- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记1.3.5 Active Transport & Bulk Transport
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of molecules and ions through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy from respiration
- Active transport requires carrier proteins (each carrier protein being specific for a particular type of molecule or ion)
- Although facilitated diffusion also uses carrier proteins, active transport is different as it requires energy
- The energy is required to make the carrier protein change shape, allowing it to transfer the molecules or ions across the cell membrane
- The energy required is provided by ATP (adenosine triphosphate) produced during respiration. The ATP is hydrolysed to release energy
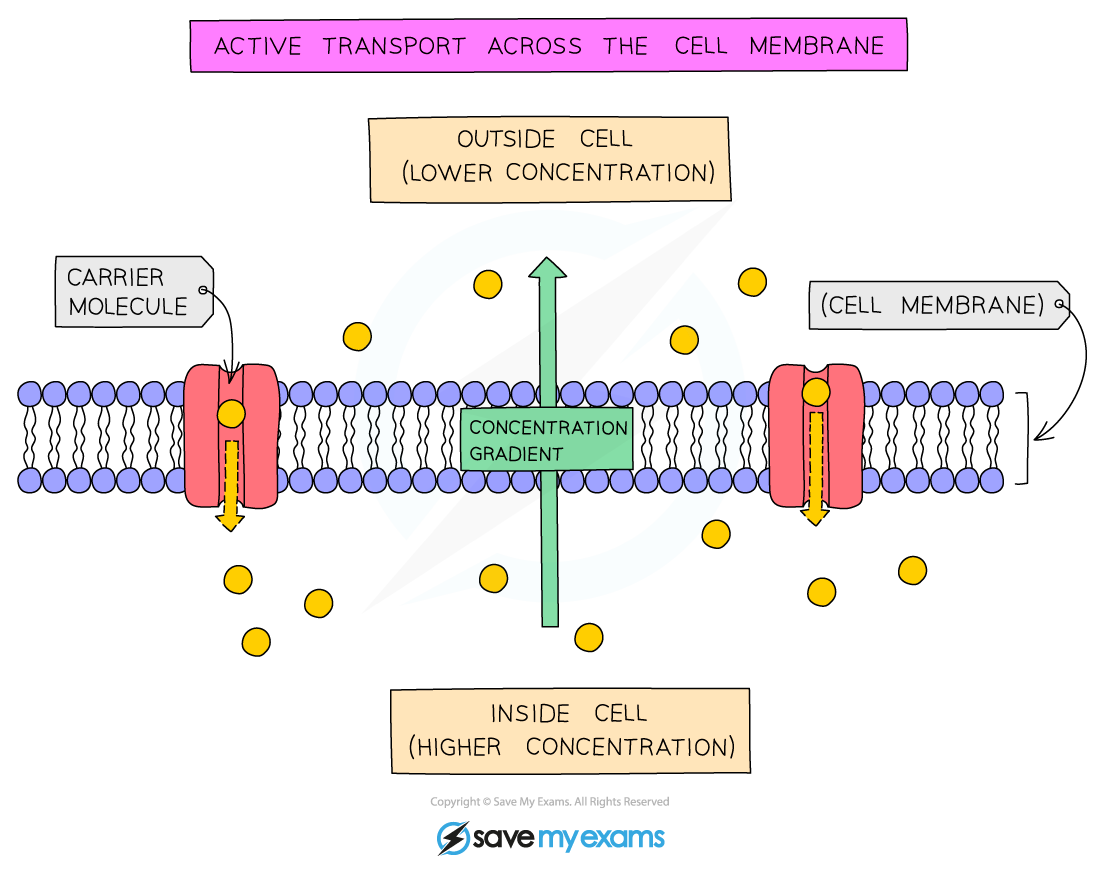
Active transport across the cell membrane
Active Transport: Example
Sodium-potassium pumps in axons
- Sodium-potassium carrier pump proteins are integral proteins that enable an electrochemical gradient (resting membrane potential) to be maintained between the inside and outside of the axon
- Nerve impulses that travel along axons are dependent on sodium and potassium ions being moved across the axon membrane to create this gradient
- The sodium-potassium pumps move three sodium ions out of the axon and two potassium ions into the axon using one ATP molecule per cycle
- The pumps are always moving the ions against their concentration gradient via active transport
- The cycle continues until the resting membrane potential is reached
- The steps to this cycle are:
- Three sodium ions from the inside of the axon bind to the pump
- ATP attaches to the pump and transfers a phosphate to the pump (phosphorylation) causing it to change shape, resulting in the pump opening to the outside of the axon
- The three sodium ions are released out of the axon
- Two potassium ions from outside the axon enter and bind to their sites
- The attached phosphate is released altering the shape of the pump again
- The change in shape causes the potassium ions to be released inside the axon
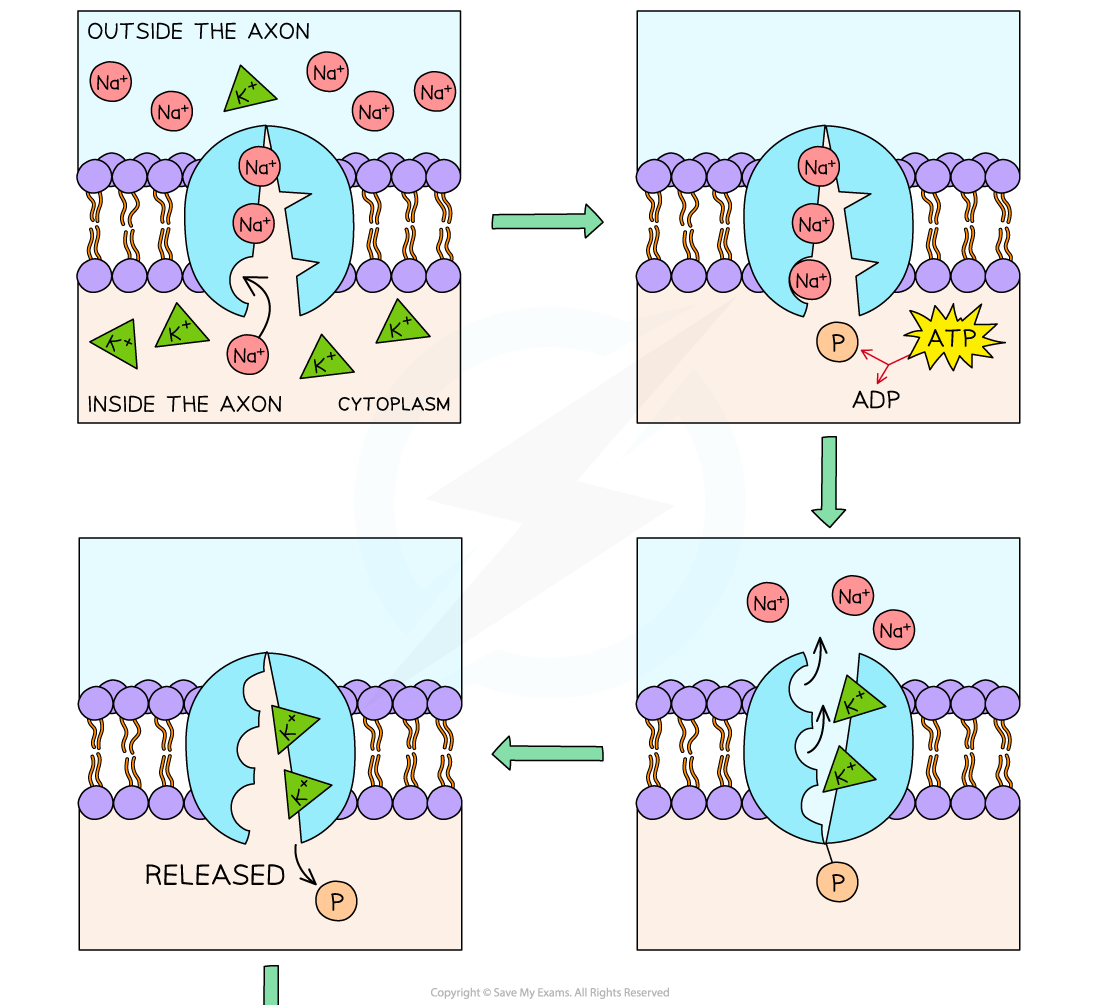
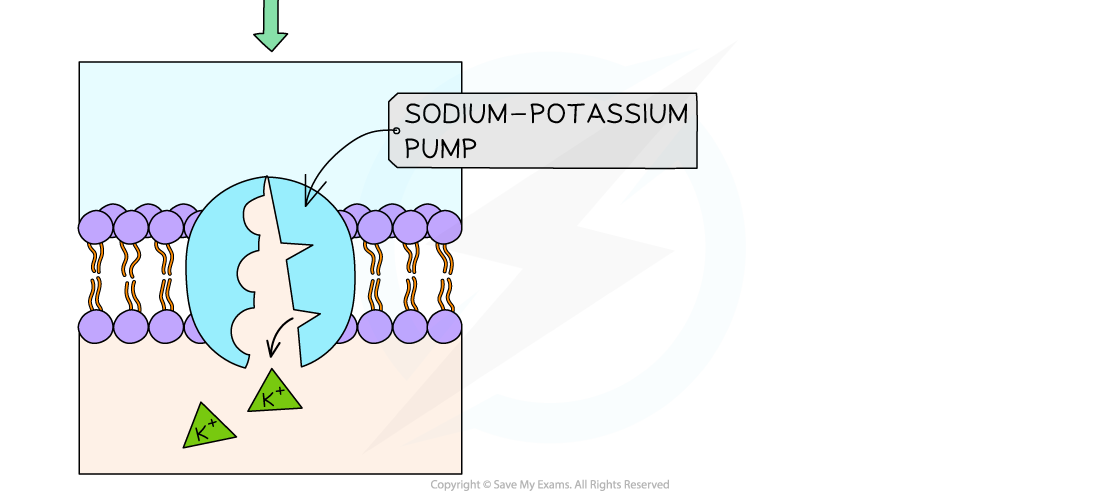
Active transport of sodium and potassium ions in axons using sodium-potassium pump carrier proteins
Bulk Transport
Bulk transport
- The processes of diffusion, osmosis and active transport are responsible for the transport of individual molecules or ions across cell membranes
- However, the bulk transport of larger quantities of materials into or out of cells is also possible
- Examples of these larger quantities of materials that might need to cross the membrane include:
- Large molecules such as proteins or polysaccharides
- Parts of cells
- Whole cells eg. bacteria
Bulk transport into cells = endocytosis
- Bulk transport out of cells = exocytosis
- These two processes require energy and are therefore forms of active transport
- They also require the formation of vesicles which is dependent on the fluidity of membranes
Fluidity of membranes
- The phospholipid bilayer is loosely held together by weak hydrophobic interactions between the hydrocarbon tails
- These weak interactions allow for some degree of membrane fluidity
- The membrane fluidity allows larger substances to move in and out of the cell in vesicles formed when proteins and ATP are used to pinch off small regions of the plasma membrane
Vesicles
- Vesicles are small spherical sacs of plasma membrane containing water and solutes
- They will often contain larger molecules that cannot pass across the plasma membrane (e.g. proteins)
- The formation of vesicles is an active process requiring ATP and proteins and involves a small region of the plasma membrane being pinched off
- Vesicles are normally present in eukaryotic cells
- Vesicles move materials within cells. These materials may be required by other organelles or may be required outside the cell
- An example of materials moved by vesicles out of the cell is digestive enzymes
- In exocrine pancreatic gland cells, proteins synthesised by ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum are packaged into vesicles that move them to Golgi apparatus. Here the vesicles fuse with the membrane of the Golgi apparatus and the proteins are modified. New vesicles then pinch off and move to the plasma membrane to secrete the digestive enzymes into the pancreatic ducts
Vesicles can also be used to move membrane proteins and phospholipids to the plasma membrane so cells can grow or to organelles in the cytoplasm so they can increase in size
Endocytosis
- Endocytosis is the process by which the plasma membrane engulfs material, forming a small sac (or ‘endocytic vacuole’) around it
- There are two forms of endocytosis:
- Phagocytosis:
- This is the bulk intake of solid material by a cell
- Cells that specialise in this process are called phagocytes
- The vacuoles formed are called phagocytic vacuoles
- An example is the engulfing of bacteria by phagocytic white blood cells
Pinocytosis:
- This is the bulk intake of liquids
- If the vacuole (or vesicle) that is formed is extremely small then the process is called micropinocytosis
- Phagocytosis:
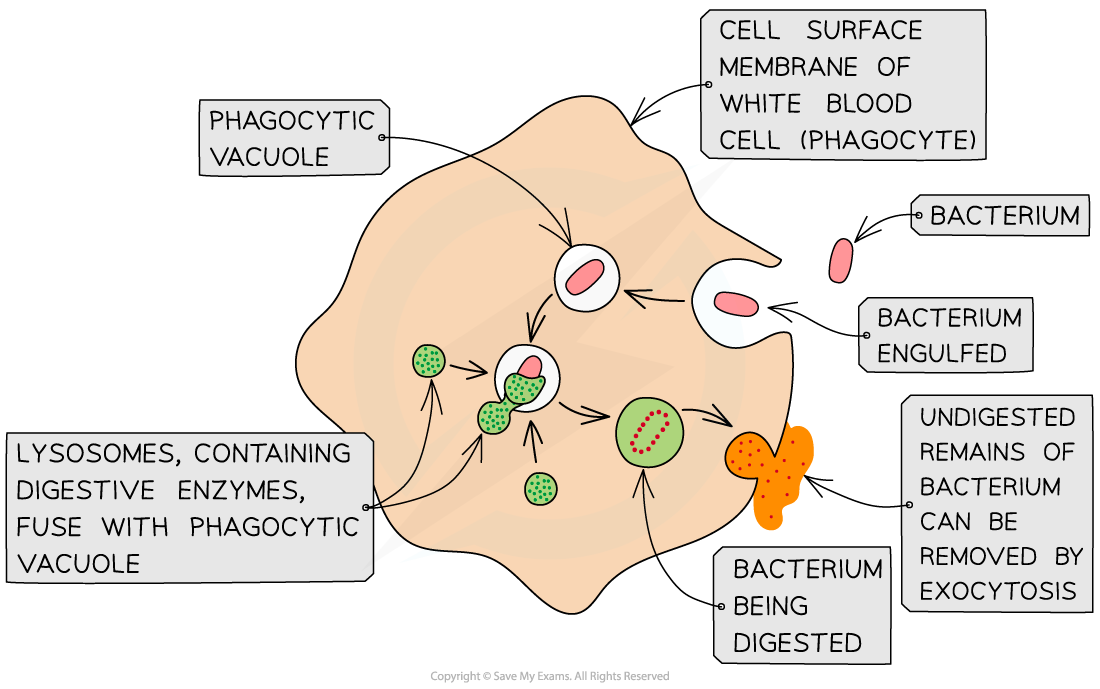
The process of phagocytosis of a bacterium by a phagocyte (white blood cell)
Exocytosis
- Exocytosis is the process by which materials are removed from, or transported out of, cells (the reverse of endocytosis)
- The substances to be released (such as enzymes, hormones or cell wall building materials) are packaged into secretory vesicles formed from the Golgi body
- These vesicles then travel to the cell surface membrane
- Here they fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents outside of the cell
- An example is the secretion of digestive enzymes from pancreatic cells
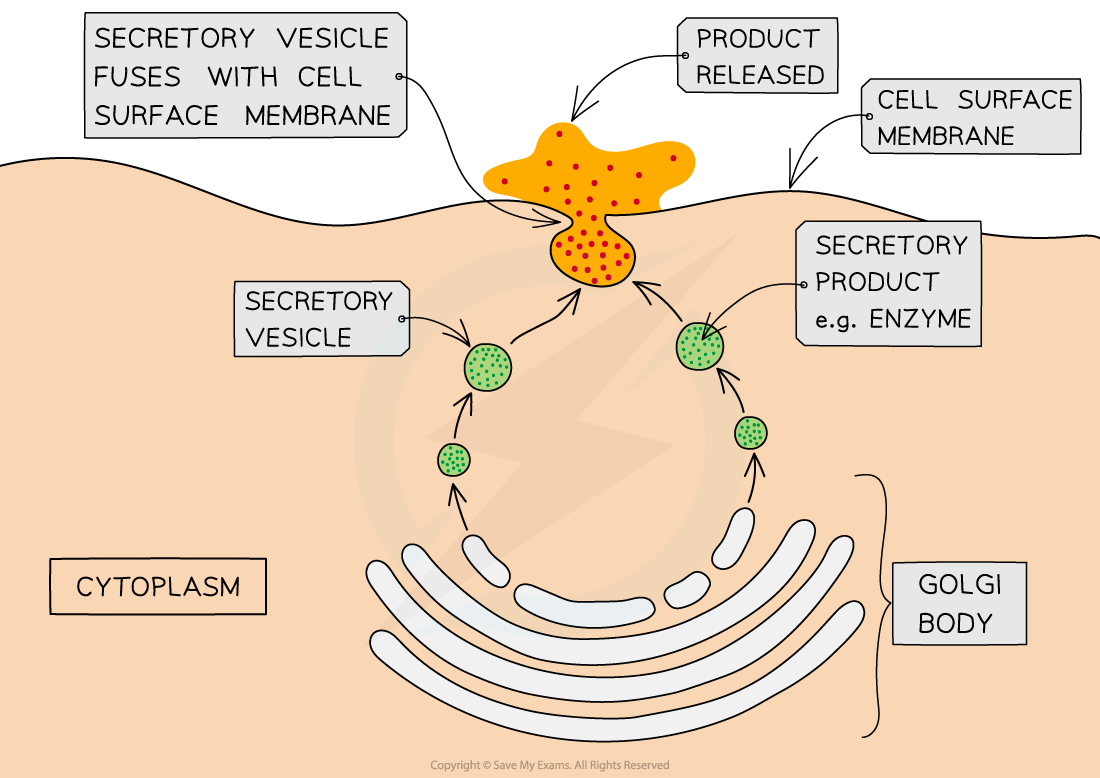
The process of exocytosis
Exam Tip
Remember – active transport, endocytosis and exocytosis all require energy. This energy is provided by ATP produced during respiration.To get the mark in the exam you have to specifically state 'exocytosis' for bulk transport out of the cell and 'endocytosis' (or even better: phagocytosis, pinocytosis) for bulk transport into the cell. Simply stating 'bulk transport' is not specific enough, the examiner will want to know what type of bulk transport and for this you need to state the scientific name!
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









