- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记6.4.3 Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity
- When a substance is heated, its temperature rises causing the particles within it to gain kinetic energy
- The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance is given by its specific heat capacity
- The specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as:
The amount of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 °C (or 1 K) without a change of state
- This quantity determines the amount of energy needed to change the temperature of a substance
- Specific heat capacity has the symbol c and is measured in units of Joules per kilogram per Kelvin (J kg–1 K–1) or Joules per kilogram per Celsius (J kg–1 °C–1)
- Different substances have different specific heat capacities
- Specific heat capacity is mainly used for liquids and solids
- From the definition of specific heat capacity, it follows that:
- The heavier the material, the more thermal energy required to raise its temperature
- The larger the change in temperature, the higher the thermal energy required to achieve this change
Calculating Specific Heat Capacity
- The amount of thermal energy Q needed to raise the temperature by Δθ for a mass m with specific heat capacity c is equal to:
ΔQ = mcΔθ
- Where:
- ΔQ = change in thermal energy (J)
- m = mass of the substance you are heating up (kg)
- c = specific heat capacity of the substance (J kg–1 K–1 or J kg–1 °C–1)
- Δθ = change in temperature (K or °C)
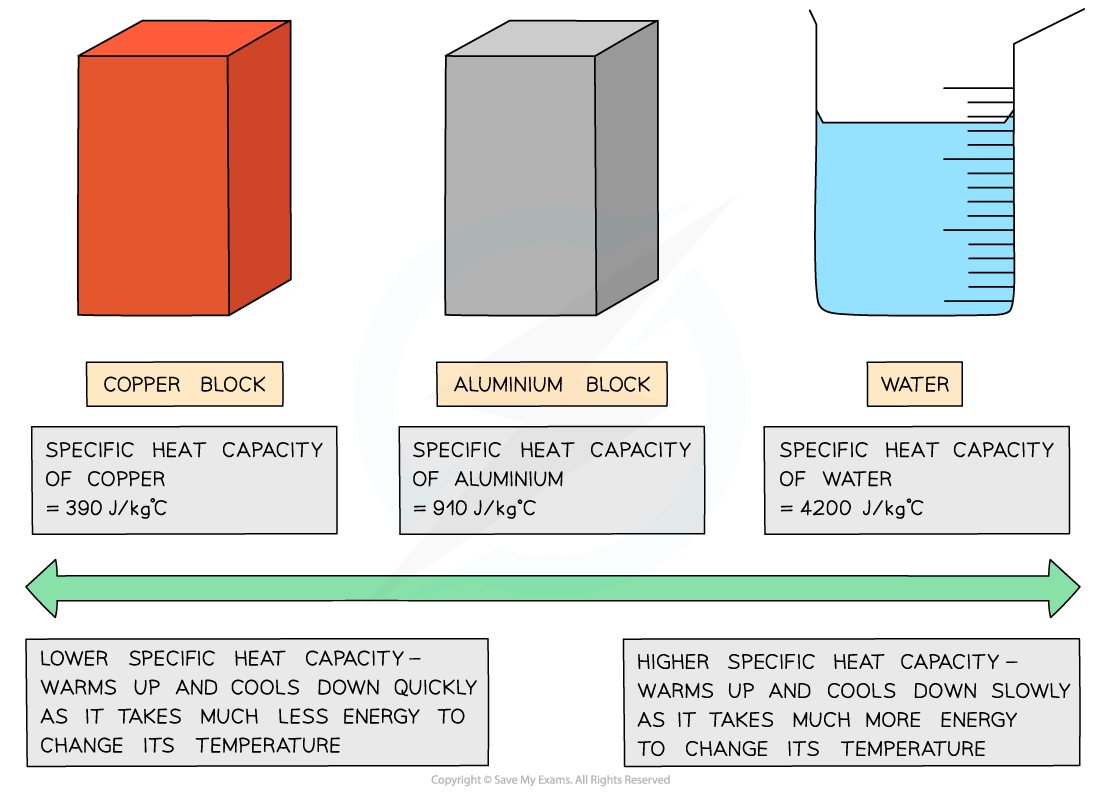
Low v high specific heat capacity
- If a substance has a low specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down quickly
- If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly
- The specific heat capacity of different substances determines how useful they would be for a specific purpose eg. choosing the best material for kitchen appliances
Table of values of specific heat capacity for various substances

- Good electrical conductors, such as copper and lead, are excellent conductors of heat due to their low specific heat capacity
Worked Example
A kettle is rated at 1.7 kW. A mass of 650 g of a liquid at 25 °C is poured into a kettle.When the kettle is switched on, it takes 3.5 minutes to start boiling.Calculate the specific heat capacity of the liquid.
Step 1: Calculate the Energy from the power and time
Energy = Power × Time
Power = 1.7 kW = 1.7 × 103 W
Time = 3.5 minutes = 3.5 × 60 = 210 s
Energy = 1.7 × 103 × 210 = 3.57 × 105 J
Step 2: Thermal energy equation
ΔQ = mcΔθ
Step 3: Rearrange for specific heat capacity
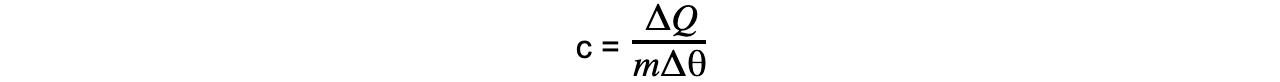
Step 4: Substitute in values
m = 650 g = 650 × 10–3 kg
Δθ = 100 – 25 = 75oC
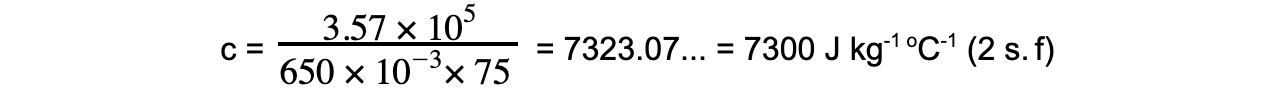
Exam Tip
The difference in temperature Δθ will be exactly the same whether the temperature is given in Celsius or Kelvin. Therefore, there is no need to convert between the two since the difference in temperature will be the same for both units.
Continuous Flow
- The specific heat capacity of a fluid can be found using a continuous-flow calorimeter
- A fluid flows continuously over a heating element where energy is transferred to the fluid
- It is assumed that the heat transferred from the apparatus to the surroundings is constant
- For this experiment, the flow rate and the potential difference is changed, keeping the change in temperature of the fluid constant
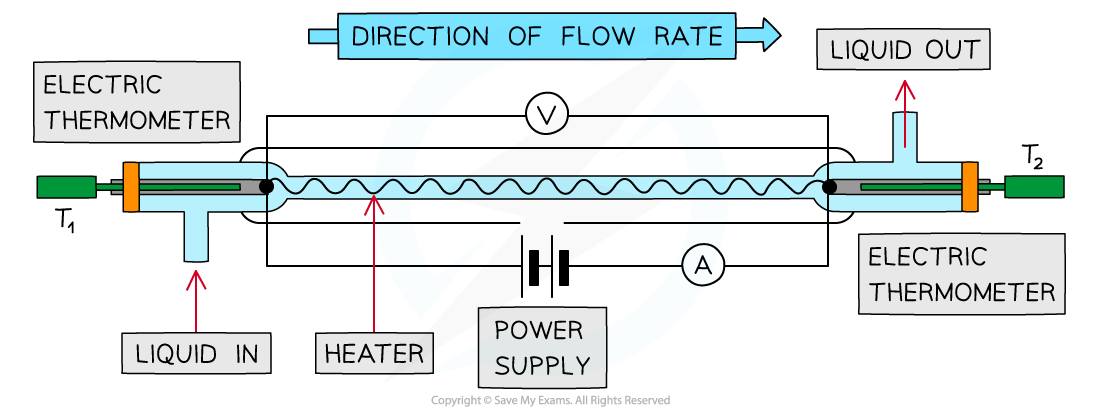
A continuous-flow calorimeter
- A fluid flows through an electrical heating wire. The rise in temperature of the fluid is measured using the electric thermometers and is calculated by:
Δθ = T2 – T1
- To find the mass of the fluid, the flow rate is recorded and multiplied by the time taken t to give the mass of the fluid that flows in as m1
- The current I and potential difference V are also recorded
- The flow rate is then altered to give a mass m2 and the potential difference of the power supply is changed so the temperature difference, Δθ stays the same
- The specific heat capacity is found by assuming the thermal losses to the surroundings are constant for both flow rates
- For the first flow rate, the electrical energy supplied to the fluid in time t1 is:
I1V1t1 = Q1 = m1cΔθ + Elost
- Where Elost is the thermal energy lost to the surroundings
- The second flow rate is:
I2V2t2 = Q2 = m2cΔθ + Elost
- Since Elost is assumed to be the same, subtracting the first flow rate equation from the second gives the equation:
I2V2t2 – I1V1t1 = Q2 – Q1 = (m2 – m1)cΔθ
- Rearranging this for the specific heat capacity of the fluid, c gives the final equation:
Worked Example
Calculate the specific heat capacity of a liquid using the following data measured in two experiments using the continuous flow method:
- Time of each experiment = 40 s
- T1 in both experiments = 15 ºC
- T2 in both experiments = 4 ºC
- p.d across the heater in experiment 1, V1 = 14.0 V
- p.d across the heater in experiment 2, V2 = 9.0 V
- Current through heater in both experiments = 3.0 A
- Mass of water flowing in experiment 1, m1 = 136.0 g
- Mass of water flowing in experiment 2, m2 = 73.0 g
Step 1: Calculate the change in temperature, Δθ
Δθ = 15 – 4 = 11ºC
Step 2: Calculate Q2
Q2 = I2V2t2 = 3.0 × 9.0 × 40 = 1080 J
Step 3: Calculate Q1
Q1 = I1V1t1 = 3.0 × 14.0 × 40 = 1680 J
Step 4: Substitute values into the specific heat capacity equation
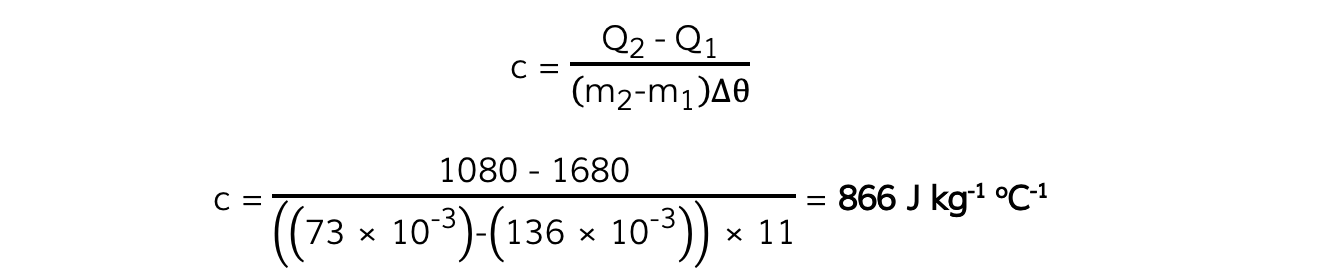
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








