- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记6.6.2 Kinetic Theory of Gases Equation
Kinetic Theory of Gases Equation
Assumptions in Kinetic Theory
- Gases consist of atoms or molecules randomly moving around at high speeds
- The kinetic theory of gases models the thermodynamic behaviour of gases by linking the microscopic properties of particles (mass and speed) to macroscopic properties of particles (pressure and volume)
- The theory is based on a set of the following assumptions:
- Molecules of a gas behave as identical (or all have the same mass)
- Molecules of gas are hard, perfectly elastic spheres
- The volume of the molecules is negligible compared to the volume of the container
- The time of a collision is negligible compared to the time between collisions
- There are no intermolecular forces between the molecules (except during impact)
- The molecules move in continuous random motion
- Newton's laws apply
- There are a very large number of molecules
- The number of molecules of gas in a container is very large, therefore the average behaviour (eg. speed) is usually considered
Derivation of the Kinetic Theory of Gases Equation
- When molecules rebound from a wall in a container, the change in momentum gives rise to a force exerted by the particle on the wall
- Many molecules moving in random motion exert forces on the walls which create an average overall pressure (since pressure is the force per unit area)
- Take a single molecule in a cube-shaped box with sides of equal length L
- The molecule has a mass m and moves with speed c, parallel to one side of the box
- It collides at regular intervals with the sides of the box, exerting a force and contributing to the pressure of the gas
- By calculating the pressure this one molecule exerts on one end of the box, the total pressure produced by a total of N molecules can be deduced
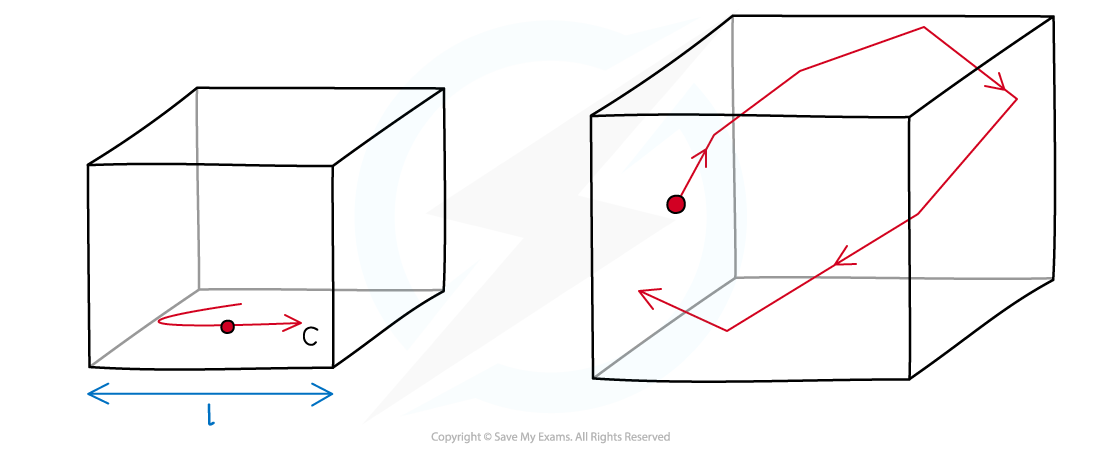
A single molecule in a box collides with the walls and exerts a pressure
1. Determine the change in momentum as a single molecule hits a wall perpendicularly
- One assumption of the kinetic theory is that molecules rebound elastically
- This means there is no kinetic energy lost in the collision
- If the particle hits one side of the wall and rebounds elastically in the opposite direction to their initial velocity, their final velocity is –c
- The change in momentum is therefore:
p = mc
Δp = final p – initial p = −mc − (+mc) = −mc − mc = −2mc
- Where:
- Δp = change in momentum (kg m s-1)
- m = mass of the molecule (kg)
- c = speed of the molecule (m s-1)
2. Calculate the number of collisions per second by the molecule on a wall
- The time between collisions of the molecule travelling to the opposite facing wall and back is calculated by travelling a distance of 2L with speed c:
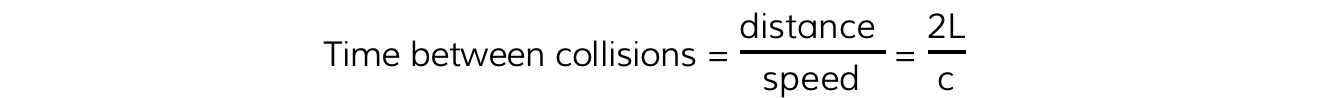
- Note: c is not taken as the speed of light in this scenario
3. Calculate the force exerted by the molecule on the wall
- The force the molecule exerts on one wall is found using Newton’s second law of motion:

- The change in momentum is +2mc since the force on the molecule from the wall is in the opposite direction to its change in momentum
4. Calculate the total pressure for one molecule
- The area of one wall is L2
- The pressure is defined as the force per unit area:
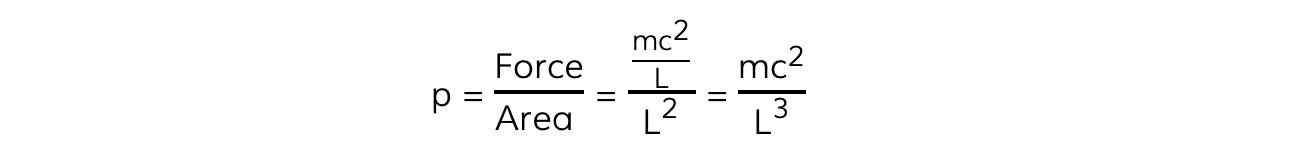
- This is the pressure exerted from one molecule in a particular direction
5. Consider the effect of N molecules moving randomly in 3D space
- The pressure equation still assumes that all the molecules are travelling in the same direction and collide with the same pair of opposite faces of the cube
- In reality, all molecules will be moving in three dimensions equally and randomly
- By splitting the velocity into its components cx, cy and cz to denote the amount in the x, y and z directions, c2 can be defined using Pythagoras' theorem in 3D:
c2 = cx2 + cy2 + cz2
- Since there is nothing special about any particular direction, it can be deduced that:
cx2 = cy2 = cz2
- Therefore, cx2 can be defined as:
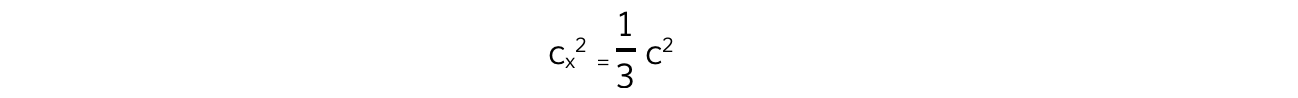
- Where c2 is the sum of the squared speeds of all the molecules
c2 = c12 + c22 + c32 +... + cN2
6. Consider the speed of the molecules as an average speed
- Each molecule has a different speed and they all contribute to the pressure
- Therefore, the square root of the average of the square velocities is taken as the speed instead
- This is called the root-mean-square speed or crms
- crms is defined as:
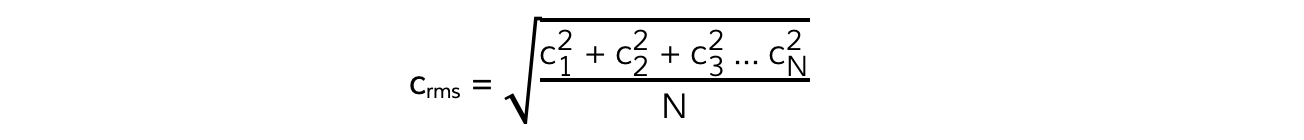
- Therefore
N(crms)2 = c12 + c22 + c32 +... + cN2
7. Consider the volume of the box
- The box is a cube and all the sides are of length l
- This means L3 is equal to the volume of the cube, V
- Substituting N(crms)2 and L3 back into the pressure equation obtains the equation:
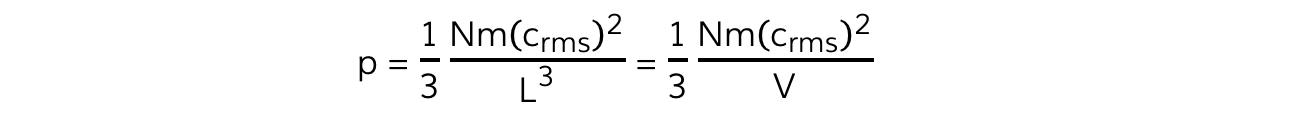
- This is the pressure parallel to the x (or y or z axis)
- Multiplying both sides by the volume V gives the final Kinetic Theory of Gases Equation:
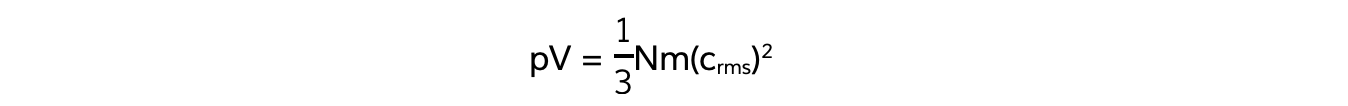
- Where:
- p = pressure (Pa)
- V = volume (m3)
- N = number of molecules
- m = mass of one molecule of gas (kg)
- crms = root mean square speed of the molecules (m s-1)
- The equation can also be written using the density ρ of the gas:
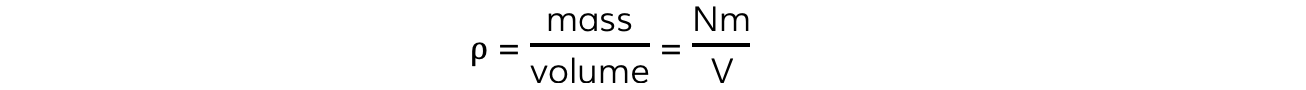
- Rearranging the equation for pressure p and substituting the density ρ gives the equation:
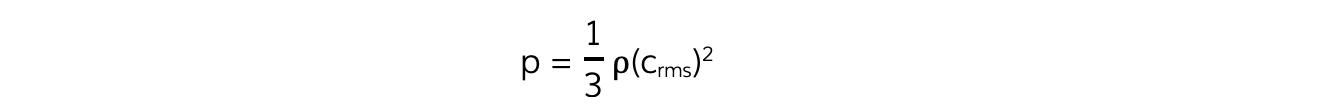
Worked Example
An ideal gas has a density of 4.5 kg m-3 at a pressure of 9.3 × 105 Pa and a temperature of 504 K.
Determine crms of the gas atoms at 504 K.

Exam Tip
Make sure to revise and understand each step for the whole of the derivation as you may be asked to derive all, or part, of the equation in an exam question. Ensure you also write the appropriate commentary instead of simply stating equations in your answers to get full marks.
Also, make sure to memorise all the assumptions for your exams, as it is a common exam question to be asked to recall them.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









