- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记7.10.1 Alternating Current & Voltage
Sinusoidal & Root-Mean-Square Current & Voltage
- An alternating current (a.c) is defined as:
A current which periodically varies between a positive to a negative value with time
- This means the direction of an alternating current varies every half cycle
- The variation of current, or p.d., with time can be described as a sine curve ie. sinusoidal
- Therefore, the electrons in a wire carrying a.c. move back and forth with simple harmonic motion
- As with SHM, the relationship between time period T and frequency f for a.c is:
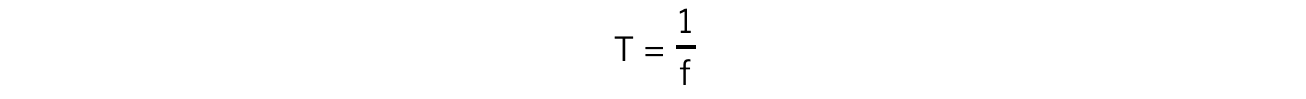
- Peak current (I0), or peak voltage (V0), is defined as:
The maximum value of the alternating current or voltage
- Peak current, or voltage, can be determined from the amplitude of a current-time or voltage-time graph
- The peak-to-peak current or voltage is the distance between a positive and consecutive negative peak. This means:
peak voltage V0 = peak-to-peak voltage ÷ 2
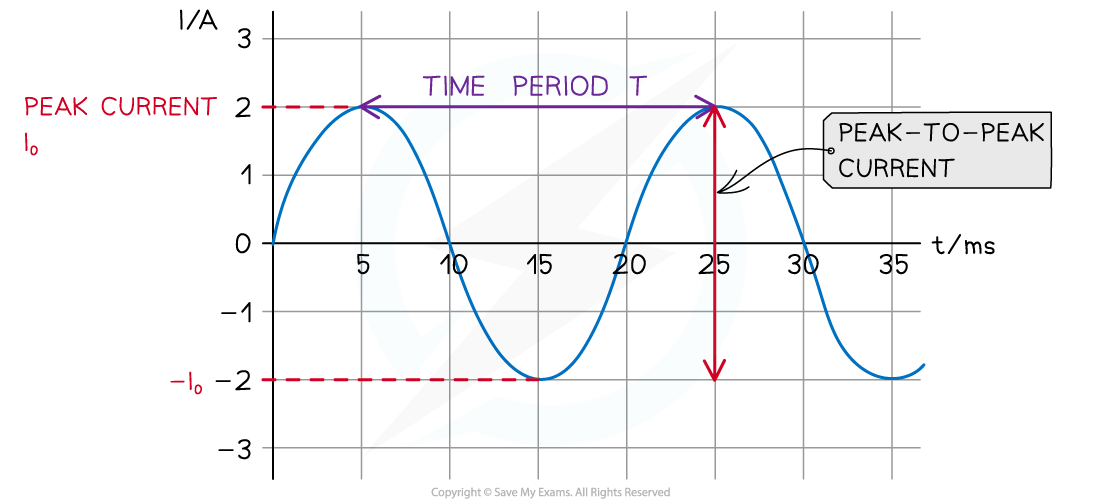
Graph of alternating current against time showing the time period, peak current and peak-to-peak current
Worked Example
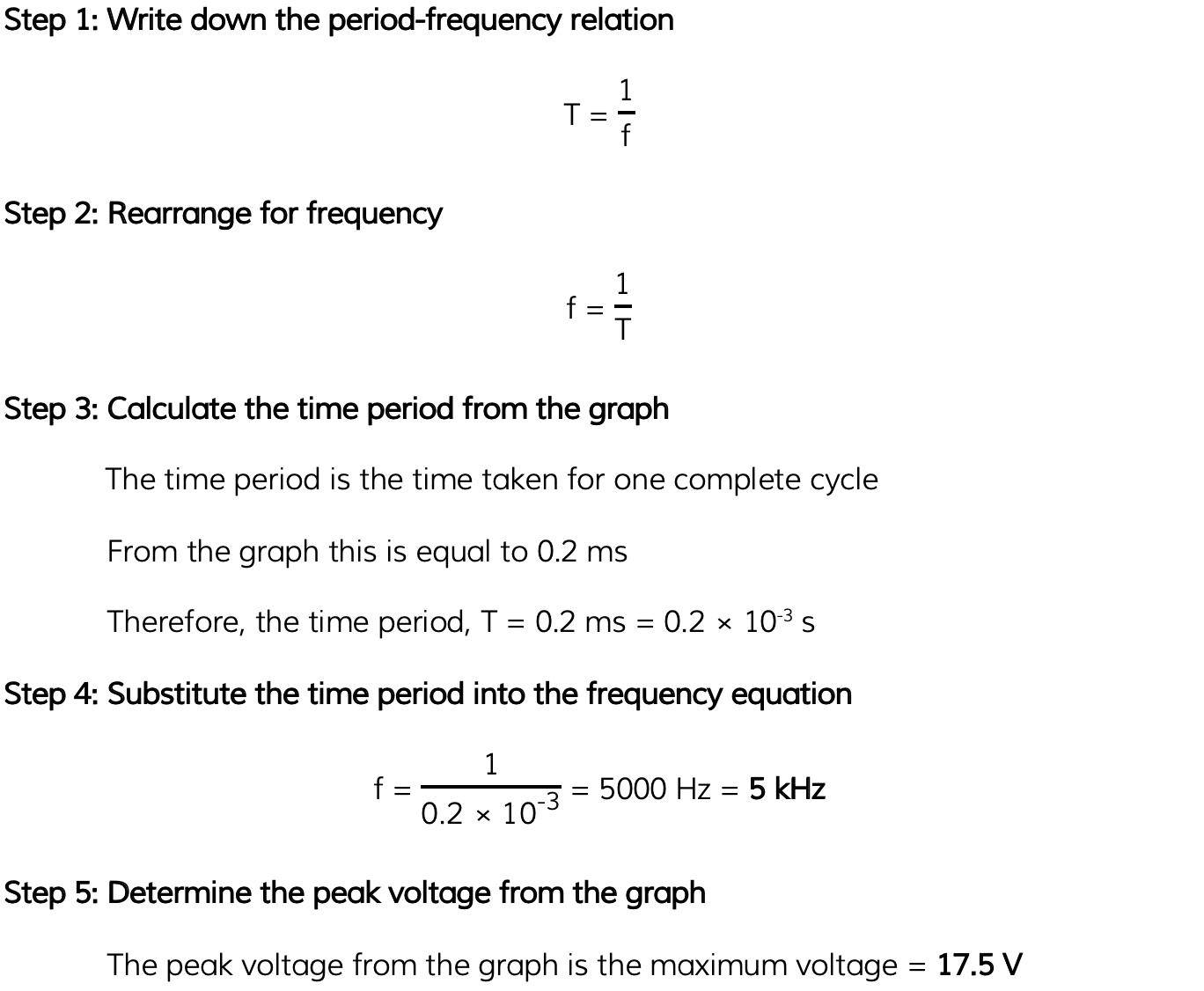
The variation with time t of the output voltage V of an alternating voltage supply is shown in the graph below. Use the graph to calculate the frequency of the supply and the peak voltage.
Use the graph to calculate the frequency of the supply and the peak voltage.
Root-Mean-Square Current & Voltage
- Root-mean-square (rms) values of current, or voltage, are a useful way of comparing a.c current, or voltage, to its equivalent direct current (d.c), or voltage
- The rms values represent the direct current, or voltage, values that will produce the same heating effect, or power dissipation, as the alternating current, or voltage
- The rms value of an alternating current is defined as:
The square root of the mean of the squares of all the values of the current in one cycle
- Or:
The equivalent direct current that produces the same power
- The rms current Irms is defined by the equation:
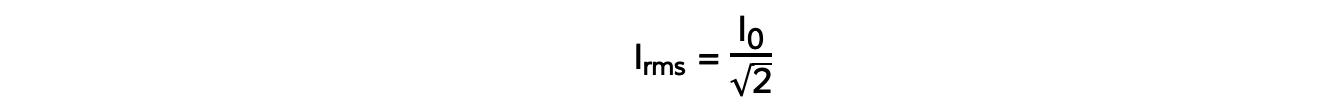
- Where:
- I0 = peak current (A)
- The rms value of an alternating voltage is defined as:
The square root of the mean of the squares of all the values of the voltage in one cycle
- Or:
The equivalent dc voltage that produces the same power
- The rms voltage Vrms is defined by the equation:

- Where:
- V0 = peak voltage (V)
- Rms current is equal to 0.707 × I0, which is about 70% of the peak current I0
- This is also the case for rms voltage
- The rms value is therefore defined as:
The steady direct current, or voltage, that delivers the same average power in a resistor as the alternating current, or voltage
- A resistive load is any electrical component with resistance eg. a lamp
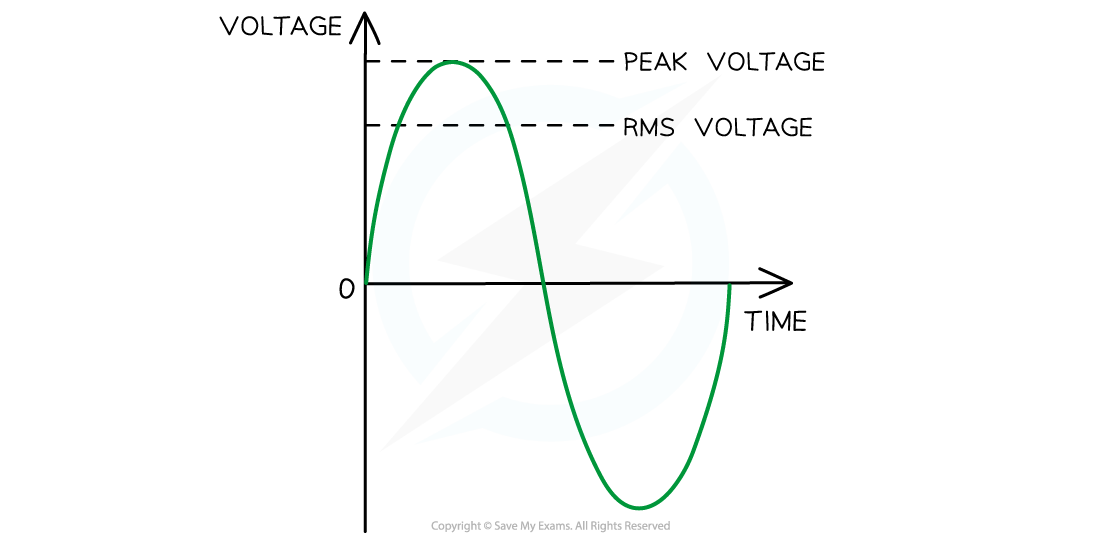
Vrms and peak voltage. The rms voltage is about 70% of the peak voltage
- The average power of a supply is the product of the rms current and voltage:
Average power = Irms × Vrms
Worked Example
An electric oven is connected to a 230 V root mean square (rms) mains supply using a cable of negligible resistance.Calculate the peak-to-peak voltage of the mains supply.
Step 1: Write down the Vrms equation

Step 2: Rearrange for the peak voltage, V0
V0 = √2 × Vrms
Step 3: Substitute in the values
V0 = √2 × 230
Step 4: Calculate the peak-to-peak voltage
-
- The peak-to-peak voltage is the peak voltage (V0) × 2
Peak-to-peak voltage = (√2 × 230) × 2 = 650.538 = 651 V (3 s.f)
Exam Tip
Remember to double-check the units on the alternating current and voltage graphs. These are often shown in milliseconds (ms) instead of seconds (s) on the x-axis.
Applications of Alternating Current & Voltage
- Mains electricity is supplied as alternating current by the National Grid
- This means that power stations produce alternating current
- This is the type of current supplied when devices are plugged into sockets
- In the UK, the mains electricity supplied to households is 230 V at 50 Hz. This is its rms value
- However, this varies depending on the customer (larger buildings and factories will require more)
- The mains voltage varies throughout the day depending on the demand and supply of electricity
- It is only lamps, heaters, cookers and devices with large electric motors (such as vacuum cleaners) that use a.c from the mains
- Most other devices such as televisions, computers and games consoles work with d.c
- This means they are built with a step-down transformer that converts the 230 V a.c into (for example) 12 V d.c
- The peak and peak-to-peak values for the current and voltage for mains electricity are used to calculate the rms value and vice versa
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









