- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记3.3.3 Young's Double-Slit Experiment
Double Slit Interference
Two Source Interference
- For two-source interference fringes to be observed, the sources of the wave must be:
- Coherent (constant phase difference)
- Monochromatic (single wavelength)
- When two waves interfere, the resultant wave depends on the phase difference between the two waves
- This is proportional to the path difference between the waves which can be written in terms of the wavelength λ of the wave
- As seen from the diagram, the wave from slit S2 has to travel slightly further than that from S1 to reach the same point on the screen
- The difference in this distance is the path difference
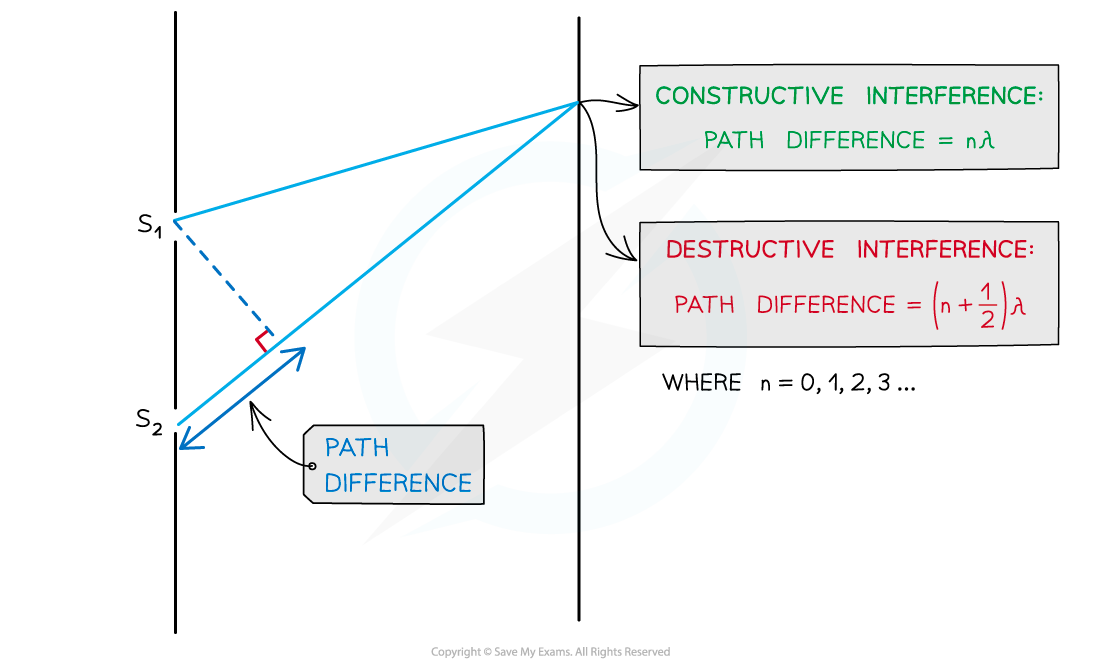
Path difference of constructive and destructive interference is determined by wavelength
- For constructive interference (or maxima), the difference in wavelengths will be an integer number of whole wavelengths
- For destructive interference (or minima) it will be an integer number of whole wavelengths plus a half wavelength
- n is the order of the maxima/minima since there is usually more than one of these produced by the interference pattern
- An example of the orders of maxima is shown below:
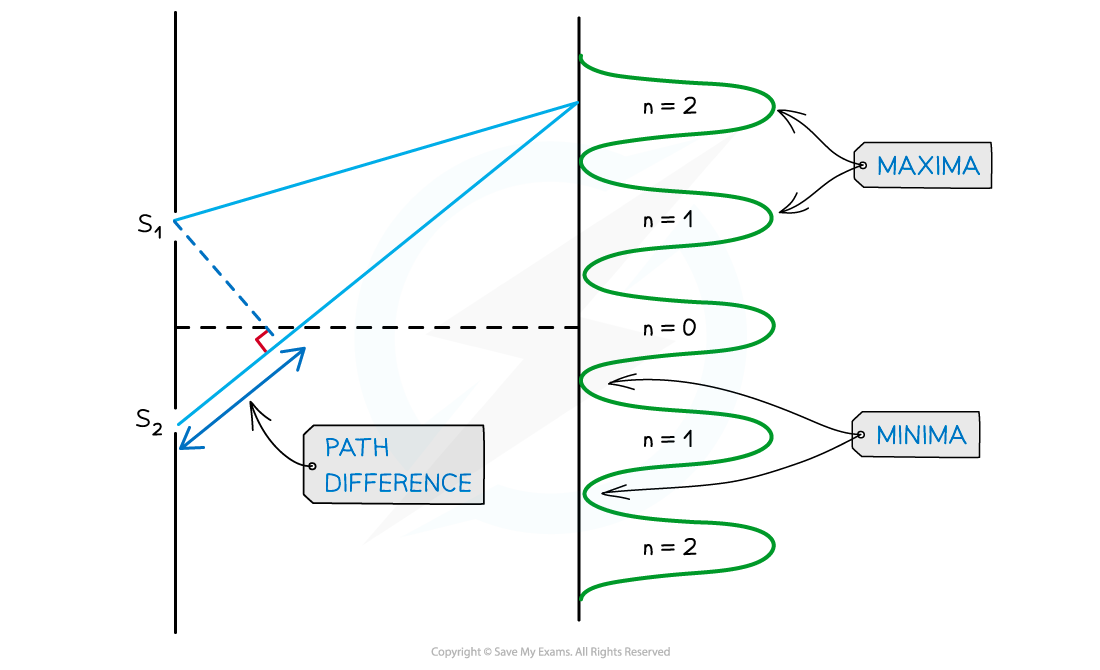
Interference pattern of light waves shown with orders of maxima
- n = 0 is taken from the middle, n = 1 is one either side and so on
Young's Double Slit Experiment
- Young’s double-slit experiment demonstrates how light waves can produce an interference pattern
- The setup of the experiment is shown below:
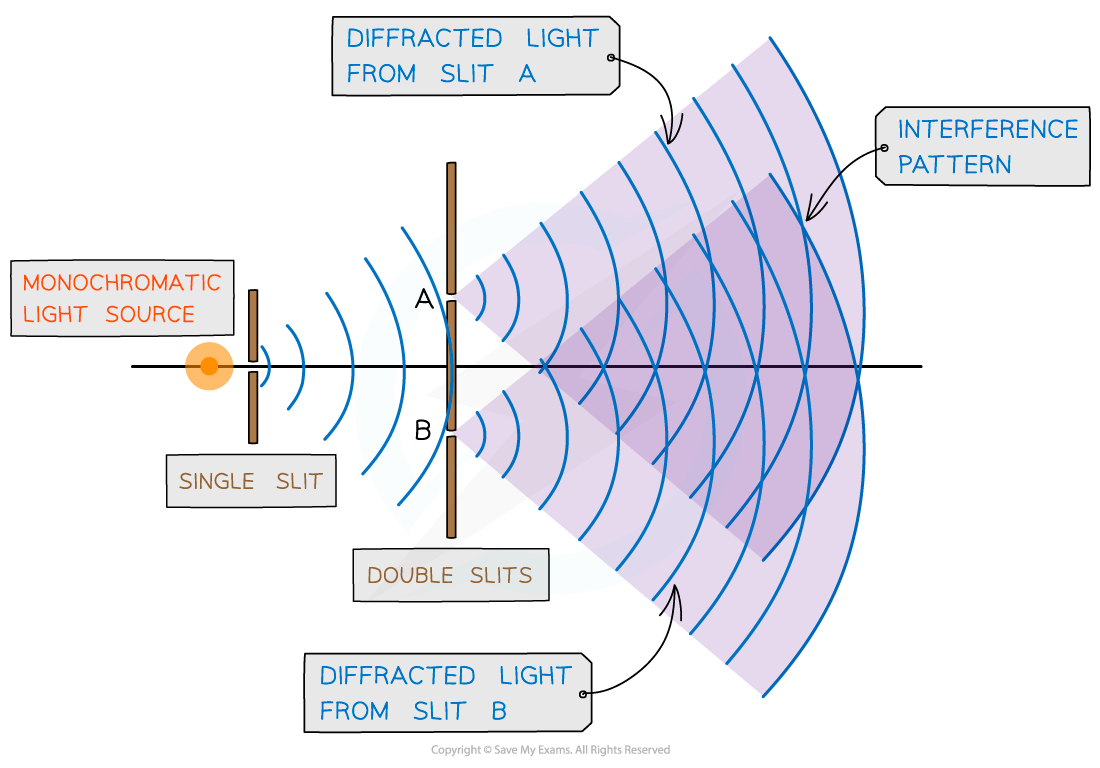
Young’s double-slit experiment arrangement
- When a monochromatic light source is placed behind a single slit, the light is diffracted producing two light sources at the double slits A and B
- Since both light sources originate from the same primary source, they are coherent and will therefore create an observable interference pattern
- Both diffracted light from the double slits create an interference pattern made up of bright and dark fringes
Worked Example
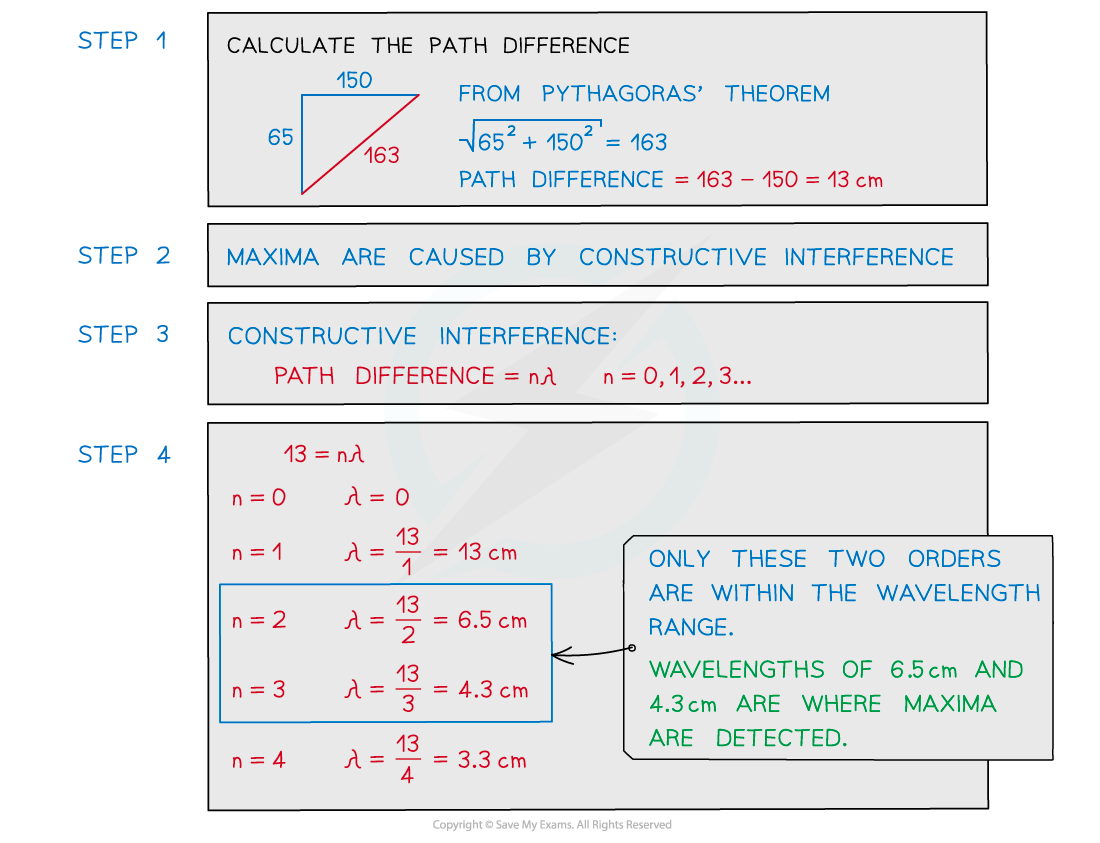
Two coherent sources of sound waves S1 and S2 are situated 65 cm apart in air as shown below.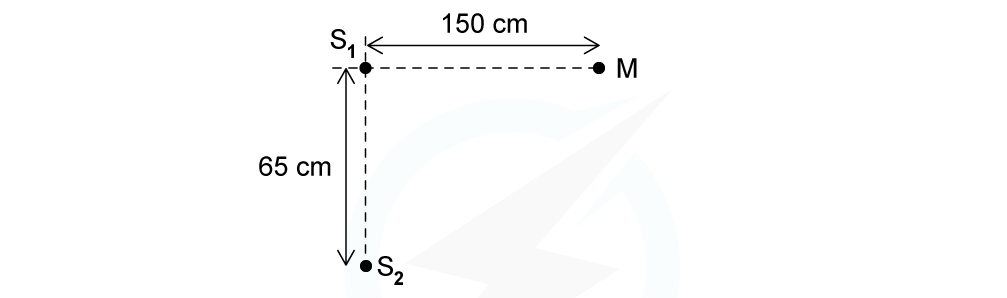 The two sources vibrate in phase but have different amplitudes of vibration. A microphone M is situated 150 cm from S1 along the line normal to S1 and S2. The microphone detects maxima and minima of the intensity of the sound. The wavelength of the sound from S1 to S2 is decreased by increasing the frequency.Determine which orders of maxima are detected at M as the wavelength is increased from 3.5 cm to 12.5 cm.
The two sources vibrate in phase but have different amplitudes of vibration. A microphone M is situated 150 cm from S1 along the line normal to S1 and S2. The microphone detects maxima and minima of the intensity of the sound. The wavelength of the sound from S1 to S2 is decreased by increasing the frequency.Determine which orders of maxima are detected at M as the wavelength is increased from 3.5 cm to 12.5 cm.
Exam Tip
The path difference is more specifically how much longer, or shorter, one path is than the other. In other words, the difference in the distances. Make sure not to confuse this with the distance between the two paths.
Fringe Spacing Equation
- The fringe spacing can be calculated from the interference pattern and the experimental setup
- These are related using the double-slit equation:
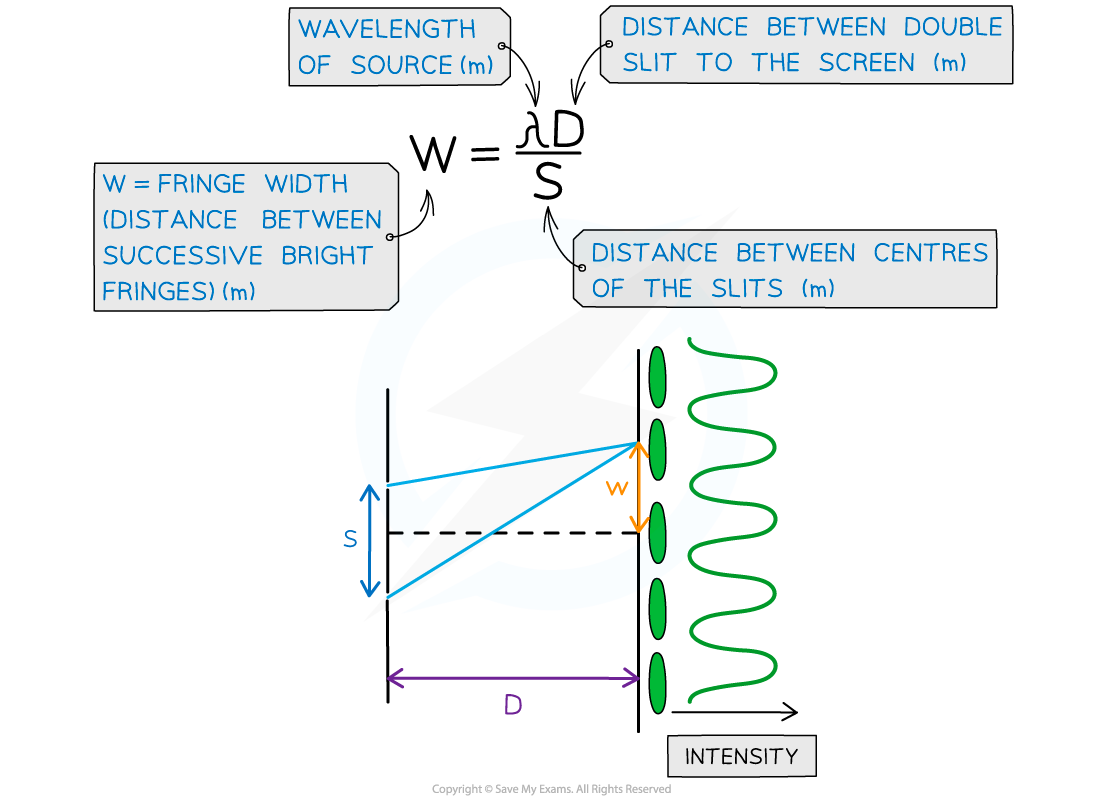
Double slit interference equation with w, s and D represented on a diagram
- The interference pattern on a screen will show as ‘fringes’ which are dark or bright bands
- Constructive interference is shown through bright fringes with varying intensity (most intense in the middle)
- Destructive interference is shown from dark fringes where no light is seen
- The distance between fringes is very small due to the short wavelength of visible light
- A monochromatic light source makes the fringes easier to observe
Worked Example
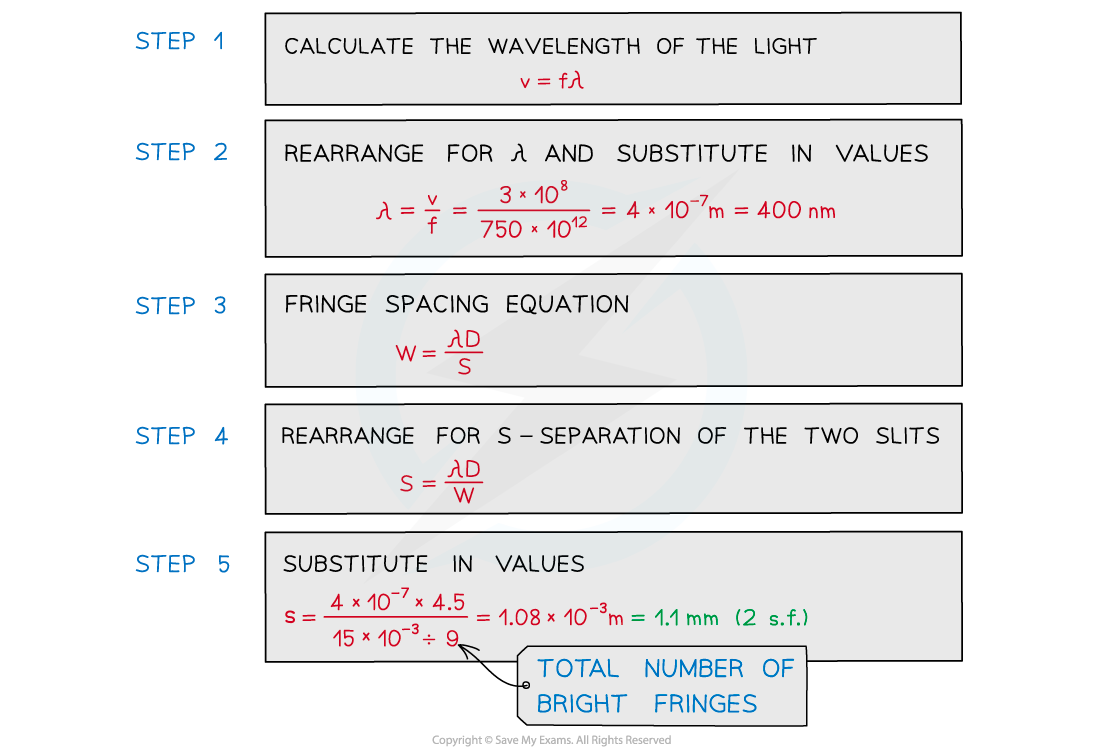
A laser is placed in front of a double-slit as shown in the diagram below.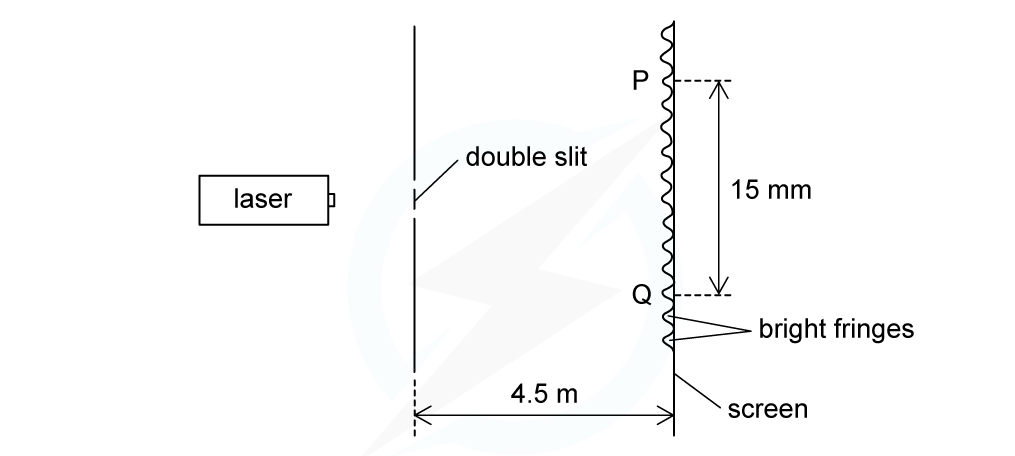 The laser emits light of frequency 750 THz. The separation of the maxima P and Q observed on the screen is 15 mm. The distance between the double slit and the screen is 4.5 m.Calculate the separation of the two slits.
The laser emits light of frequency 750 THz. The separation of the maxima P and Q observed on the screen is 15 mm. The distance between the double slit and the screen is 4.5 m.Calculate the separation of the two slits.
Exam Tip
Since w, s and D are all distances, it's easy to mix up which they refer to. Labelling the double-slit diagram as shown in the notes above will help to remember the order i.e. w and s in the numerator and D underneath in the denominator.
Interference Patterns
- If the monochromatic laser light is replaced with a white light source, the interference pattern observed is slightly different
- White light is composed of all the colours of visible light, so, each wavelength of white light produces its own interference pattern
- The central fringe is white because, at that position, the path difference for all wavelengths present is zero, therefore all wavelengths will arrive in phase
- The central fringe is, therefore, the same colour as the source i.e. white
- The first maximum occurs when the path difference is λ
- Since blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light, the path difference will be smaller, so the blue maximum will appear closer to the centre
- Each colour will produce a maximum in a slightly different position and so the colours spread out into a spectrum
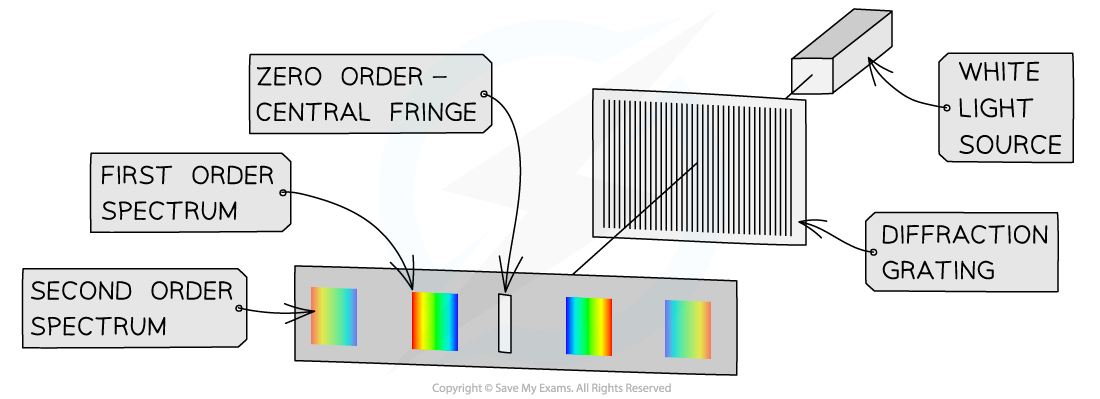
Each fringe appears as a visible spectrum apart from the central white fringe. Red is diffracted the most, violet is diffracted the least
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









