- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记1.3.4 Membrane Transport
Passive Transport
Simple diffusion
- Simple diffusion is a type of transportation that involves particles passing between phospholipids in the plasma membrane
- It can be defined as:
- The net movement, as a result of the random motion of its molecules or ions, of a substance from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration
- The molecules or ions move down a concentration gradient
- The random movement is caused by the natural kinetic energy of the molecules or ions
- As a result of diffusion, molecules or ions tend to reach an equilibrium (given sufficient time), where they are evenly spread within a given volume of space
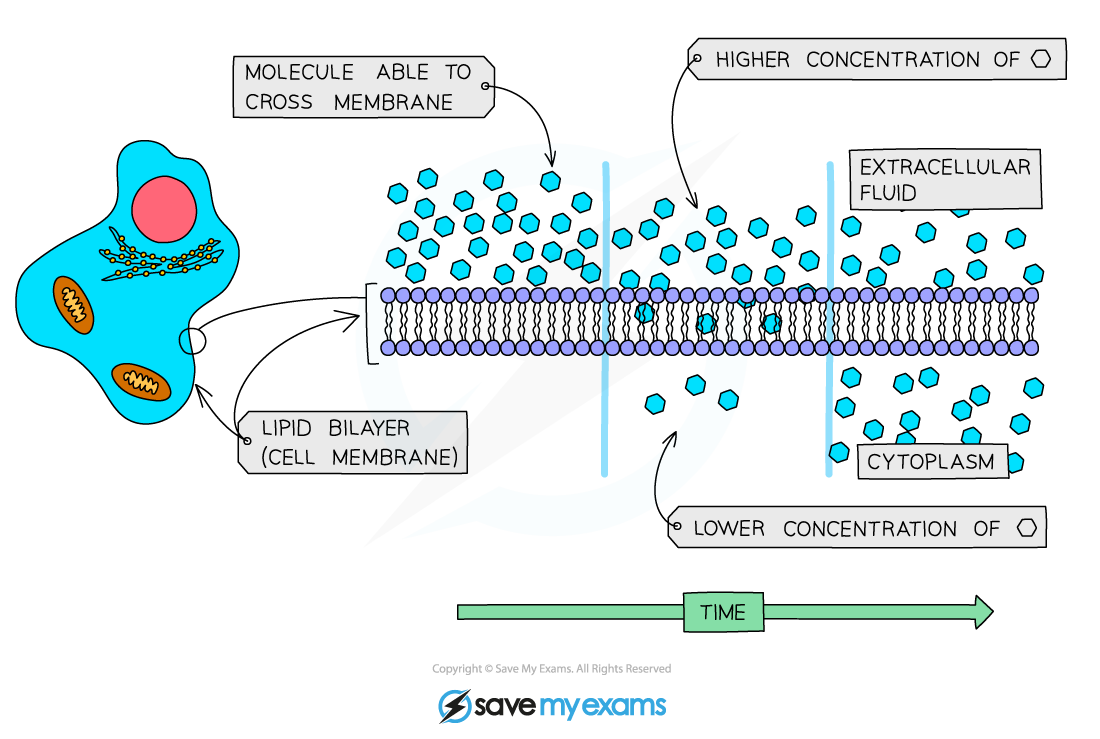
Diffusion across the cell membrane
- The rate at which a substance diffuses across a membrane depends on several factors:
- 'Steepness' of the concentration gradient - the greater the difference the higher the rate of diffusion
- Temperature - the higher the temperature the higher the rate of diffusion
- Surface area - the greater the surface area the higher the rate of diffusion
-
- Large molecules diffuse more slowly as they require more energy to move
- Uncharged molecules (e.g. oxygen) diffuse faster as they move directly across the phospholipid bilayer
- Non-polar molecules diffuse more quickly as they are soluble in the non-polar phospholipid bilayer
- Although polar molecules cannot easily pass through the hydrophobic part of the membrane, smaller polar molecules (e.g. urea) can diffuse at low ratesProperties of the molecules or ions
Facilitated diffusion
- Certain substances cannot diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. These include:
- Large polar molecules such as glucose and amino acids
- Ions such as sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-)
- These substances can only cross the phospholipid bilayer with the help of certain proteins
- This form of diffusion is known as facilitated diffusion
- There are two types of proteins that enable facilitated diffusion:
- Channel proteins
- Carrier proteins (these can also be used during active transport)
- They are highly specific (they only allow one type of molecule or ion to pass through)
Channel proteins
- Channel proteins are water-filled pores
- They allow charged substances (eg. ions) to diffuse through the cell membrane
- The diffusion of these ions does not occur freely, most channel proteins are ‘gated’, meaning that part of the channel protein on the inside surface of the membrane can move in order to close or open the pore
- This allows the channel protein to control the exchange of ions
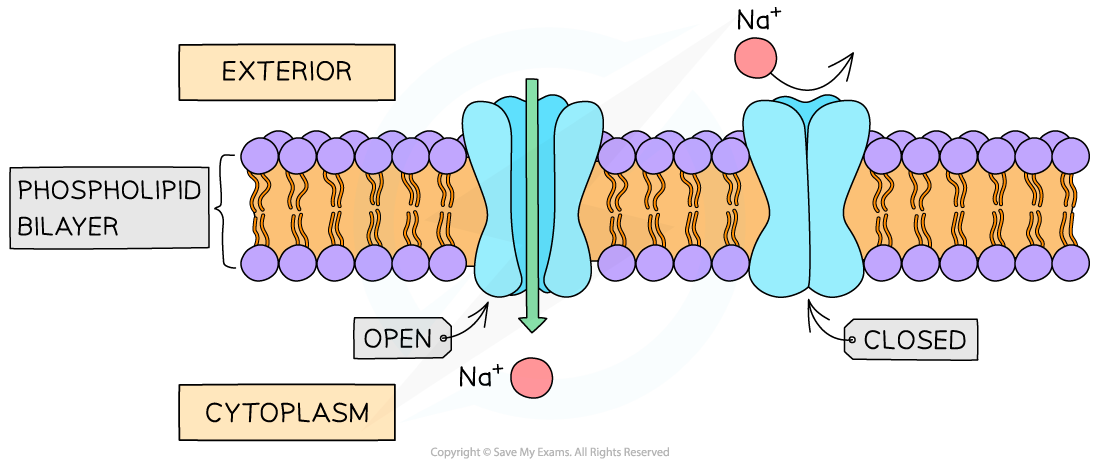
A channel protein (open and closed)
Carrier proteins
- Unlike channel proteins which have a fixed shape, carrier proteins can switch between two shapes
- Initially, the binding site of the carrier protein is open to one side of the membrane
- When the carrier protein switches shape it opens to the other side of the membrane
- The direction of movement of molecules diffusing across the membrane depends on their relative concentration on each side of the membrane
- During facilitated diffusion, the net diffusion of molecules or ions into or out of a cell will occur down a concentration gradient (from an area containing many of that specific molecule to an area containing less of that molecule)
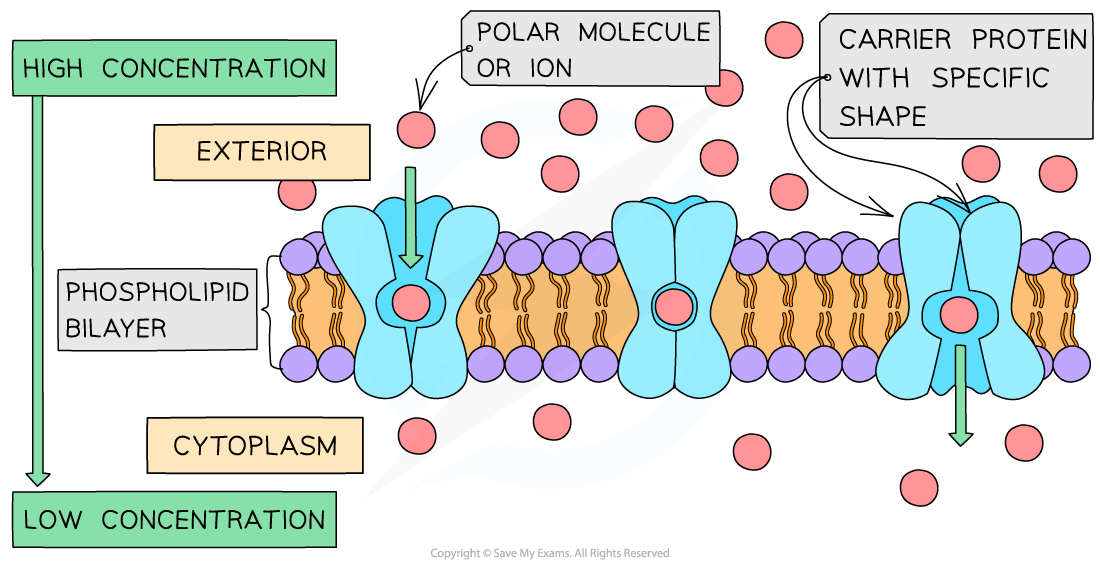
A carrier protein changing shape during facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
- All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane which is partially permeable
- Water can move in and out of cells by osmosis
- Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution across a partially permeable membrane
- In doing this, water is moving down its concentration gradient
The cell membrane is partially permeable which means it allows small molecules (like water) through but not larger molecules (like solute molecules)
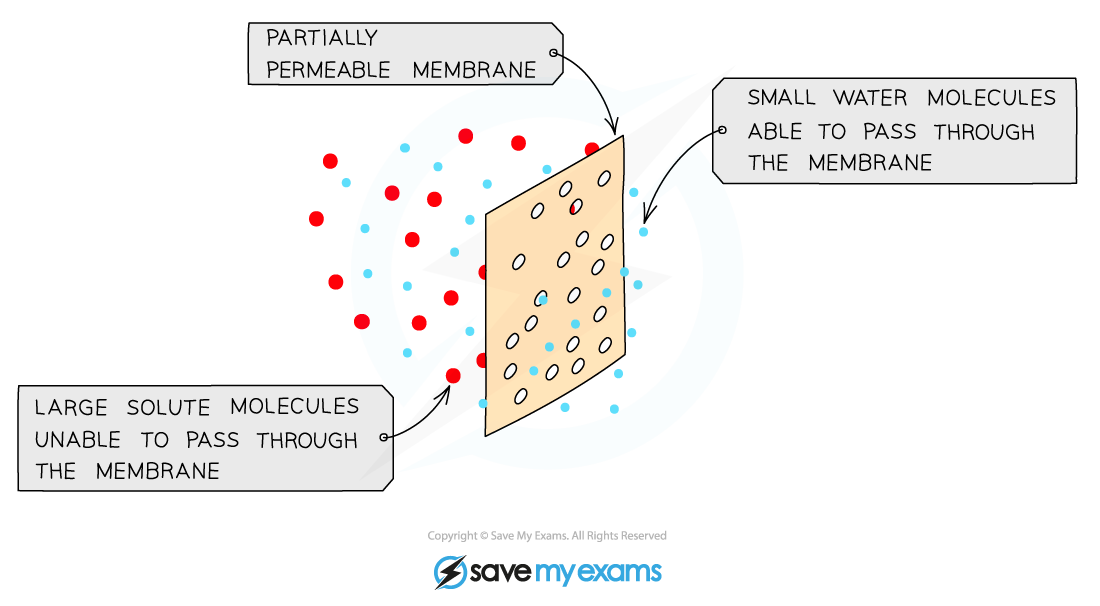 Osmosis and the partially permeable membrane
Osmosis and the partially permeable membrane
- Osmosis can also be described as the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential, through a partially permeable membrane
- Water potential describes the tendency of water to move out of a solution. This term is used to avoid confusion between water concentration and concentration of a solution
- A dilute solution has a low solute concentration and a high water potential (the right-hand side of the diagram below)
- A concentrated solution has a high solute concentration and a low water potential (the left-hand side of the diagram below)
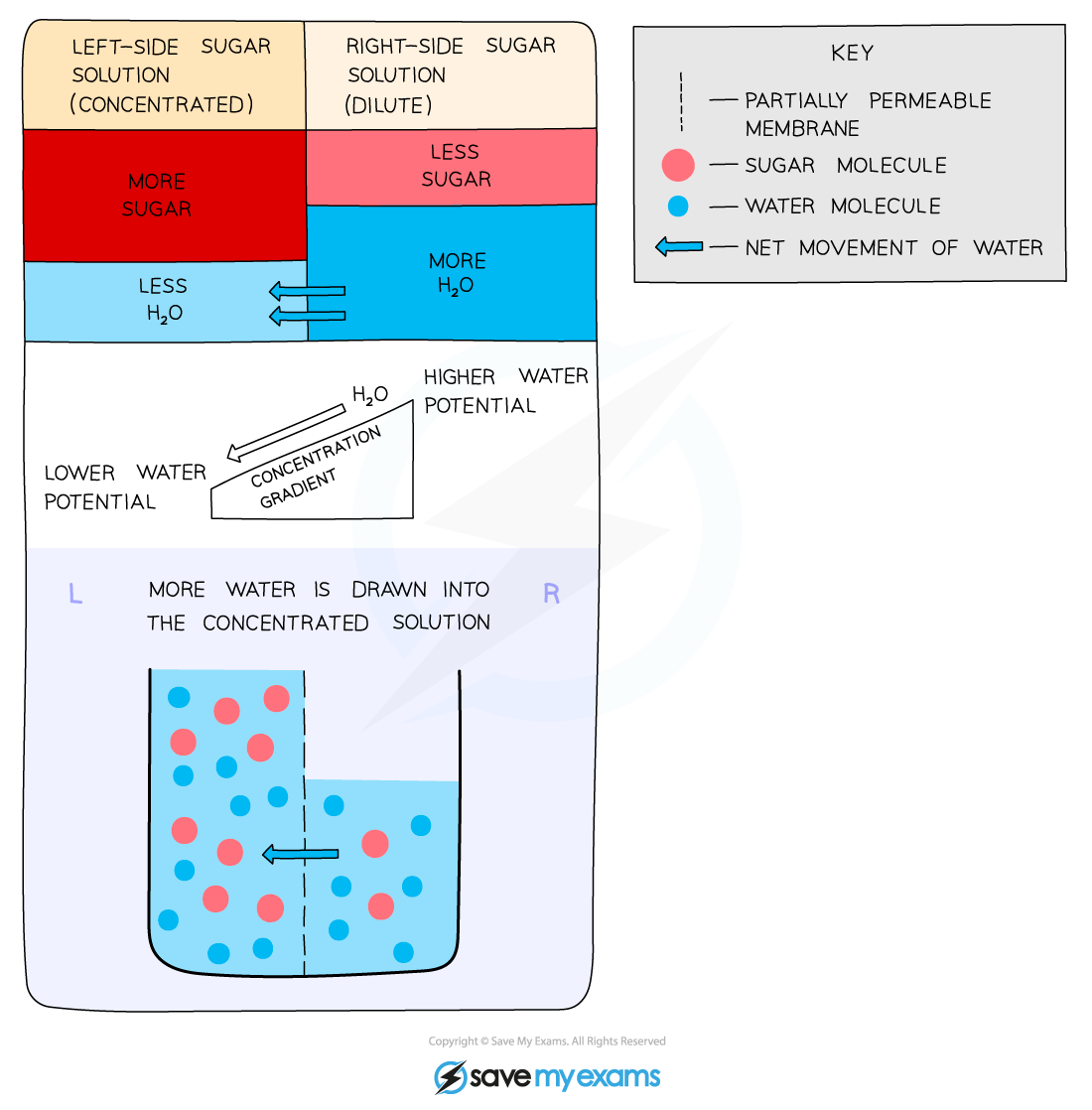 How osmosis works. The water moves from the region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to the region of lower water potential (concentrated solution).
How osmosis works. The water moves from the region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to the region of lower water potential (concentrated solution).
Exam Tip
Remember – the movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration is diffusion. If this movement requires the aid of a protein (for example because the molecule is charged and cannot pass directly through the phospholipid bilayer) this is facilitated diffusion.
Facilitated Diffusion: Example
Axons
- The axon is part of a nerve cell (neuron)
- It is a long, narrow tube (it can be one metre in length with a diameter of one micron) containing cytoplasm surrounded by a membrane
- Axons transmit nerve impulses
- These nerve impulses occur because sodium and potassium ions are being moved across the axon membrane creating a voltage difference
Facilitated diffusion of potassium
- Voltage-gated channel proteins (enabling facilitated diffusion) allow the movement of the potassium ions
- Potassium ions require channel proteins to diffuse across the axon as they are charged and bond with water when they dissolve in the cytoplasm
- Potassium channels are integral proteins and allow only potassium ions through because:
- Other positively charged ions are too large to move through the channel
- Other ions are too small to form bonds with the amino acids located in the channel so they remain attached to water molecules
The potassium channels in axons are voltaged gated
- The channel proteins will open (to allow potassium ions to diffuse out) when the charge inside the axon is relatively more positive than outside
- However, the channel proteins rapidly close due to the presence of an extra globular protein subunit. This subunit fits inside the open channel within milliseconds of the channel opening blocking any further diffusion out of the potassium ions
- The subunit remains in place until the potassium channel closes
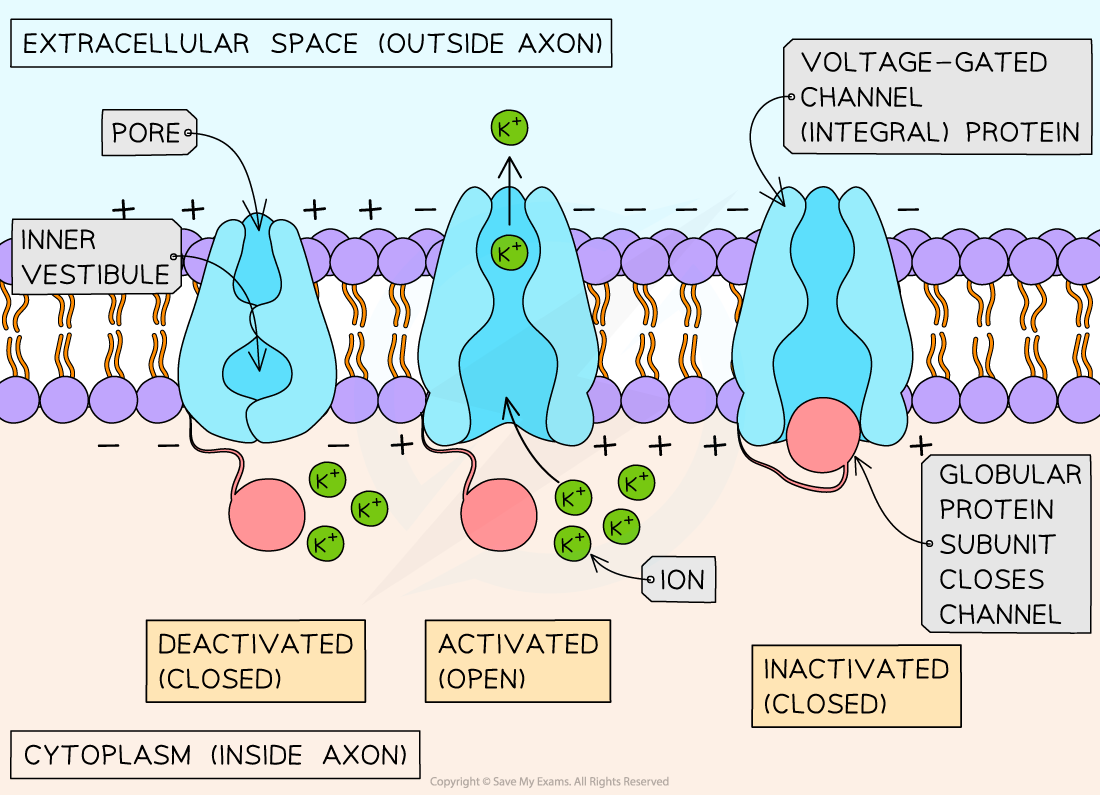
Voltage-gated potassium channels facilitate the diffusion of potassium ions
Prevention of Osmosis in Medical Procedures
Animal cells can lose and gain water as a result of osmosis
- As animal cells do not have a supporting cell wall (unlike plant cells), the results of this loss or gain of water on the cell are severe
- This is why a constant water potential must be maintained inside the bodies of animals
Animal cells losing water
- If an animal cell is placed in a solution with a lower water potential than the cell, water will leave the cell through its partially permeable cell surface membrane by osmosis and the cell will shrink and shrivel up
- This is crenation (the cell has become crenated), which is usually fatal for the cell
Crenation occurs when the cell is in a hypertonic environment (the solution outside of the cell has a higher solute concentration than the inside of the cell)
Animal cells gaining water
- If an animal cell is placed in pure water or a dilute solution, water will enter the cell through its partially permeable cell surface membrane by osmosis, as the pure water or dilute solution has a higher water potential
- The cell will continue to gain water by osmosis until the cell membrane is stretched too far and the cell bursts (cytolysis), as it has no cell wall to withstand the increased pressure created
- This is fatal for the cell
Lysis occurs when the cell is in a hypotonic environment (the solution outside of the cell has a lower solute concentration than the inside of the cell)
Animal cells in isotonic environments
- If an animal cell is in an isotonic environment (the solution outside of the cell has the same solute concentration as the inside of the cell)
- The movement of water molecules into and out of the cell occurs at the same rate (no net movement of water) and there is no change to the cells
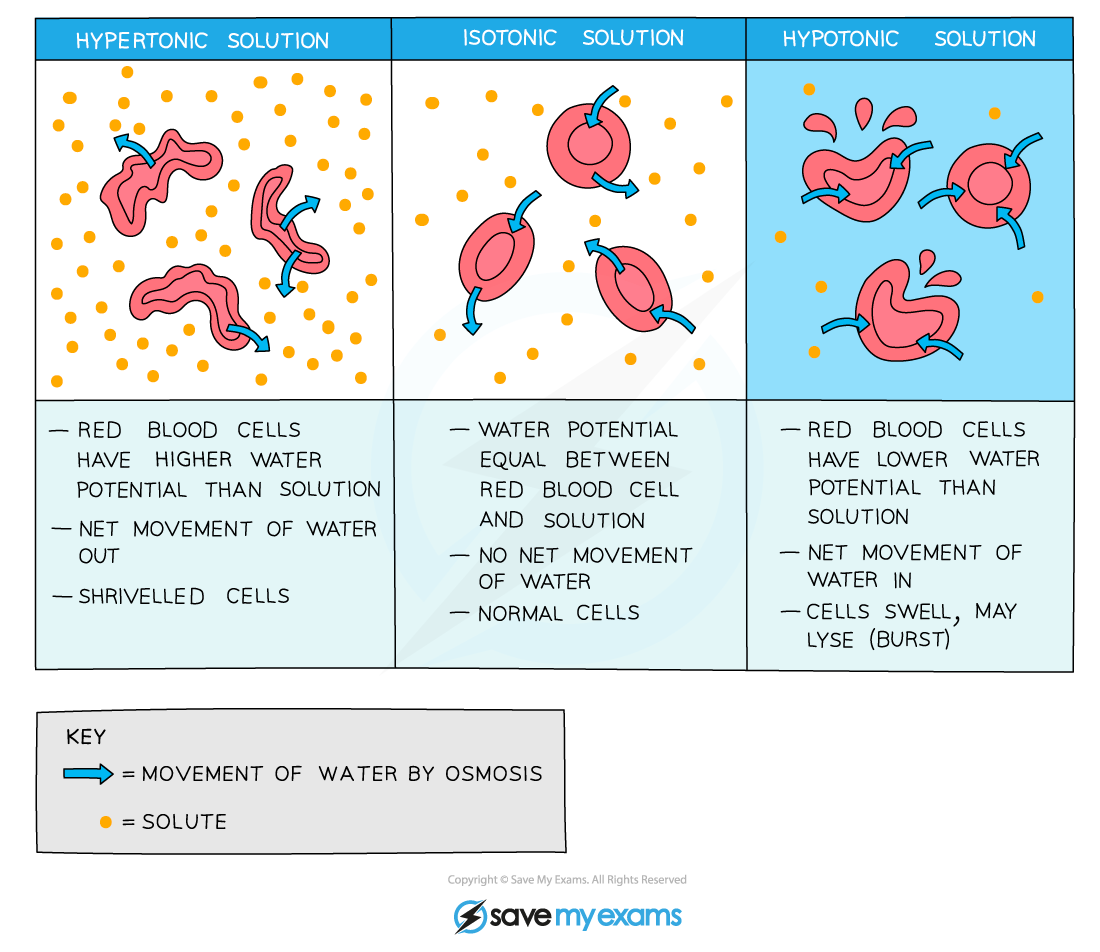
Effect of osmosis on animal cells
Osmolarity of solutions used in medical procedures
- Tissues and organs that are to be used in medical procedures must be kept in solution to prevent damage to the cells
- The osmolarity of the solution is key
- The osmolarity of a solution measures the number of solute particles (that can form bonds with water) per 1 L of solvent
- Osmolarity is expressed as [popover id="XqIR9B3GzVySI6JG" label ="osmoles"] or milliosmoles per litre of solution (Osm/L or mOsm/L)
- Human tissue is normally 306 mOsm/L
- A solution with the same osmolarity = isotonic
- A solution with a higher osmolarity = hypertonic
- A solution with a lower osmolarity = hypotonic
Isotonic sodium chloride solutions (normal saline) are generally used as they can be:
- Frozen to create a slush used to pack donor organs for transportation
- Injected into a patient's blood system
- Used to sterilise wounds
- Used as eye drops
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









