- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Maths: AA HL复习笔记4.6.2 Calculations with Normal Distribution
Calculating Normal Probabilities
 How do I find probabilities using a normal distribution?
How do I find probabilities using a normal distribution?
 How do I calculate P(X = x): the probability of a single value for a normal distribution?
How do I calculate P(X = x): the probability of a single value for a normal distribution?
- The probability of a single value is always zero for a normal distribution
- You can picture this as the area of a single line is zero
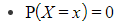 Your GDC is likely to have a "Normal Probability Density" function
Your GDC is likely to have a "Normal Probability Density" function
- This is sometimes shortened to NPD, Normal PD or Normal Pdf
- IGNORE THIS FUNCTION for this course!
- This calculates the probability density function at a point NOT the probability
How do I calculate P(a < X < b): the probability of a range of values for a normal distribution?
- You need a GDC that can calculate cumulative normal probabilities
- You want to use the "Normal Cumulative Distribution" function
- This is sometimes shortened to NCD, Normal CD or Normal Cdf
- You will need to enter:
- The 'lower bound' - this is the value a
- The 'upper bound' - this is the value b
- The 'μ' value - this is the mean
- The 'σ' value - this is the standard deviation
- Check the order carefully as some calculators ask for standard deviation before mean
- Remember it is the standard deviation
- so if you have the variance then square root it
- Remember it is the standard deviation
- Always sketch a quick diagram to visualise which area you are looking for
How do I calculate P(X > a) or P(X < b) for a normal distribution?
- You will still use the "Normal Cumulative Distribution" function
-
 Using a value that is more than 4 standard deviations smaller than the mean is quite accurate
Using a value that is more than 4 standard deviations smaller than the mean is quite accurate- Or an easier option is just to input lots of 9's for the lower bound with a negative sign (-99999999... or -1099)
Are there any useful identities?
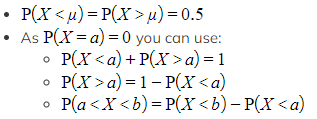 These are useful when:
These are useful when:-
- The mean and/or standard deviation are unknown
- You only have a diagram
- You are working with the inverse distribution
Exam Tip
- Check carefully whether you have entered the standard deviation or variance into your GDC
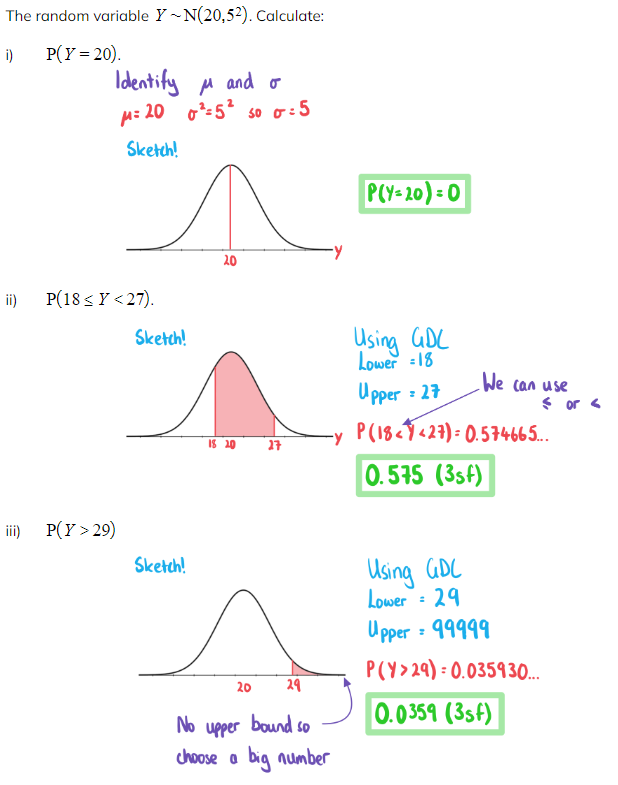
Worked Example
 Inverse Normal Distribution
Inverse Normal Distribution
Given the value of P(X < a) how do I find the value of a?
- Your GDC will have a function called "Inverse Normal Distribution"
- Some calculators call this InvN
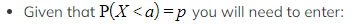
- The 'area' - this is the value p
- Some calculators might ask for the 'tail' - this is the left tail as you know the area to the left of a
- The 'μ' value - this is the mean
- The 'σ' value - this is the standard deviation
- The 'area' - this is the value p
Given the value of P(X > a) how do I find the value of a?
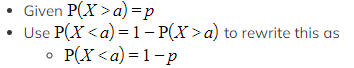 Then use the method for P(X < a) to find a
Then use the method for P(X < a) to find a- If your calculator does have the tail option (left, right or centre) then you can use the "Inverse Normal Distribution" function straightaway by:
- Selecting 'right' for the tail
- Entering the area as 'p'
Exam Tip
- Always check your answer makes sense
- If P(X < a) is less than 0.5 then a should be smaller than the mean
- If P(X < a) is more than 0.5 then a should be bigger than the mean
- A sketch will help you see this
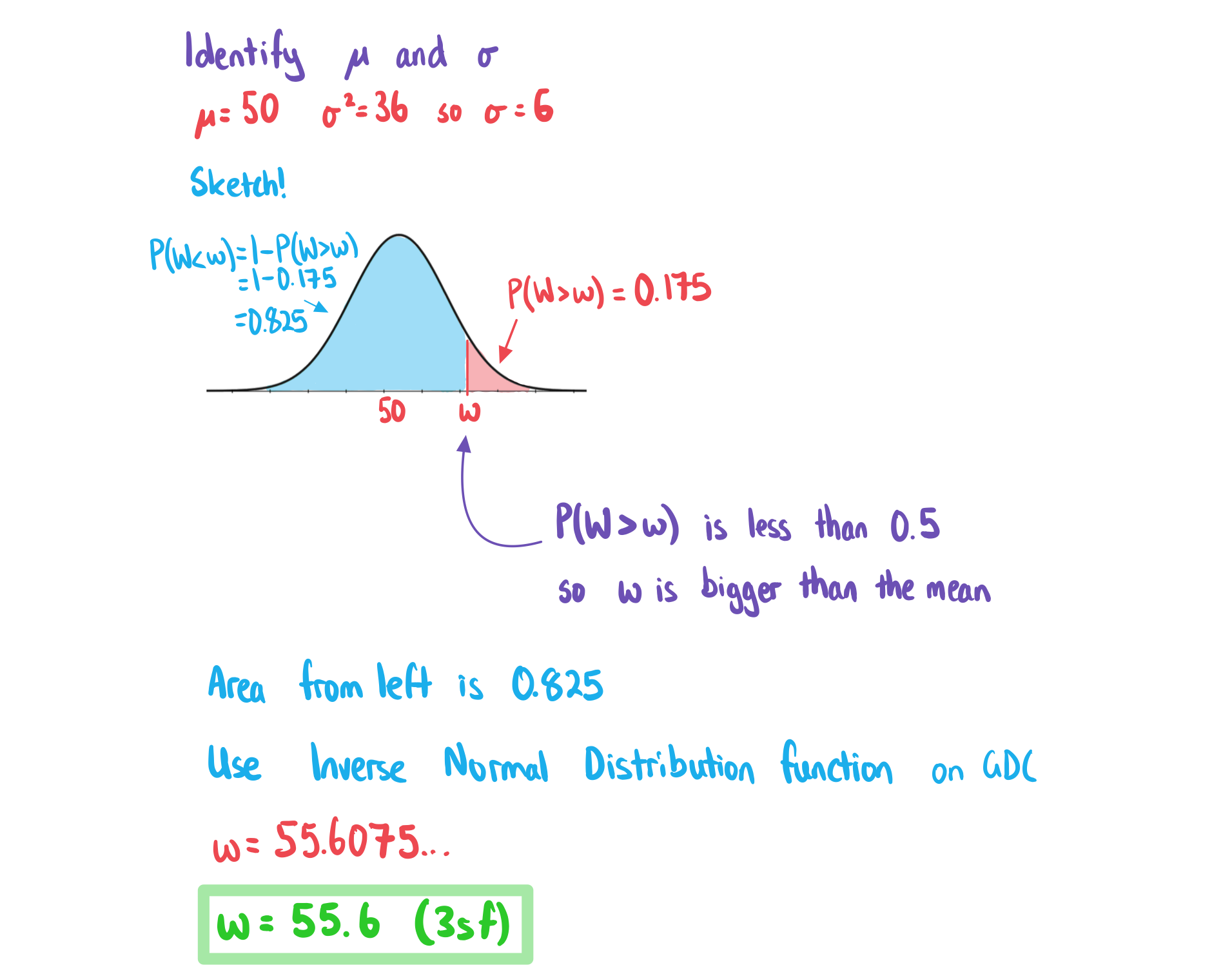
Worked Example
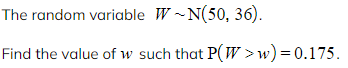
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








