Electrical Power
- Power is defined as
The rate of energy transfer or the amount of energy transferred per second
- The power of a device depends on:
- The voltage (potential difference) of the device
- The current of the device
- The power of an electrical component (or appliance) is given by the equation:

- The unit of power is the Watt (W), which is the same as a joule per second (J/s)
- This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle:
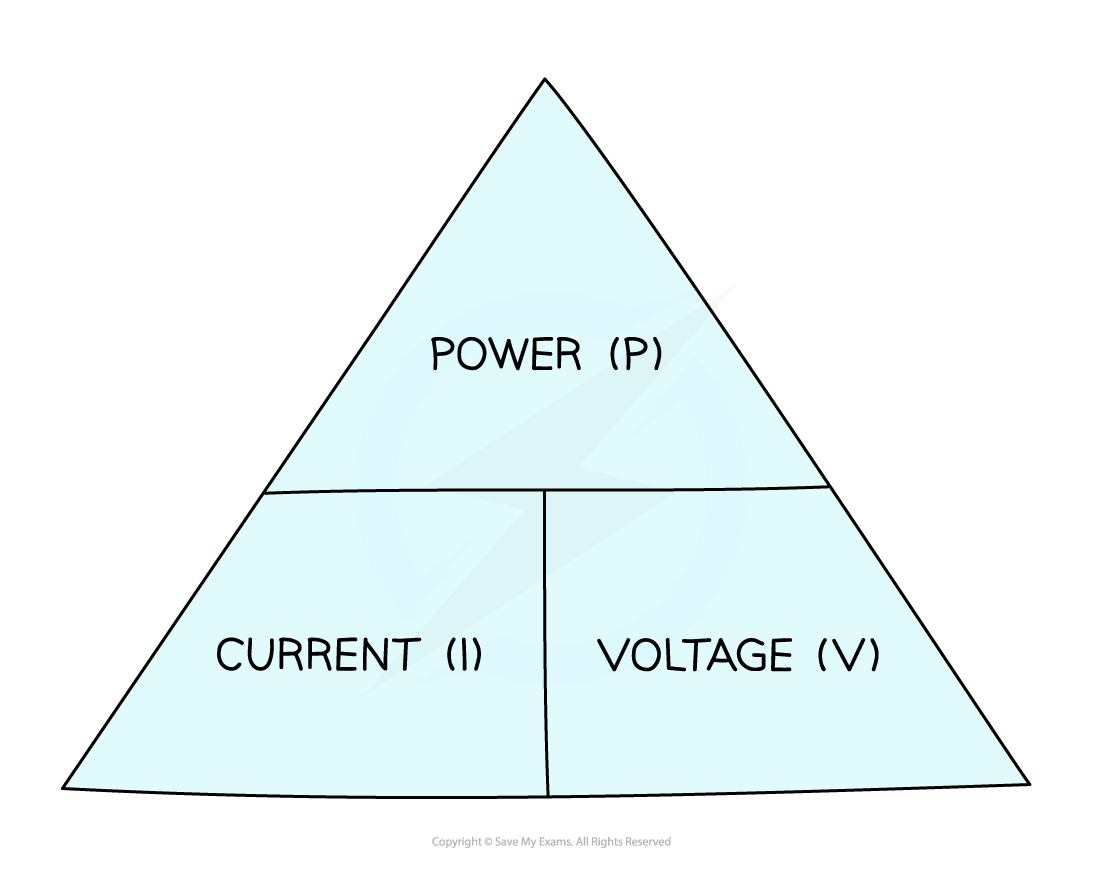
Power, current, voltage formula triangle
Worked Example
Calculate the potential difference through a 48 W electric motor with a current of 4 A.
Step 1: List the known quantities
-
- Power, P = 48 W
- Current, I = 4 A
Step 2: Write down the relevant equation
P = IV
Step 3: Rearrange for potential difference, V
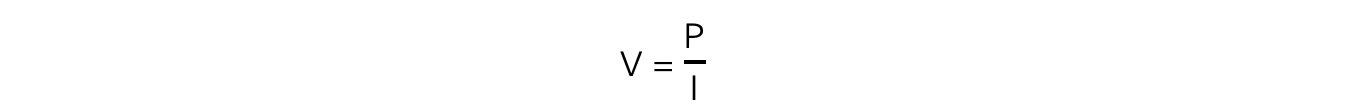
Step 4: Substitute in the values
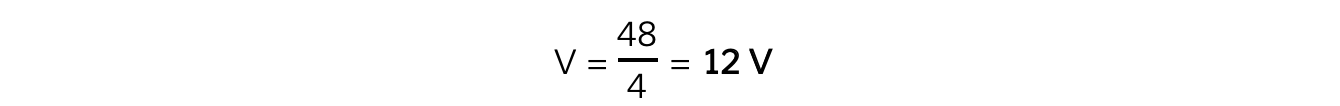
Exam Tip
Remember: Power is just energy per second. Think of it this way will help you to remember the relationship between power and energyYou can remember the unit by the phrase: “Watt is the unit of power?”
Selecting Fuses
- A fuse is a safety device designed to cut off the flow of electricity to an appliance if the current becomes too large (due to a fault or a surge)

The circuit symbol for a fuse - take care not to confuse this with a resistor
- Fuses usually consist of a glass cylinder which contains a thin metal wire
- If the current in the wire becomes too large:
- The wire heats up and melts
- This causes the wire to break, breaking the circuit and stopping the current
- This makes sure that more current doesn't keep flowing through the circuit and causing more damage to the equipment, or, causing a fire
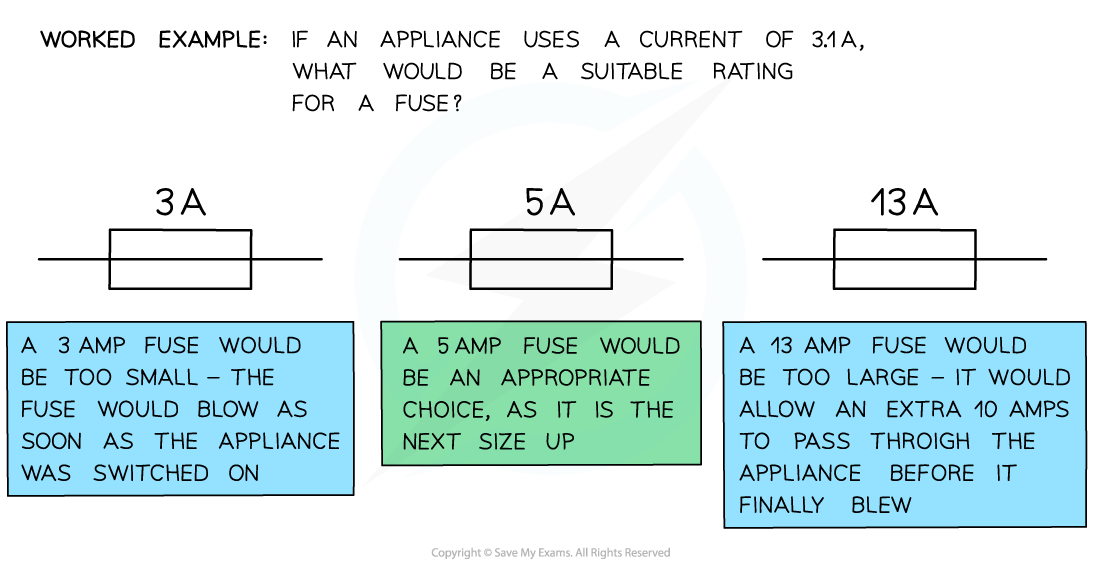
- Fuses come in a variety of sizes, typically 3 A, 5 A and 13 A
- In order to select the right fuse for the job, the current through an appliance needs to be known
- If the power of the appliance is known (along with mains voltage), the current can be calculated using the equation:
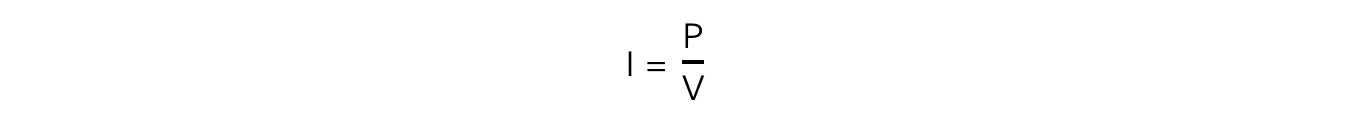
- Where:
- I = current in amps (A)
- P = power in watts (W)
- V = voltage in volts (V)
- The fuse should always have a current rating that is higher than the current needed by the appliance, without being too high
- Because of this, the rule of thumb is to always choose the next size up
- If the fuse current rating is low, it will break the circuit even when an acceptable current is flowing through
- If the fuse current rating is too high, it will not be breaking the circuit in enough time before damage occurs
Worked Example
转载自savemyexam










