as [popover id="XqIR9B3GzVySI6JG" label ="osmoles"] or milliosmoles per litre of solution (Osm/L or mOsm/L)
- A hypotonic solution has a lower osmolarity than the tissue being bathed in it (so the tissue will increase in mass or length) whereas a hypertonic solution has a higher osmolarity (so the tissue will decrease in mass or length)
- An isotonic solution will have the same osmolarity as the tissue (so the mass or length will remain unchanged)
- It is possible to investigate the effects of immersing plant tissue in solutions of different osmotic concentrations (osmolarity) and to use the results to estimate the osmolarity of the plant tissue itself
- The most common osmosis practical of this kind involves cutting cylinders of potato and placing them into solutions with a range of different osmotic concentrations
- Usually sucrose solutions of increasing concentration – at least 5 different concentrations are usually required
Apparatus
- Potato x 2 (same variety)
- Cork borer (e.g. 5mm)
- White tile
- Scalpel
- 10cm ruler or vernier calipers
- Weighing balance (2dp)
- 10 cm³ sucrose solution (0 mol/dm³, 0.25 mol/dm³, 0.5 mol/dm³, 0.75 mol/dm³, 1.00 mol/dm³)
- 5 test tubes (in test tube rack)
- 10 cm³ measuring cylinder
- Paper towels
Method
- The required number of potato cylinders are cut
- At least 5 for each of the solutions you are testing to ensure you have sufficient repeats
They are all cut to the same length and, once blotted dry to remove any excess moisture, their initial mass is measured and recorded before placing into the solutions
- The potato cylinders are left in the solutions for a set amount of time (eg. 30 minutes), usually in a water bath (set at around 30o)
- The solutions are prepared by serial dilutions of a specific solute concentration determined during the preliminary research/trials)
The cylinders are then removed and dried
- This is done to remove excess liquid
The final length and mass of each potato cylinder is then measured and recorded
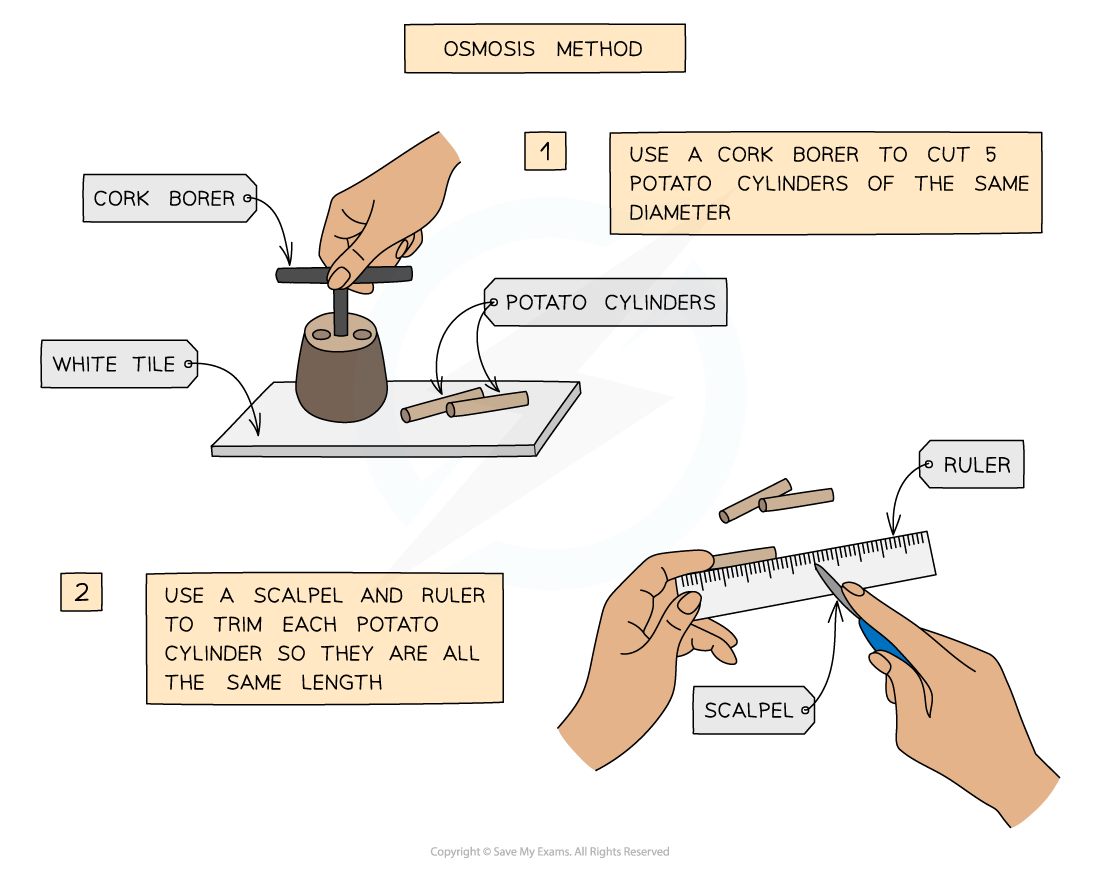
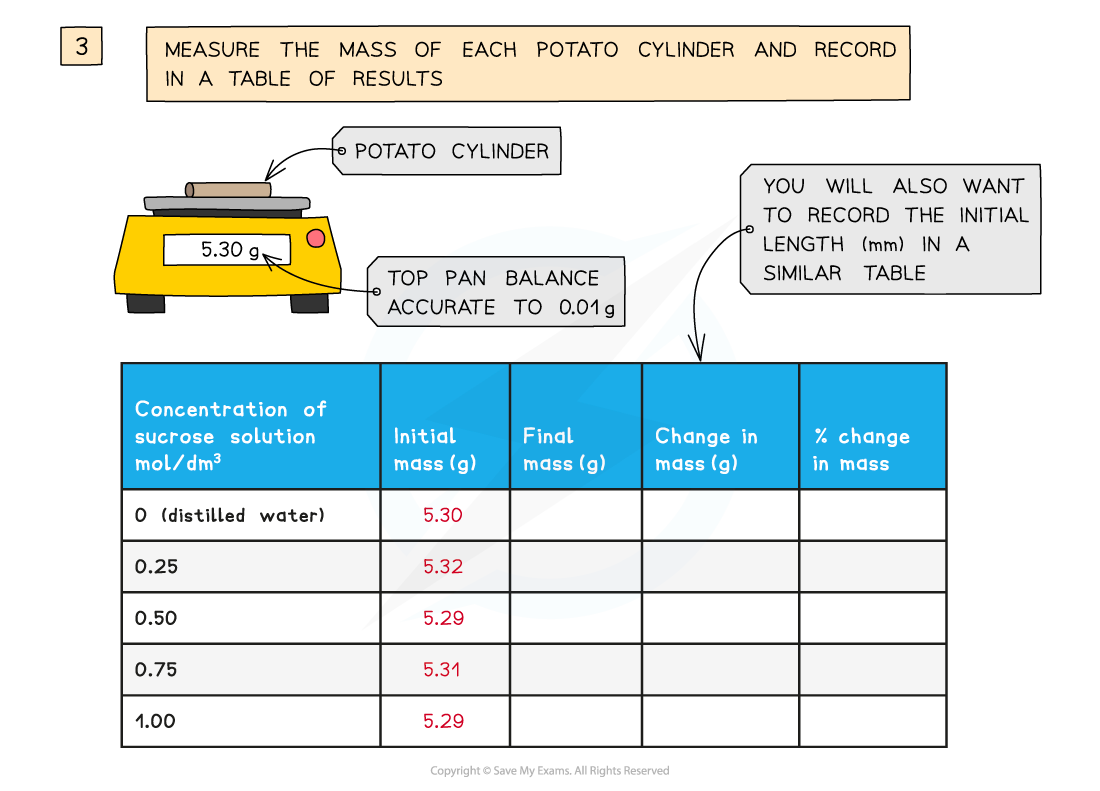
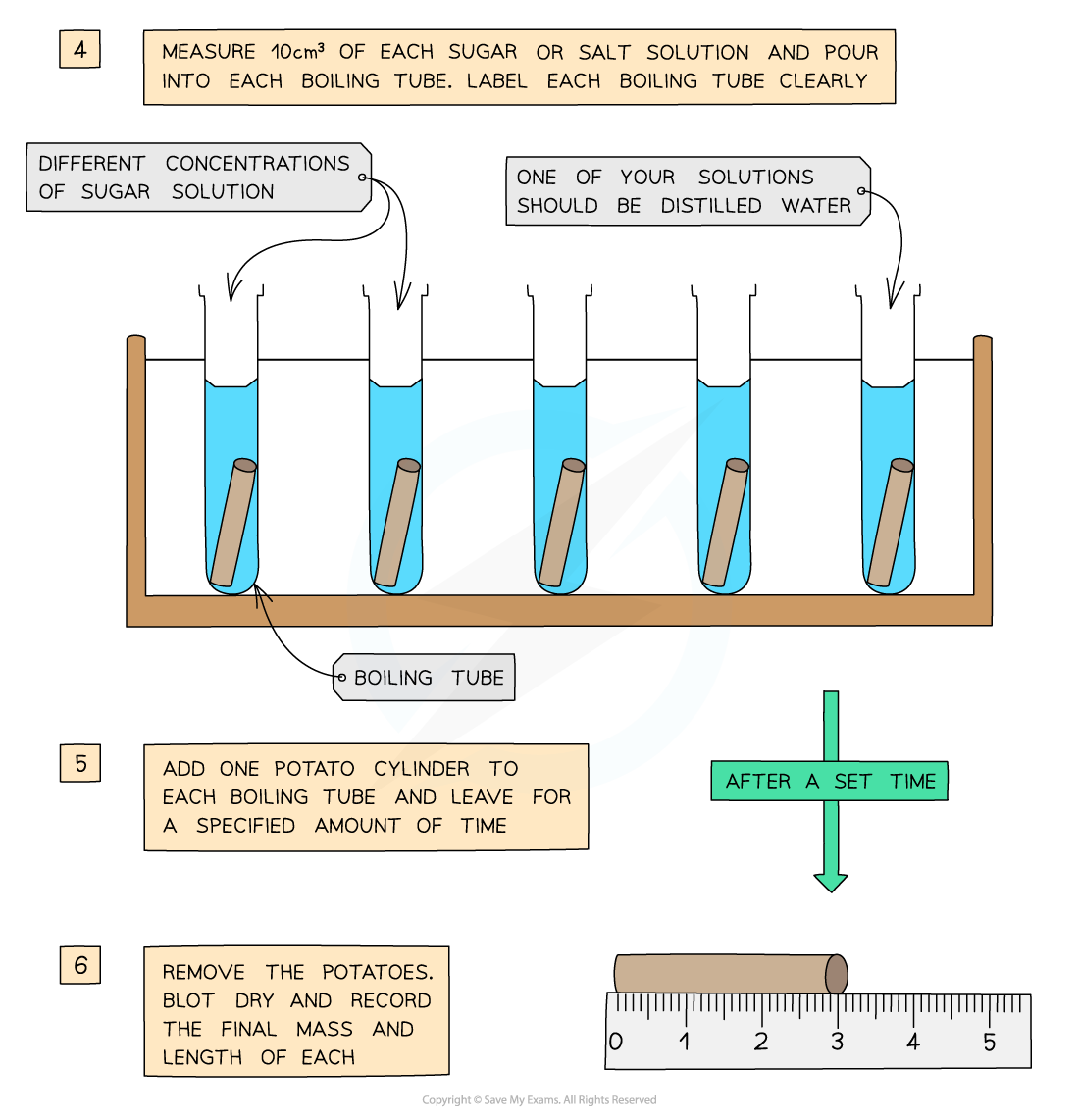
You will need to use apparatus appropriately to measure out the volumes of your solutions and record your measurements
Analysis
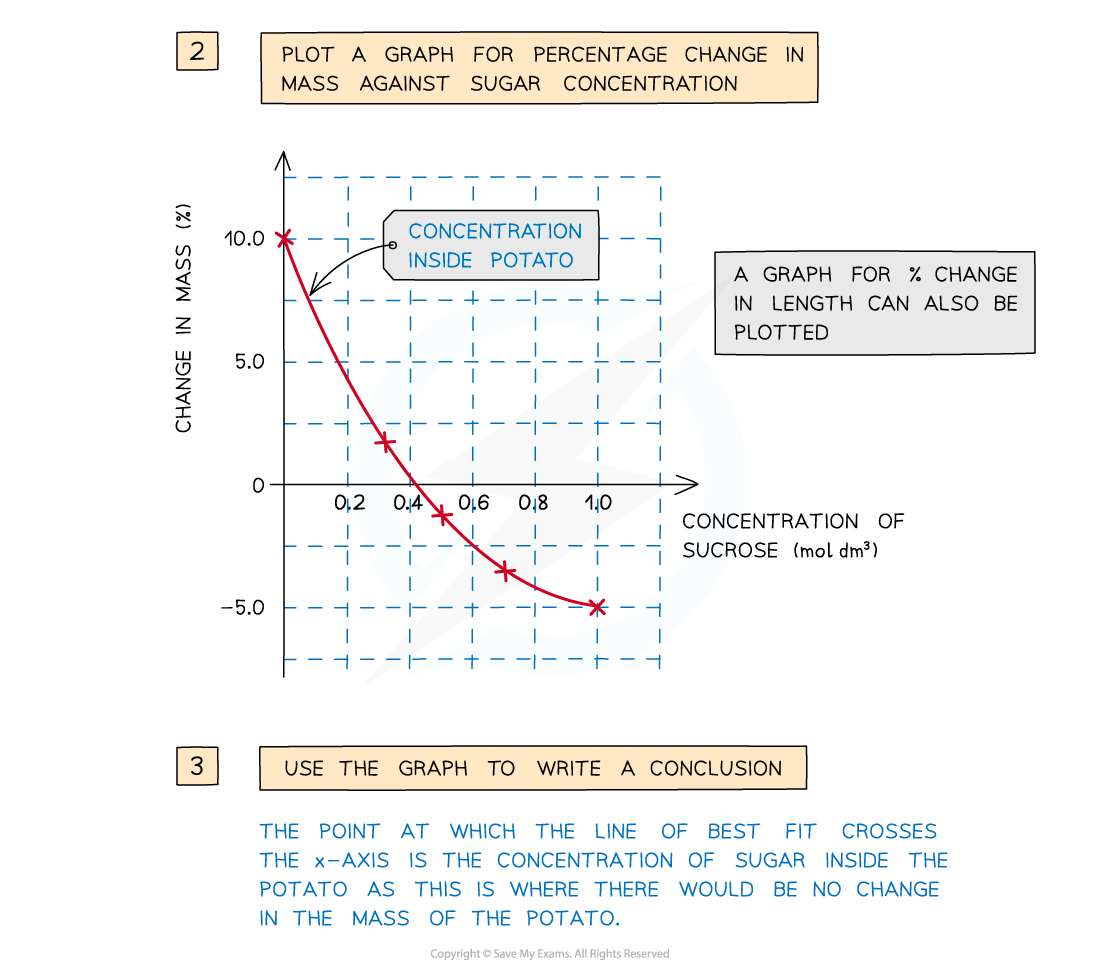
- The percentage change in mass for each potato cylinder is calculated and then plotted
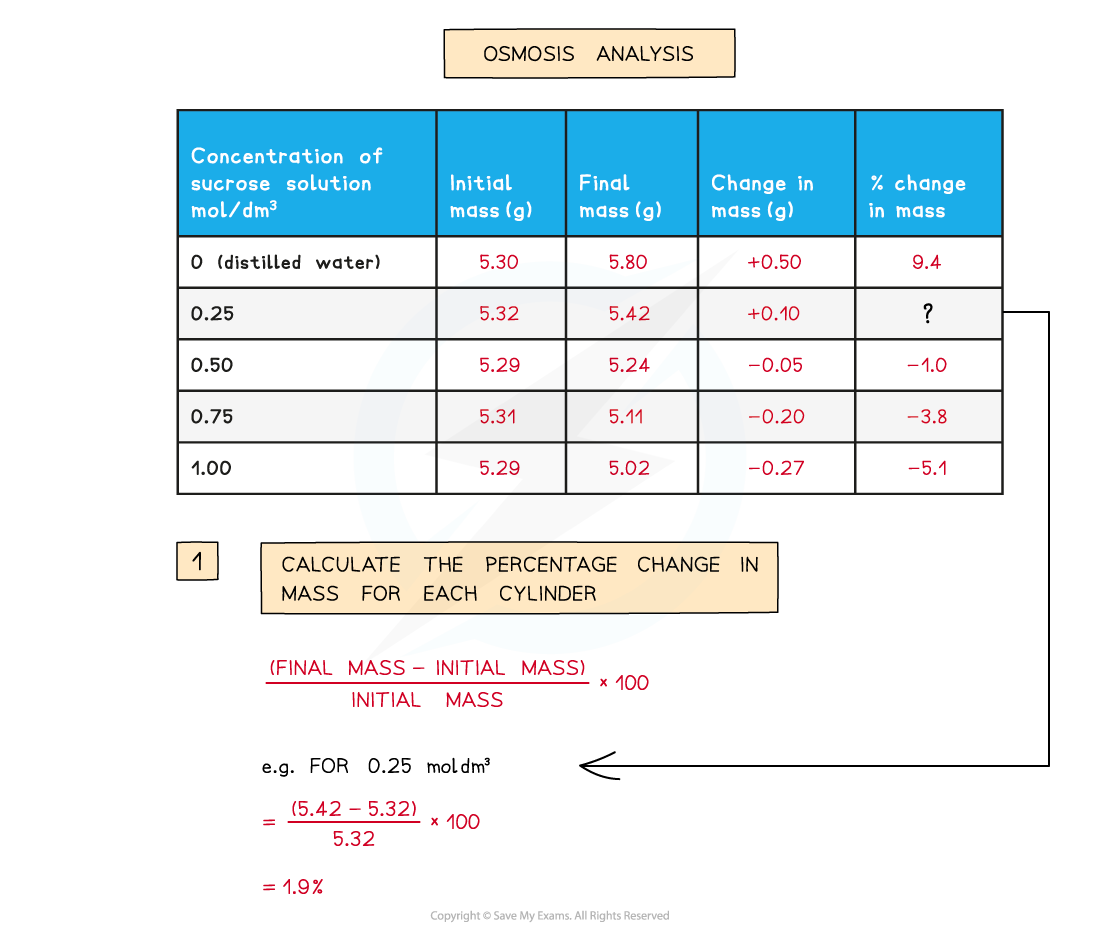
To find the percentage change in mass, the change in mass must be divided by the initial mass and then multiplied by 100
A positive percentage change in mass indicates that the potato has gained water by osmosis
- A positive percentage change in mass indicates that the potato has gained water by osmosis (net movement of water from the solution into the potato) meaning the solution had a lower osmolarity than the potato
- The gain of water makes the potato cells turgid, as the water exerts turgor pressure (or hydrostatic pressure) on the cell walls – the potatoes will feel hard
A negative percentage change suggests the opposite, that is, the solution had a higher osmolarity than the potato
- The potato cylinder in the strongest sucrose concentration will have decreased in mass the most as there is the greatest concentration gradient in this tube between the potato cells (lower osmolarity) and the sucrose solution (higher osmolarity)
- More water molecules will move out of the potato cells by osmosis, making them flaccid and decreasing the mass of the potato cylinder – the potato cylinders will feel floppy
- If looked at underneath the microscope, cells from this potato cylinder might be plasmolysed, meaning the cell membrane has pulled away from the cell wall
If there is a potato cylinder that has neither increased nor decreased in mass, it means there was no overall net movement of water into or out of the potato cells
- The solution that this particular potato cylinder was in had the same osmolarity as the solution found in the cytoplasm of the potato cells, so there was no concentration gradient and therefore no net movement of water into or out of the potato cells
- The concentration of sucrose inside the potato cylinders can be found if a graph is drawn showing how the percentage change in mass changes with the concentration of sucrose solution
- The point at which the line of best fit crosses the x-axis is the concentration of sucrose inside the potato cylinders
Investigating osmolarity using onion cells
- Evidence of osmosis occurring in plant cells can be shown when the cells undergo plasmolysis:
- If a plant cell is placed in a solution with a higher osmolarity than the cell (such as a concentrated sucrose solution), water will leave the cell through its partially permeable cell surface membrane by osmosis
- As water leaves the vacuole of the plant cell, the volume of the cell decreases
- The protoplast (living part of the cell inside the cell wall) gradually shrinks and no longer exerts pressure on the cell wall
- As the protoplast continues to shrink, it begins to pull away from the cell wall
- This process is known as plasmolysis – the plant cell is plasmolysed
This process can be observed using epidermal strips (sections of the very thin outer layer of tissue in plants)
- Plants with coloured sap (such as red onion bulbs, rhubarb petioles and red cabbage) make observations easier
The epidermal strips are placed in a range of molarities of sucrose solution or sodium chloride solutions, of gradually decreasing water potential
- The strips are then viewed under a light microscope and the total number or percentage of onion cells that have undergone plasmolysis can be counted
- Plasmolysis may take several minutes to occur
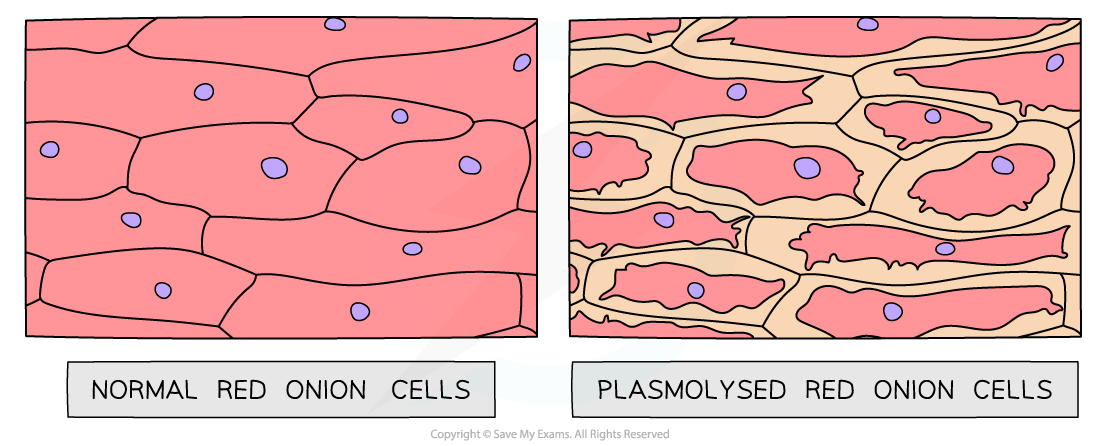
Light micrographs of normal red onion cells alongside those that have plasmolysed (artistic impression). The cells on the left are epidermal cells that have been immersed in distilled water, whilst the cells on the right are epidermal cells that have been immersed in 1.0 mol dm⁻³ sucrose solution.
Exam Tip
Questions involving experiments investigating osmolarity and osmosis are common and you should be able to use your knowledge of osmosis to explain the results obtained. Don’t worry if it is an experiment you haven’t done – simply figure out where the higher concentration of water molecules is – this is the solution with the lower osmolarity – and explain which way the molecules move due to the differences in osmolarity.
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








