- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记4.5.4 Impulse on a Force-Time Graph
Impulse of a Force-Time Graph
- In real life, forces are often not constant and will vary over time
- If the force is plotted against time, the impulse is equal to the area under the force-time graph
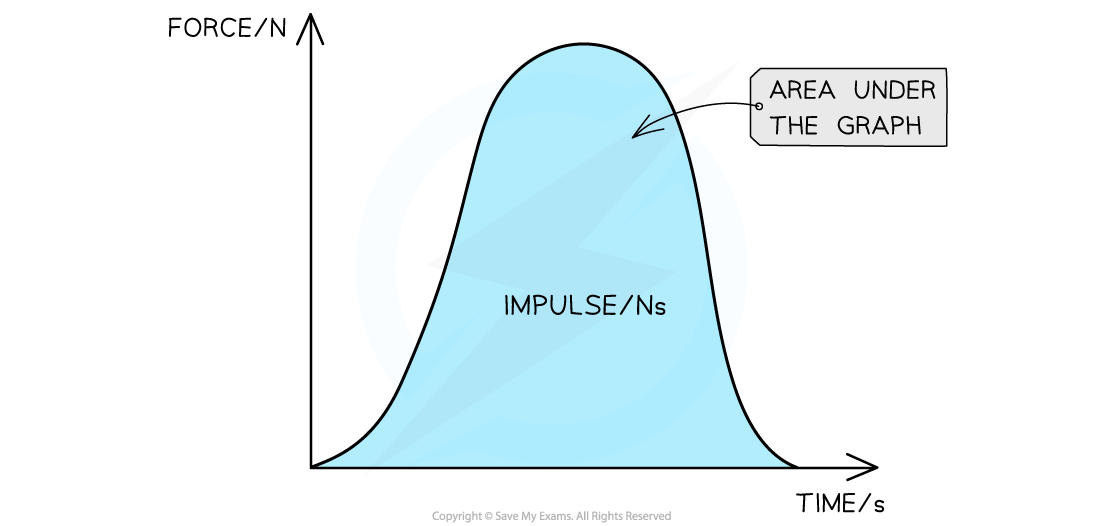
When the force is not constant, the impulse is the area under a force–time graph
- This is because
Impulse = Force × Change in time
- The impulse is therefore equal whether there is a small force over a long period of time or a large force over a small period of time
- The force-time graph may be a curve or a straight line
- If the graph is a curve, the area can be found by counting the squares underneath
- If the graph is made up of straight lines, split the graph into sections. The total area is the sum of the areas of each section

Worked Example
A ball of mass 3.0 kg, initially at rest, is acted on by a force F which varies with t as shown by the graph. Calculate the velocity of the ball after 16 s.
Calculate the velocity of the ball after 16 s.
Step 1: List the known quantities
m = 3.0 kg
u = 0 m s-1 (since it is initially at rest)
Step 2: Calculate the impulse
The impulse is the area under the graph. The graph can be split up into two right-angled triangles with a base of 8 s and a height of 4 kN
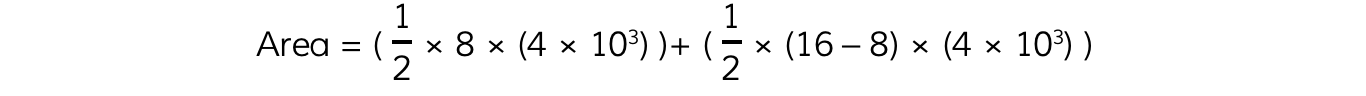
Area = impulse = 32 × 103 Ns
Step 3: Write the equation for impulse
Impulse, I = Δp = m(v – u)
Step 4: Substitute in the values
I = mv
32 × 103 = 3.0 × v
v = (32 × 103) ÷ 3.0
v = 10666 m s–1 = 11 km s-1
Exam Tip
Some maths tips for this section:Rate of Change
- ‘Rate of change’ describes how one variable changes with respect to another
- In maths, how fast something changes with time is represented as dividing by Δt (e.g. acceleration is the rate of change in velocity)
- More specifically, Δt is used for finite and quantifiable changes such as the difference in time between two events
Areas
- The area under a graph may be split up into different shapes, so make sure you’re comfortable with calculating the area of squares, rectangles, right-angled triangles and trapeziums!
Impact Forces
- Impact forces are reduced by increasing the contact time
- This fact is used in everyday life to lower the risk of injury
- Some example of where reducing impact force is important:
- In sport
- In packaging
In Sports
- For example, in cricket:
- When a cricket fielder relaxes their hands and pulls them back when catching a ball
- A cricket ball travels at very high speeds and therefore has a high momentum
- When a fielder catches the ball, it exerts a force onto their hands
- Stopping a ball with high momentum at once will cause a large force onto their hands
- This is because a change in momentum (impulse) acts over a short period of time which creates a large force on the fielder's hands and could cause serious injury
- A fielder moves their hands back when they catch the ball, which increases the time for its change in momentum to reduce
- This means there will be less force exerted on the fielder's hands and therefore less chance of injury
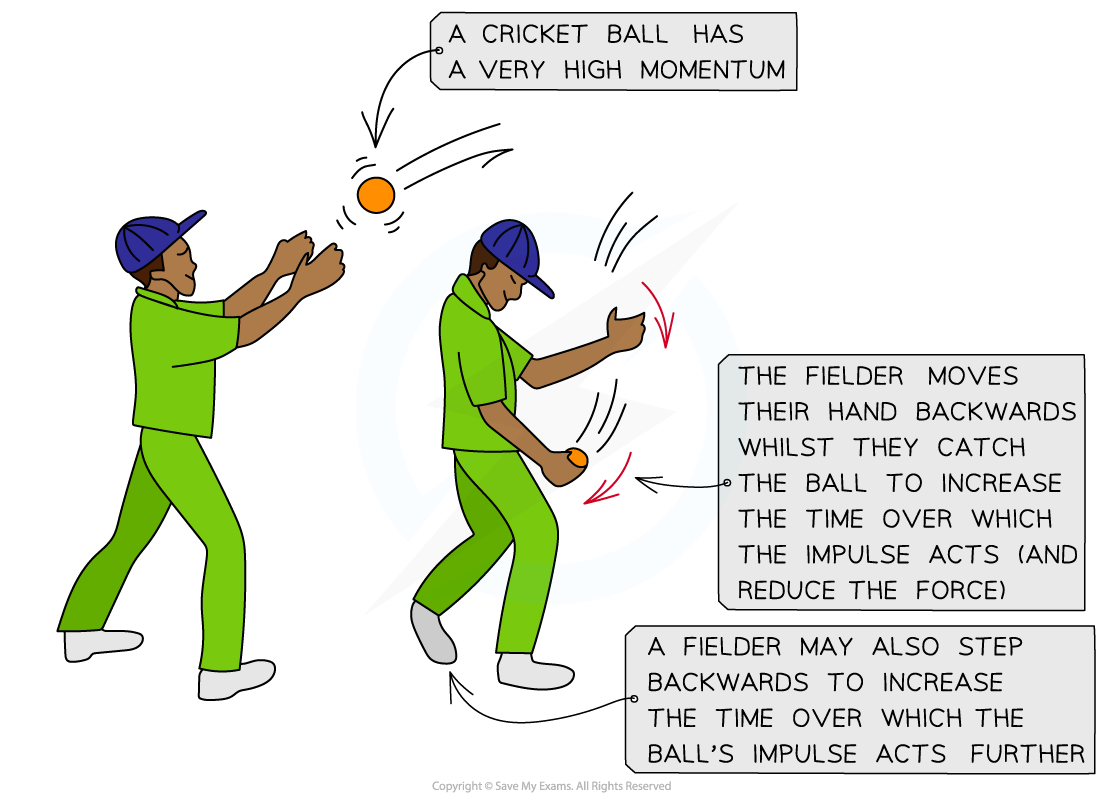
A cricket fielder moves their hands backwards when catching a cricket ball to reduce the force it will exert on their hands
- In football:
- Increasing the contact time is sometimes used to advantage, as the longer the contact time, the larger change in momentum
- When kicking a football, after a strong kick the motion is followed through
- The momentum from the foot is transferred to the ball
- This creates a large impulse and the ball then has a higher velocity
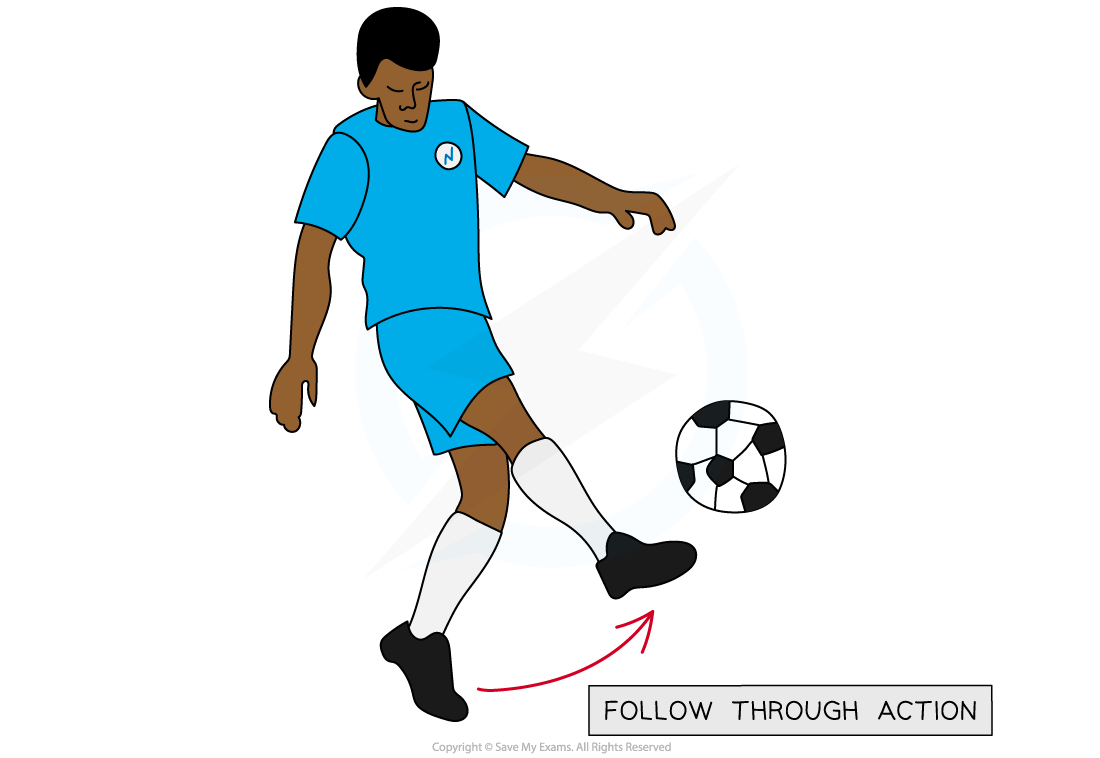
The follow through action of a football kick increases the change in momentum of the ball
In Packaging
- Packaging, especially for fragile items, uses bubble wrap or polyester packaging to reduce the impact forces that items experience in transit
- These help cushion the items by increasing the time over which they experience a force, which reduces the risk of damage
Worked Example
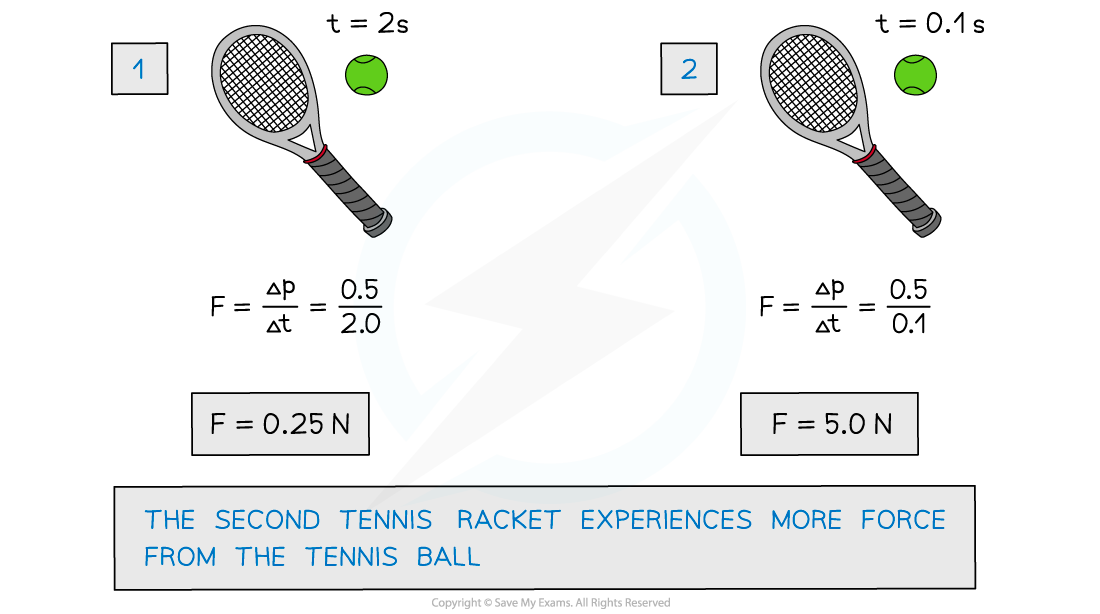
A tennis ball hits a racket with a change in momentum of 0.5 kg m s-1.For the different contact times, which tennis racket experiences more force from the tennis ball?
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









