- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Maths: AI SL复习笔记2.3.6 Strategy for Modelling Functions
Modelling with Functions
What is a mathematical model?
- A mathematical model simplifies a real-world situation so it can be described using mathematics
- The model can then be used to make predictions
- Assumptions about the situation are made in order to simplify the mathematics
- Models can be refined (improved) if further information is available or if the model is compared to real-world data
How do I set up the model?
- The question could:
- give you the equation of the model
- tell you about the relationship
- It might say the relationship is linear, quadratic, etc
- ask you to suggest a suitable model
- Use your knowledge of each model
- E.g. if it is compound interest then an exponential model is the most appropriate
- You may have to determine a reasonable domain
- Consider real-life context
- E.g. if dealing with hours in a day then
- E.g. if dealing with physical quantities (such as length) then
- Consider the possible ranges
- If the outcome cannot be negative then you want to choose a domain which corresponds to a range with no negative values
- Sketching the graph is helpful to determine a suitable domain
- Consider real-life context
Which models do I need to know?
- Linear
- Piecewise linear
- Quadratic
- Cubic
- Exponential
- Direct variation
- Inverse variation
- Sinusoidal
Exam Tip
- You need to be familiar with the format of the different types of equations and the general shape of the graphs they produce, you need to always be thinking "does my answer seem appropriate for the given situation?"
- Sketching graphs is key
- Make sure that you use your GDC to plot the relevant function(s)
- Sometimes you may have to play around with the zoom function or the axes to make sure that you are focused on the relevant domain
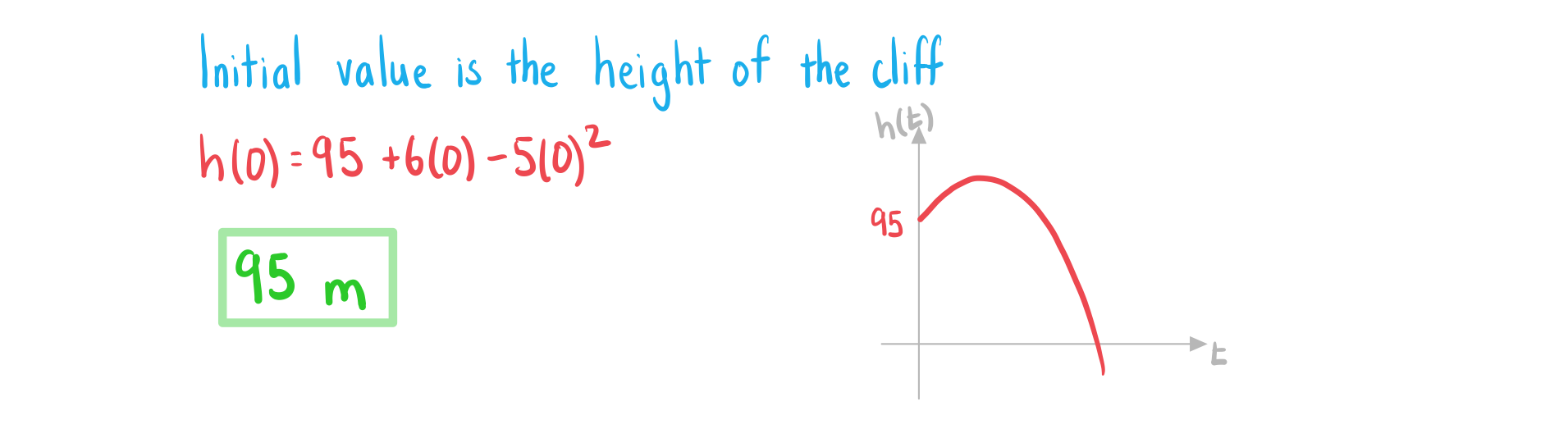
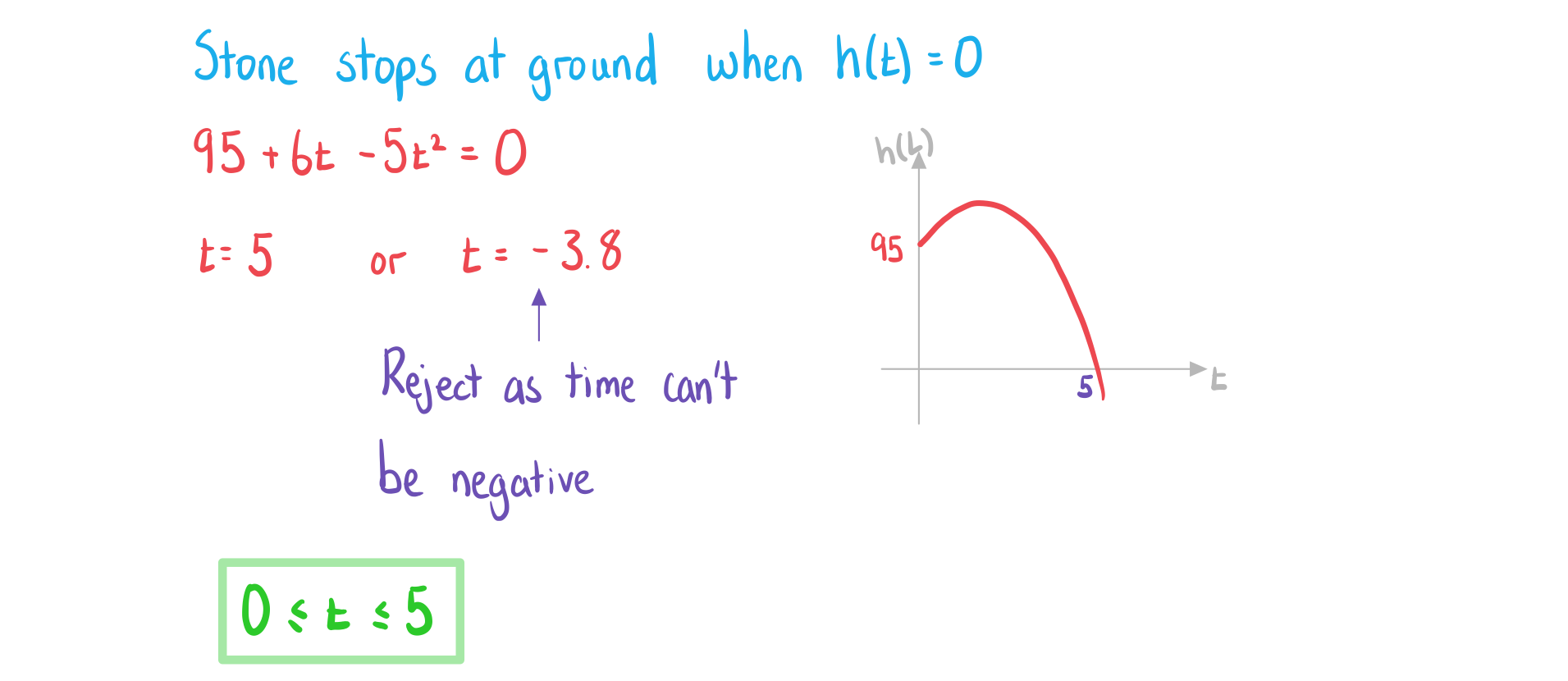
Worked Example

![]()
Finding Parameters
What do I do if some of the parameters are unknown?
- For some models you can use your knowledge to find unknown parameters
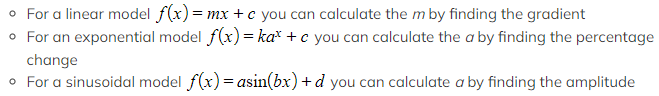 A general method is to form equations by substituting in given values
A general method is to form equations by substituting in given values
-
- You can form multiple equations and solve them simultaneously using your GDC
- You could be expected to solve a system of three simultaneous equations of three unknowns
- This method works for all models
- You can form multiple equations and solve them simultaneously using your GDC
- The initial value is the value of the function when the variable is 0
- This is normally one of the parameters in the equation of the model
Exam Tip
- Make sure that any sketches you are asked to make are fully labelled with the coordinates of any important points, e.g. intersections with the axes or other lines, local maxima/minima etc.
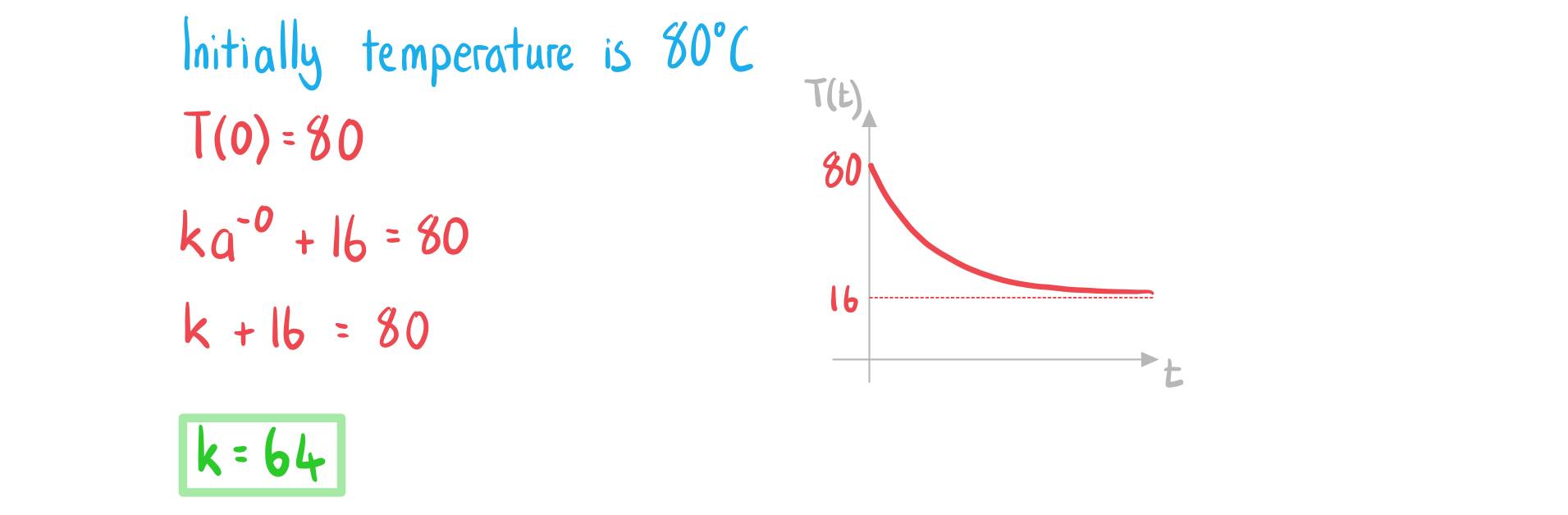
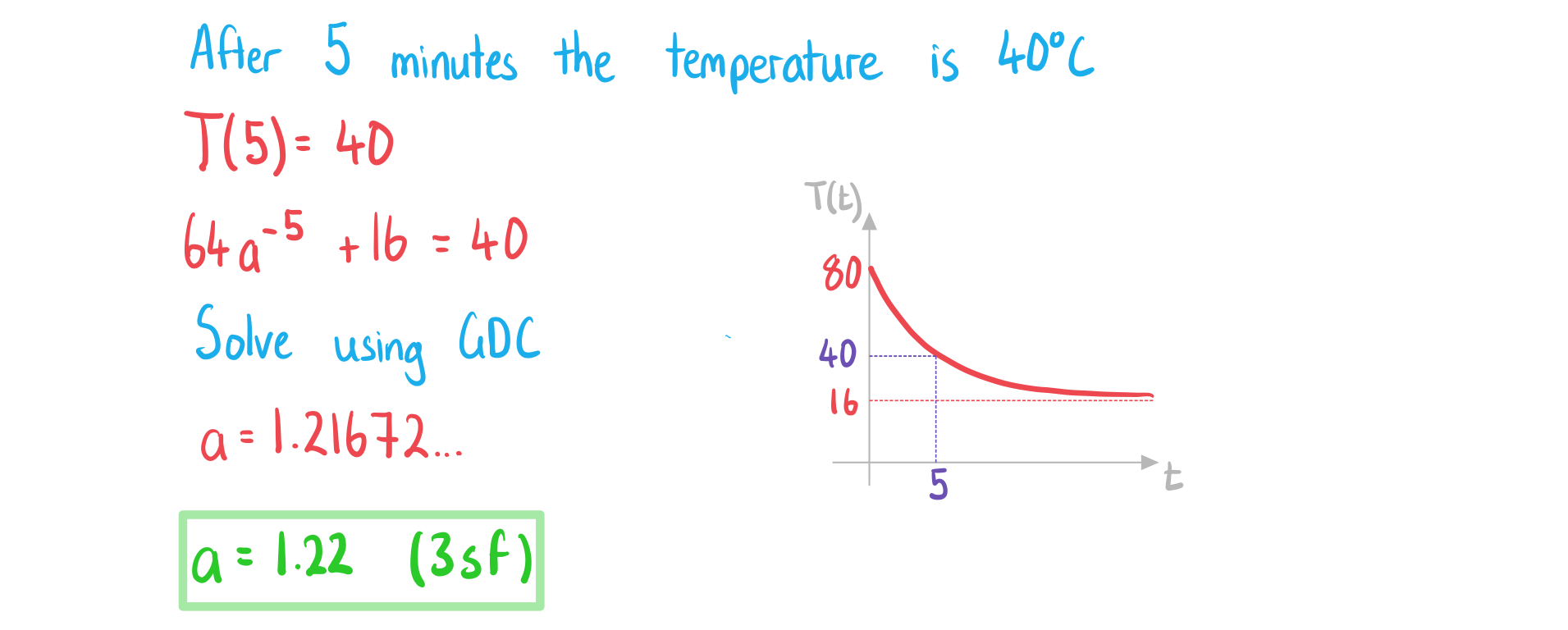
Worked Example

![]()
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









