- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.10.4 The Role of Auxin in Phototropism
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.10.4 The Role of Auxin in Phototropism
The Role of Auxin in Phototropism
- Plants produce plant growth regulators (similar to hormones in animals) called auxins to coordinate and control directional growth responses such as phototropisms and geotropism
- Auxin is mostly made in the tips of growing shoots and then diffuses down to the region where cell division occurs (just below the tip)
- This is an important point - only the region behind the tip of a shoot is able to contribute to growth by cell division and cell elongation
- Auxin stimulates the cells in this region to elongate (get larger); the more auxin there is, the faster they will elongate and grow
- If light shines all around the tip, auxin is distributed evenly throughout and the cells in the shoot grow at the same rate - this is what normally happens with plants growing outside
- When light shines on the shoot predominantly from one side, the auxin produced in the tip concentrates on the shaded side, making the cells on that side elongate and grow faster than the cells on the sunny side
- This unequal growth on either side of the shoot causes the shoot to bend and grow in the direction of the light
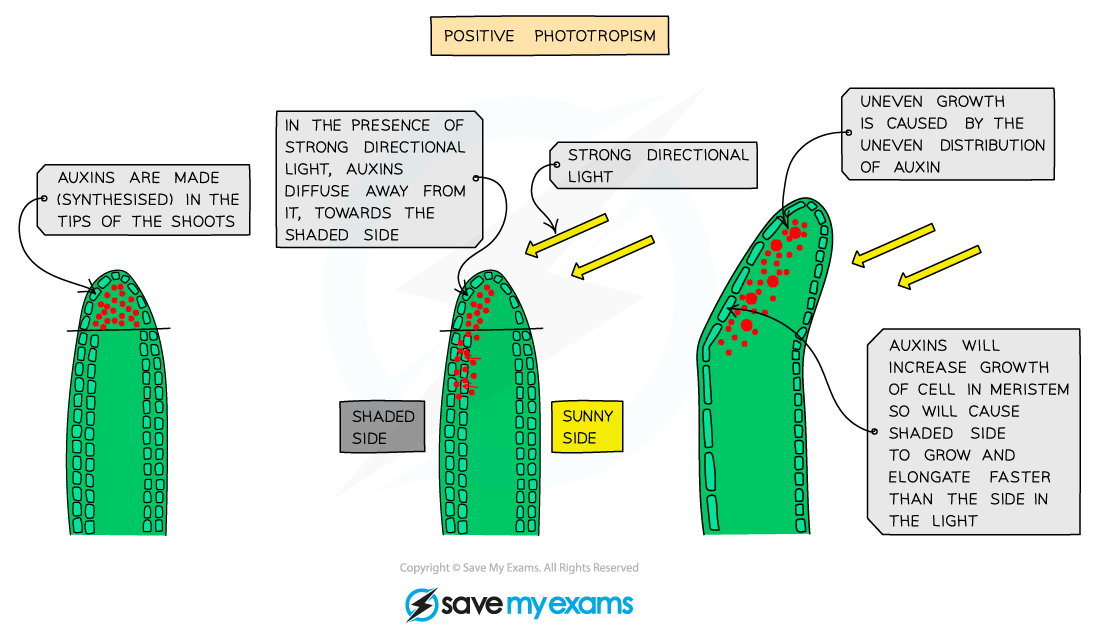
Positive phototropism in plant shoots is a result of auxin accumulating on the shaded side of a shoot
转载自savemyexam

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









