- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记5.1.1 Basics of Electricity
Electric Current & Potential Difference
Electric Current
- Electric current is defined as the rate of flow of positive charge carriers
- It is measured in units of amperes (A) or amps
- The charge, current and time are related by the equation:
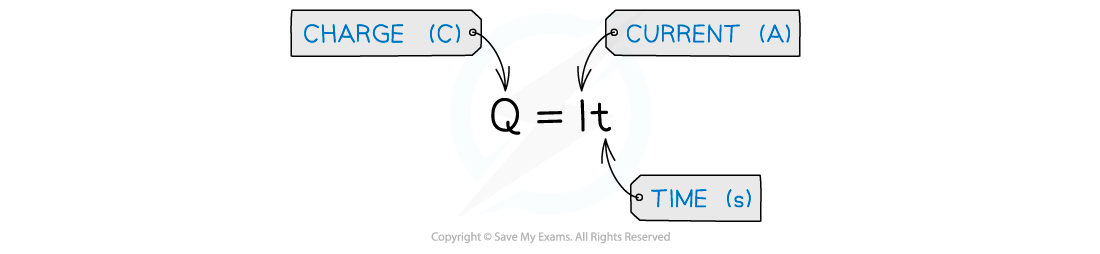
- Charge is sometimes written as ΔQ which means 'change in charge'
- Similarly, time is written as Δt means 'change in time'
- When two oppositely charged conductors are connected together (by a length of wire), charge will flow between the two conductors, causing a current
- Therefore, rearranging for current, I gives the equation:
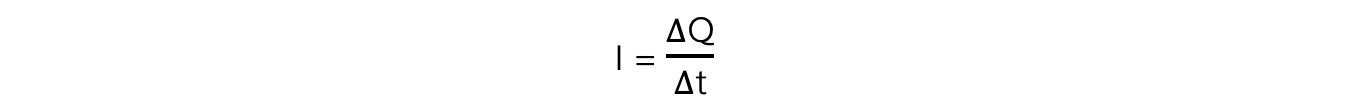
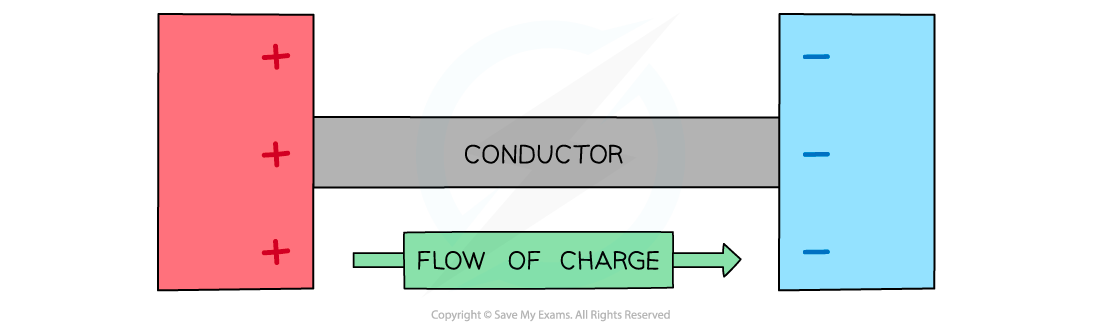
Charge can flow between two conductors. The direction of conventional current in a metal is from positive to negative
- In electrical wires, the current is a flow of electrons
- Electrons are negatively charged; they flow away from the negative terminal of a cell towards the positive terminal
- Conventional current is defined as the flow of positive charge from the positive terminal of a cell to the negative terminal
- This is the opposite to the direction of electron flow, as the conventional current was described before electric current was really understood
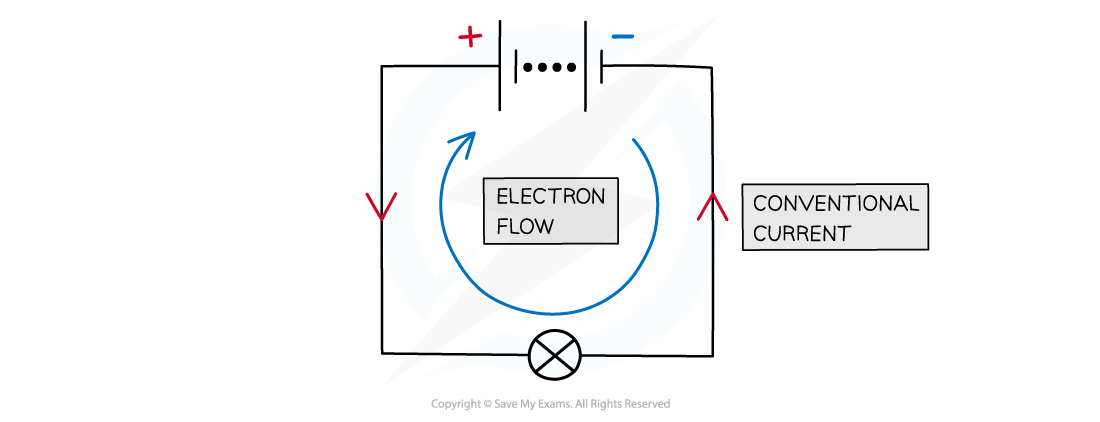
By definition, conventional current always goes from positive to negative (even through electrons go the other way)
- There are several examples of electric currents, including in household wiring and electrical appliances
- Current is measured using an ammeter
- Ammeters should always be connected in series with the part of the circuit you wish to measure the current through

An ammeter can be used to measure the current around a circuit and is always connected in series
Potential Difference
- A cell makes one end of the circuit positive and the other negative
- This sets up a potential difference across the circuit
- This is sometimes known as the voltage
- The potential difference is defined as the work done per unit charge and is measured in units of volts (V)

- Potential difference (or voltage) is measured using a voltmeter
- A voltmeter is always set up in parallel to the component you are measuring the voltage for

Potential difference can be measured by connecting a voltmeter in parallel between two points in a circuit
Worked Example
When will 8 mA of current pass through an electrical circuit?
A. When 1 J of energy is used by 1 C of charge
B. When a charge of 4 C passes in 500 s
C. When a charge of 8 C passes in 100 s
D. When a charge of 1 C passes in 8 s
ANSWER: B
Step 1: Write out the equation relating current, charge and time
Q = It
Step 2: Rule out any obviously incorrect options
-
- Option A does not contain charge or time, so can be ruled out
Step 3: Try the rest of the options to determine the correct answer
-
- Consider option B:
I = 4 / 500 = 8 × 10–3 = 8 mA
-
- Consider option C:
I = 8 / 100 = 80 × 10–3 = 80 mA
-
- Consider option D:
I = 1 / 8 = 125 × 10–3 = 125 mA
-
- Therefore, the correct answer is B
Exam Tip
Although electric charge can be positive or negative, since the conventional direction of current is the flow of positive charge the current should always be a positive value for your exam answers. Think of potential difference as being the energy per coulomb of charge transferred between two points in a circuit
Resistance
- Resistance is defined as the opposition to current
- For a given potential difference: The higher the resistance the lower the current
- Wires are often made from copper because copper has a low electrical resistance. This is also known as a good conductor
- The resistance R of a conductor is defined as the ratio of the potential difference V across to the current I in it

Resistance of a component is the ratio of the potential difference and current
- Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω)
- An Ohm is defined as one volt per ampere
- The resistance controls the size of the current in a circuit
- A higher resistance means a smaller current
- A lower resistance means a larger current
- All electrical components, including wires, have some value of resistance
Exam Tip
Although all electrical components have resistance, the resistance of wires is taken to be zero in exam questions.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









