- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry 复习笔记 1.5.8 Empirical & Molecular Formulae
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry 复习笔记 1.5.8 Empirical & Molecular Formulae
Empirical & Molecular Formulae
- The molecular formula is the formula that shows the number and type of each atom in a molecule
- E.g. the molecular formula of ethanoic acid is C2H4O2
- The empirical formula is the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms of each element present in one molecule or formula unit of the compound
- E.g. the empirical formula of ethanoic acid is CH2O
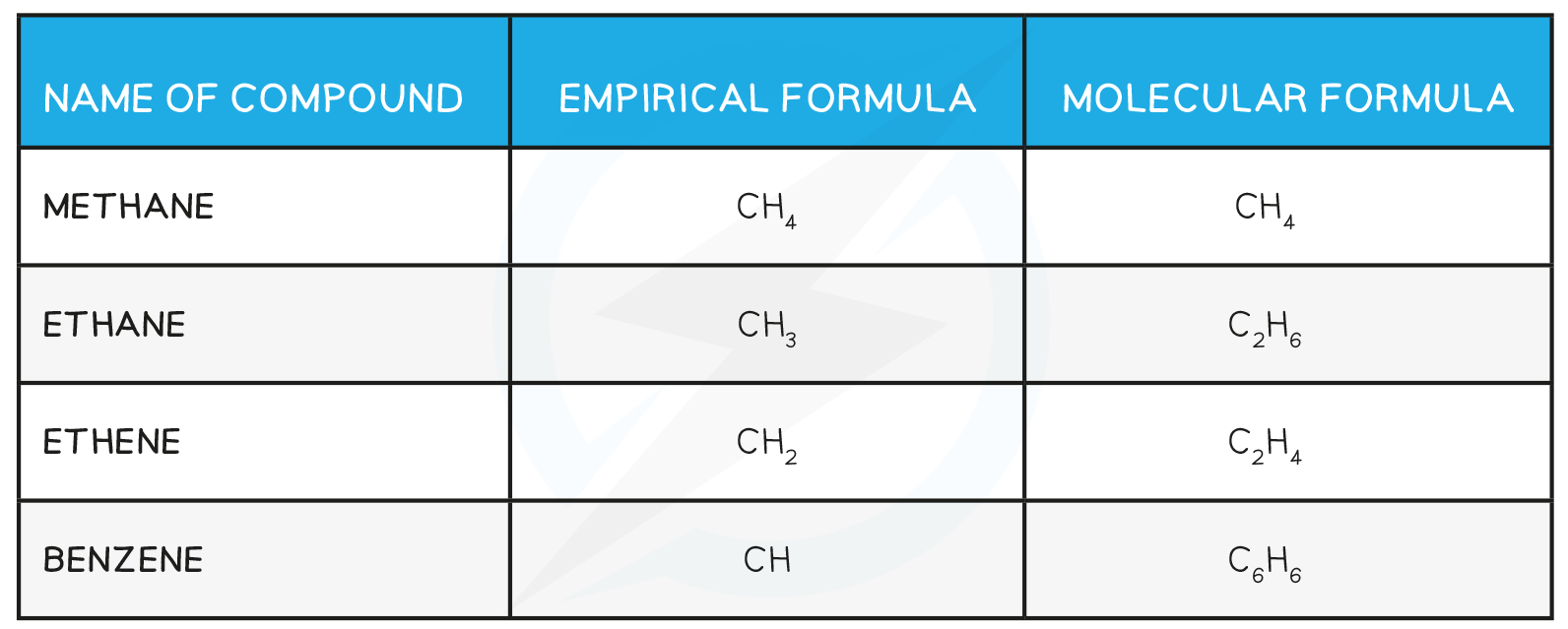
- Organic molecules often have different empirical and molecular formulae
- The formula of an ionic compound is always an empirical formula
Calculate Empirical & Molecular Formulae
Empirical formula: gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in the compound
- It is calculated from knowledge of the ratio of masses of each element in the compound
Example:A compound that contains 10 g of hydrogen and 80 g of oxygen has an empirical formula of H2O. This can be shown by the following calculations:Amount of hydrogen atoms = mass in grams ÷ Ar of hydrogen = (10 ÷ 1) = 10 molesAmount of oxygen atoms = mass in grams ÷ Ar of oxygen = (80 ÷ 16) = 5 moles
The Ratio of Moles of Hydrogen Atoms to Moles of Oxygen Atoms
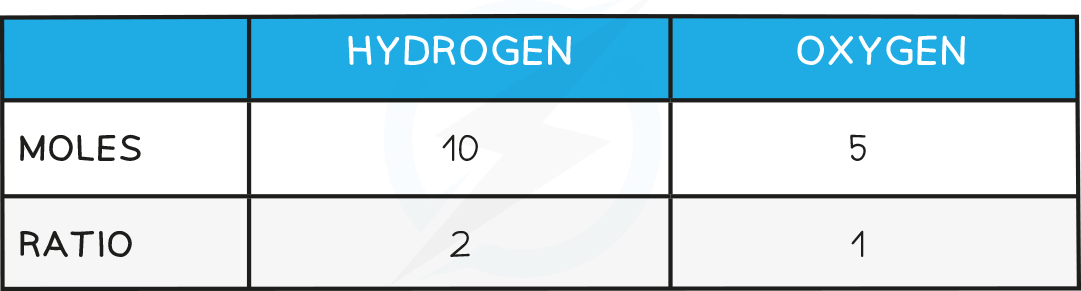 Since equal numbers of moles of atoms contain the same number of atoms, the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms is 2:1Hence the empirical formula is H2OMolecular formula: gives the exact numbers of atoms of each element present in the formula of the compound
Since equal numbers of moles of atoms contain the same number of atoms, the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms is 2:1Hence the empirical formula is H2OMolecular formula: gives the exact numbers of atoms of each element present in the formula of the compound
- Divide the relative formula mass of the molecular formula by the relative formula mass of the empirical formula
- Multiply the number of each element present in the empirical formula by this number to find the molecular formula
Relationship between Empirical and Molecular Formula
Worked Example
The empirical formula of X is C4H10S1 and the relative formula mass of X is 180. What is the molecular formula of X?Relative atomic masses: carbon : 12 hydrogen : 1 sulfur : 32
Step 1 - Calculate the relative formula mass of the empirical formula
(C x 4) + (H x 10) + (S x 1) = (12 x 4) + (1 x 10) + (32 x 1) = 90
Step 2 - Divide the relative formula mass of X by the mass of the empirical formula
180 / 90 = 2
Step 3 - Multiply each number of elements by 2
(C4 x 2) + (H10 x 2) + (S1 x 2) = (C8) + (H20) + (S2)
Molecular Formula of X = C8H20S2
转载自savemyexam

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









