- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics复习笔记2.2.3 Mesons
Pions & The Strong Nuclear Force
Pions
- Pions (π–mesons) can be positive (π+), negative (π–) or neutral (π0)
- The anti–particle of the positive pion is the negative pion (and vice versa)
- The neutral pion is its own anti–particle
- Pions are the lightest mesons, making them more stable than other types of meson
- They were originally discovered in cosmic rays and can be observed in a cloud chamber
- The strong nuclear force keeps the protons and neutrons bound together in a nucleus and is one of the four fundamental interaction. Each of these interactions is caused by a particle exchange
- The pion is the exchange particle of the strong nuclear force
- This means that the strong force is transmitted between a proton and neutron by the exchange of a pion
- Pions are said to mediate (bring about) the strong nuclear force
- The pion created is a temporary violation of energy and mass conversation but since it is a virtual particle, it is not directly observed

- The gluon is also an exchange particle of the strong force. The difference between pions and gluons as mediators of this force are:
- Gluons are responsible for binding quarks together. This is referred to as the strong interaction
- Pions are responsible for binding nucleons together. This is referred to as the strong nuclear force
- Collectively, these are referred to as the strong force
Exam Tip
For the purpose of your exam, the pion is the exchange particle of the strong nuclear force although gluons will be accepted.
Kaon Decay
Kaons
- Kaons (K–mesons) can also be positive (K+), negative (K–) or neutral (K0)
- The anti–particle of the positive kaon is the negative kaon (and vice versa)
- The neutral kaon is its own anti–particle
- Kaons can be produced by the strong interaction between pions and protons
Kaon Decay
- Kaons are heavy and unstable and normally decay into pions
- They are known to have unusually long lifetimes
- This is because kaons contain a strange quark and longer lifetimes are characteristic of particles containing strange quarks
- Kaons decay through the weak interaction
- An example of a kaon decay would be a neutral kaon decaying into a positive pion and negative pion:
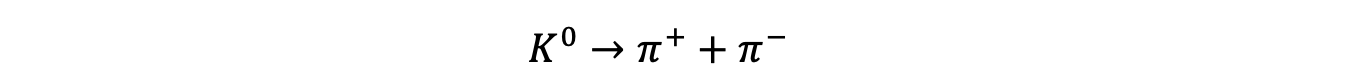
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








