- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记8.4.2 Mass Difference & Binding Energy
Mass Difference & Binding Energy
- Experiments into nuclear structure have found that the total mass of a nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons
- This difference in mass is known as the mass defect
- Mass defect is defined as:
The difference between an atom's mass and the sum of the masses of its protons and neutrons
- The mass defect Δm of a nucleus can be calculated using:
Δm = Zmp + (A – Z)mn – mtotal
- Where:
- Z = proton number
- A = nucleon number
- mp = mass of a proton (kg)
- mn = mass of a neutron (kg)
- mtotal = measured mass of the nucleus (kg)
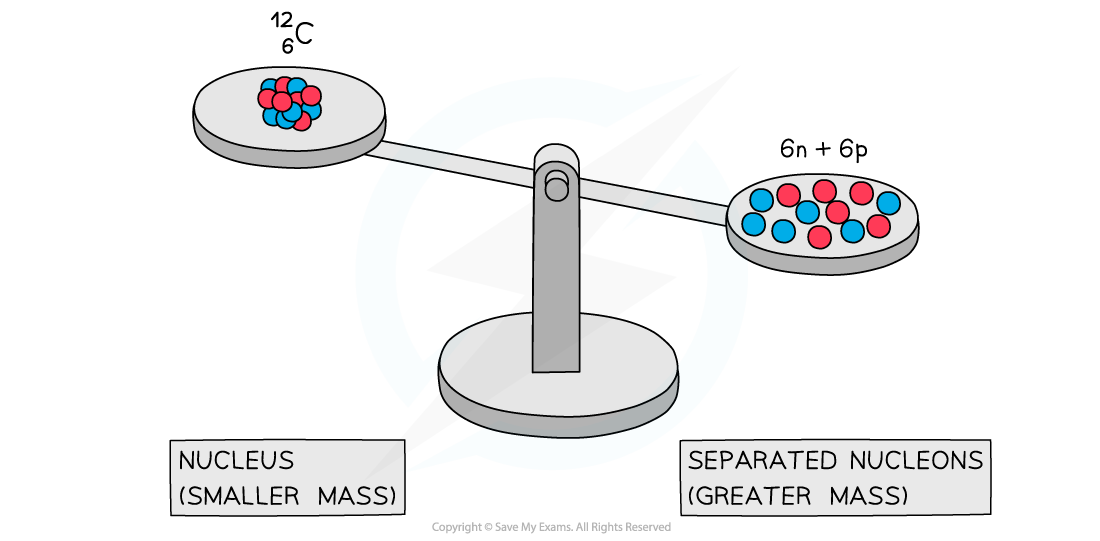
A system of separated nucleons has a greater mass than a system of bound nucleons
- Due to the equivalence of mass and energy, this decrease in mass implies that energy is released in the process
- Since nuclei are made up of neutrons and protons, there are forces of repulsion between the positive protons
- Therefore, it takes energy, ie. the binding energy, to hold nucleons together as a nucleus
- Binding energy is defined as:
The amount of energy required to separate a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons
- Energy and mass are proportional, so, the total energy of a nucleus is less than the sum of the energies of its constituent nucleons
- The formation of a nucleus from a system of isolated protons and neutrons is, therefore, an exothermic reaction - meaning that it releases energy
- This can be calculated using the equation:
E = Δmc2
- In a typical nucleus, binding energies are usually measured in MeV
- This is considerably larger than the few eV associated with the binding energy of electrons in the atom
- Nuclear reactions involve changes in the nuclear binding energy whereas chemical reactions involve changes in the electron binding energy
- This is why nuclear reactions produce much more energy than chemical reactions
Worked Example
Calculate the binding energy per nucleon, in MeV, for the radioactive isotope potassium-40 (19K).
Nuclear mass of potassium-40 = 39.953 548 u
Mass of one neutron = 1.008 665 u
Mass of one proton = 1.007 276 u
Step 1: Identify the number of protons and neutrons in potassium-40
-
- Proton number, Z = 19
- Neutron number, N = 40 – 19 = 21
Step 2: Calculate the mass defect, Δm
-
- Proton mass, mp = 1.007 276 u
- Neutron mass, mn = 1.008 665 u
- Mass of K-40, mtotal = 39.953 548 u
Δm = Zmp + Nmn – mtotal
Δm = (19 × 1.007276) + (21 × 1.008665) – 39.953 548
Δm = 0.36666 u
Step 3: Convert from u to kg
-
- 1 u = 1.661 × 10–27 kg
Δm = 0.36666 × (1.661 × 10–27) = 6.090 × 10–28 kg
Step 4: Write down the equation for mass-energy equivalence
E = Δmc2
-
- Where c = speed of light
Step 5: Calculate the binding energy, E
E = 6.090 × 10–28 × (3.0 × 108)2 = 5.5 × 10–11 J
Step 6: Determine the binding energy per nucleon and convert J to MeV
-
- Take the binding energy and divide it by the number of nucleons
- 1 MeV = 1.6 × 10–13 J
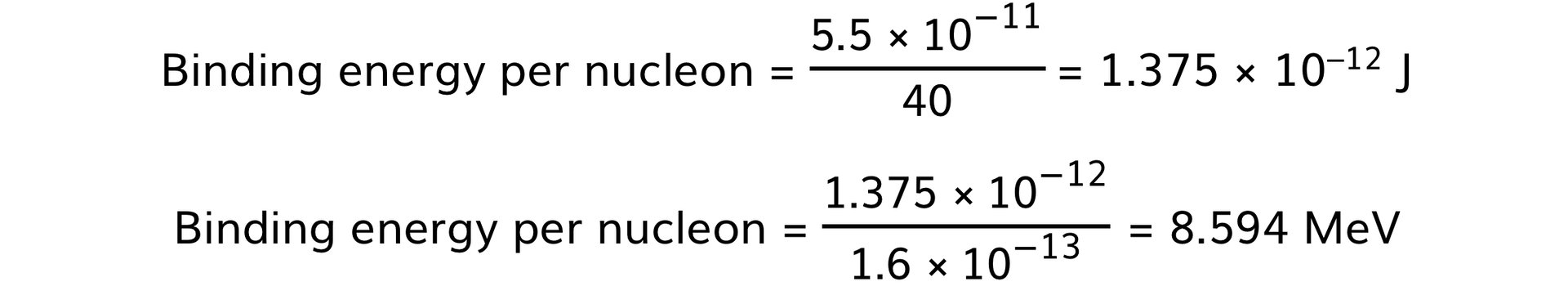
Exam Tip
Avoid describing the binding energy as the energy stored in the nucleus – this is not correct – it is energy that must be put into the nucleus to pull it apart.Make sure to learn the definitions of mass defect and binding energy as these are common exam questions!
Atomic Mass Unit (u)
- The unified atomic mass unit (u) is roughly equal to the mass of one proton or neutron:
- 1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
- It is sometimes abbreviated to a.m.u
- This value will be given on your data sheet in the exam
- The a.m.u is commonly used in nuclear physics to express the mass of subatomic particles. It is defined as
The mass of exactly one-twelfth of an atom of carbon-12
- Therefore, one atom of carbon-12 has a mass of exactly 12 u
- Since mass and energy are interchangeable, the a.m.u can also be expressed in MeV
- 1 u is equivalent to 931.5 MeV
Table of common particles with mass in a.m.u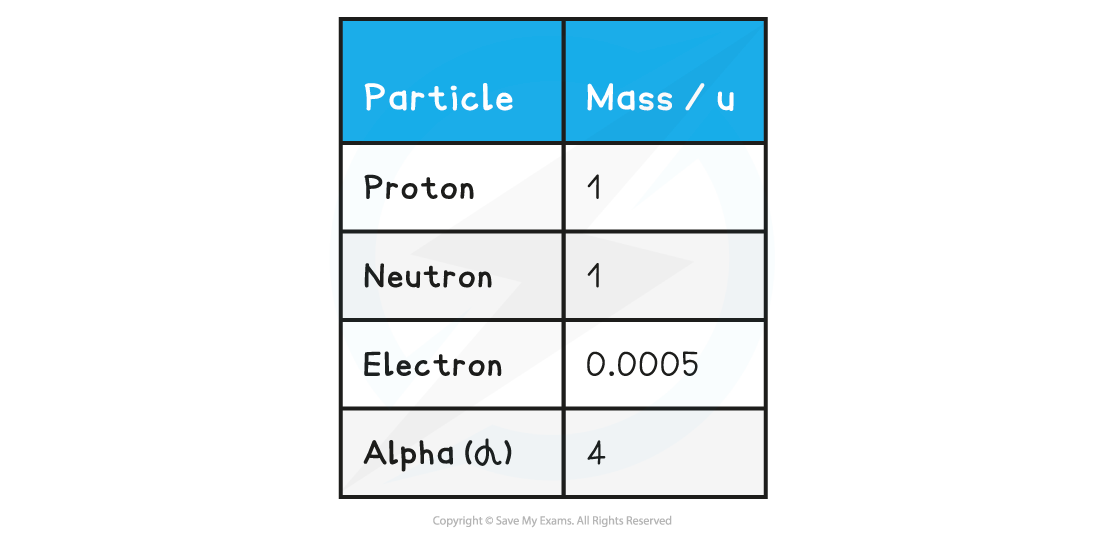
- The mass of an atom in a.m.u is roughly equal to the sum of its protons and neutrons (nucleon number)
- For example, the mass of Uranium-235 is roughly equal to 235u
- A.m.u might be quoted in kg or MeV since mass and energy are equivalent via E = mc2
- MeV is a unit of energy whilst kg is a unit of mass
Worked Example
Estimate the mass of the nucleus of the element copernicium-285 in kg.Give your answer to 2 decimal places.

转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








