- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Maths: AI SL复习笔记5.2.3 Applications of Integration
Finding the Constant of Integration
What is the constant of integration?
- When finding an anti-derivative there is a constant term to consider
 In terms of graphing an anti-derivative, there are endless possibilities
In terms of graphing an anti-derivative, there are endless possibilities
- collectively these may be referred to as the family of antiderivatives or family of curves
- the constant of integration is determined by the exact location of the curve
- if a point on the curve is known, the constant of integration can be found
How do I find the constant of integration?
 Exam Tip
Exam Tip
- If a constant of integration can be found then the question will need to give you some extra information
- If this is given then make sure you use it to find the value of c
Worked Example

Area Under a Curve Basics
What is meant by the area under a curve?
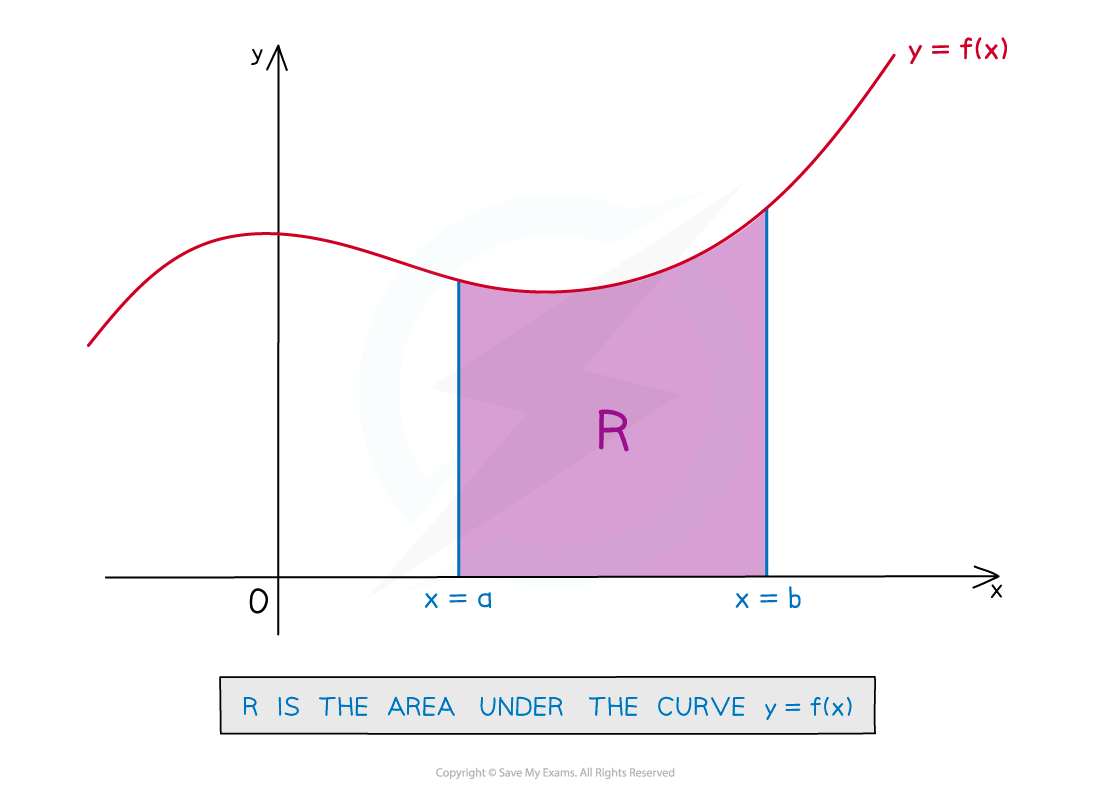
 What is a definite integral?
What is a definite integral?
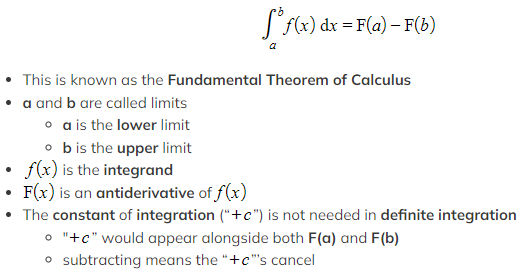 How do I form a definite integral to find the area under a curve?
How do I form a definite integral to find the area under a curve?

Exam Tip
- Look out for questions that ask you to find an indefinite integral in one part (so “+c” needed), then in a later part use the same integral as a definite integral (where “+c” is not needed)
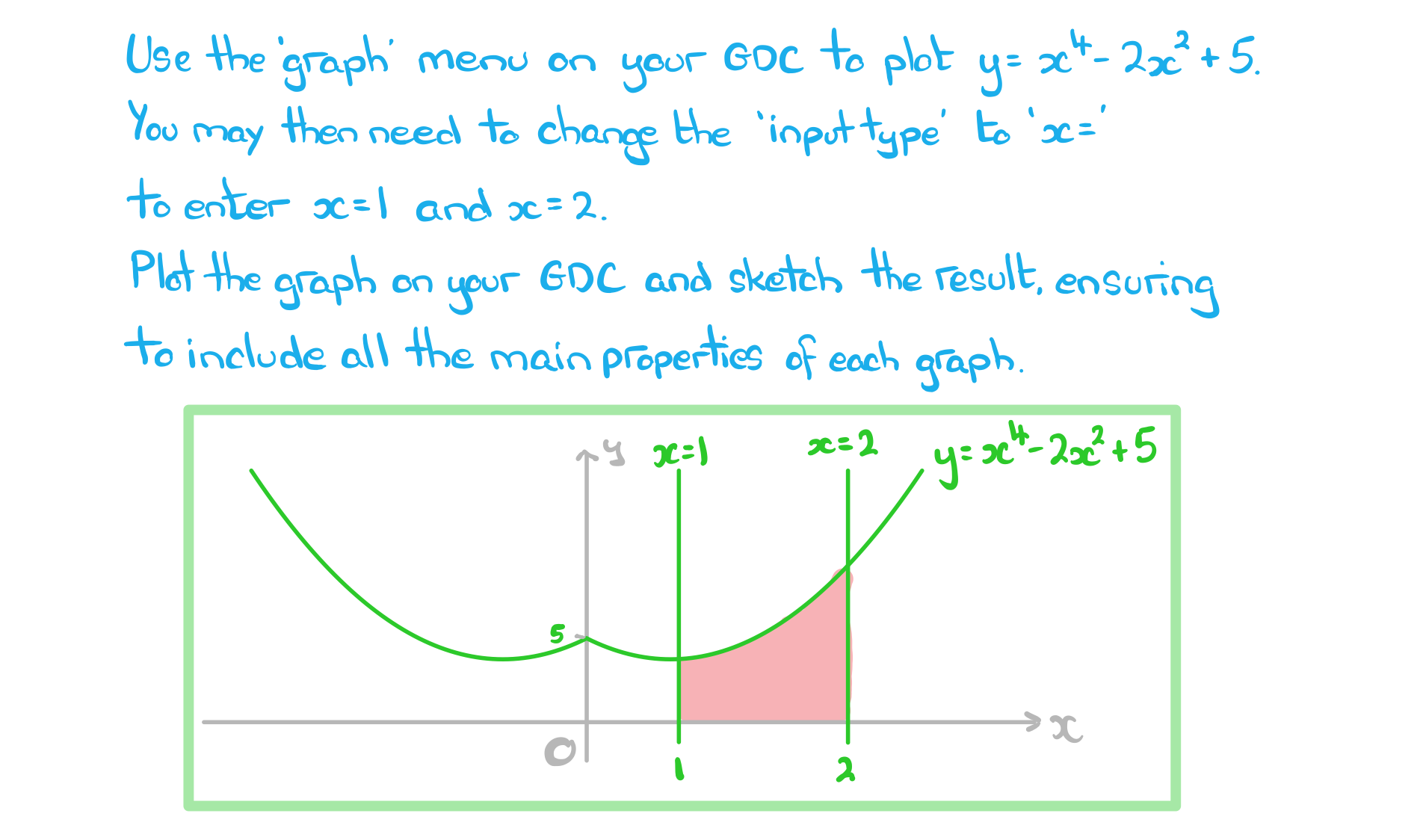
- Add information to any diagram provided in the question, as well as axes intercepts and values of limits
- Mark and shade the area you’re trying to find, and if no diagram is provided, sketch one!
Definite Integrals using GDC
Does my calculator/GDC do definite integrals?
- Modern graphic calculators (and some ‘advanced’ scientific calculators) have the functionality to evaluate definite integrals
- i.e. they can calculate the area under a curve (see above)
- If a calculator has a button for evalutaing definite integrals it will look something like
- This may be a physical button or accessed via an on-screen menu
- Some GDCs may have the ability to find the area under a curve from the graphing screen
- Be careful with any calculator/GDC, they may not produce an exact answer
How do I use my GDC to find definite integrals? Exam Tip
Exam Tip
- When revising for your exams always use your GDC to check any definite integrals you have carried out by hand
- This will ensure you are confident using the calculator you plan to take into the exam and should also get you into the habit of using you GDC to check your work, something you should do if possible
Worked Example

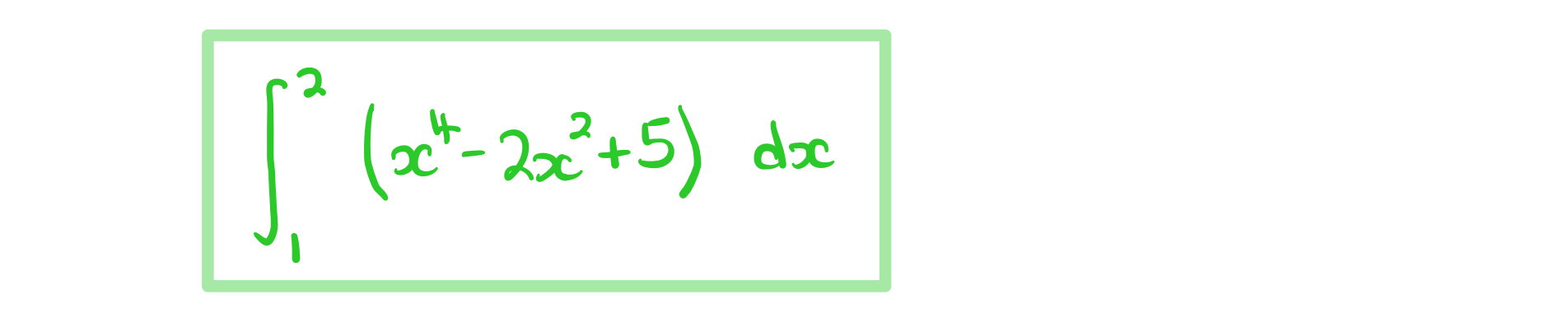


转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








