- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记7.7.3 Enzymes
Enzymes
- Enzymes are biological catalysts
- ‘Biological’ because they function in living systems
- ‘Catalysts’ because they speed up the rate of chemical reactions without being used up or changed
- Enzymes are also globular proteins
- Critical to the enzyme’s function is the active site where the substrate binds
- Metabolic pathways are controlled by enzymes in a biochemical cascade of reactions
- Virtually every metabolic reaction within living organisms is catalysed by an enzyme – enzymes are therefore essential for life to exist
- Enzymes have an active site where specific substrates bind forming an enzyme-substrate complex
- The active site of an enzyme has a specific shape to fit a specific substrate
- Extremes of heat or pH can change the shape of the active site, preventing substrate binding – this is called denaturation
- Substrates collide with the enzymes active site and this must happen at the correct orientation and speed in order for a reaction to occur
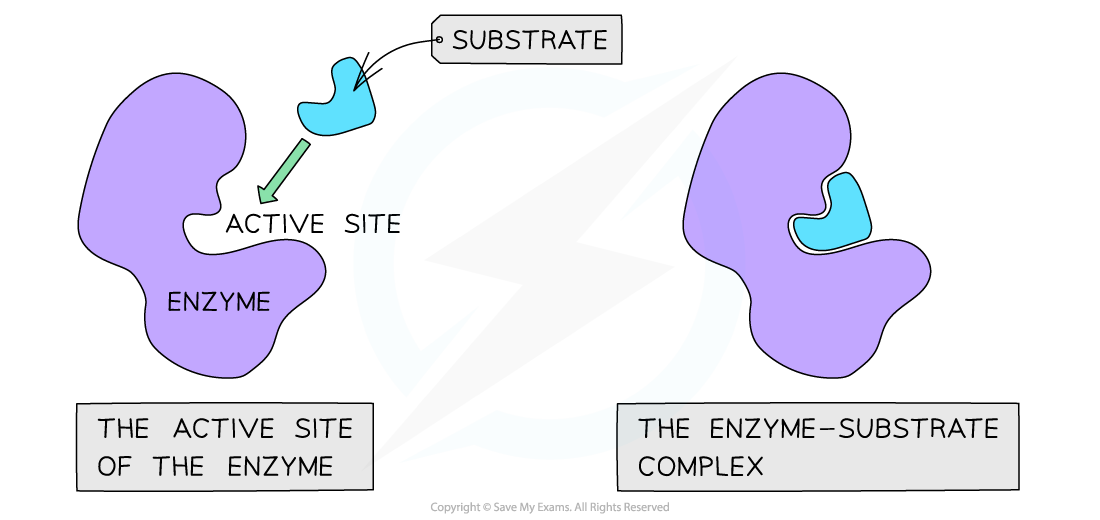
The active site of an enzyme has a specific shape to fit a specific substrate (when the substrate binds an enzyme-substrate complex is formed)
Enzyme Specificity
- The specificity of an enzyme is a result of the complementary nature between the shape of the active site on the enzyme and its substrate(s)
- The shape of the active site (and therefore the specificity of the enzyme) is determined by the complex tertiary structure of the protein that makes up the enzyme:
- Proteins are formed from chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
- The order of amino acids determines the shape of an enzyme
- If the order is altered, the resulting three-dimensional shape changes
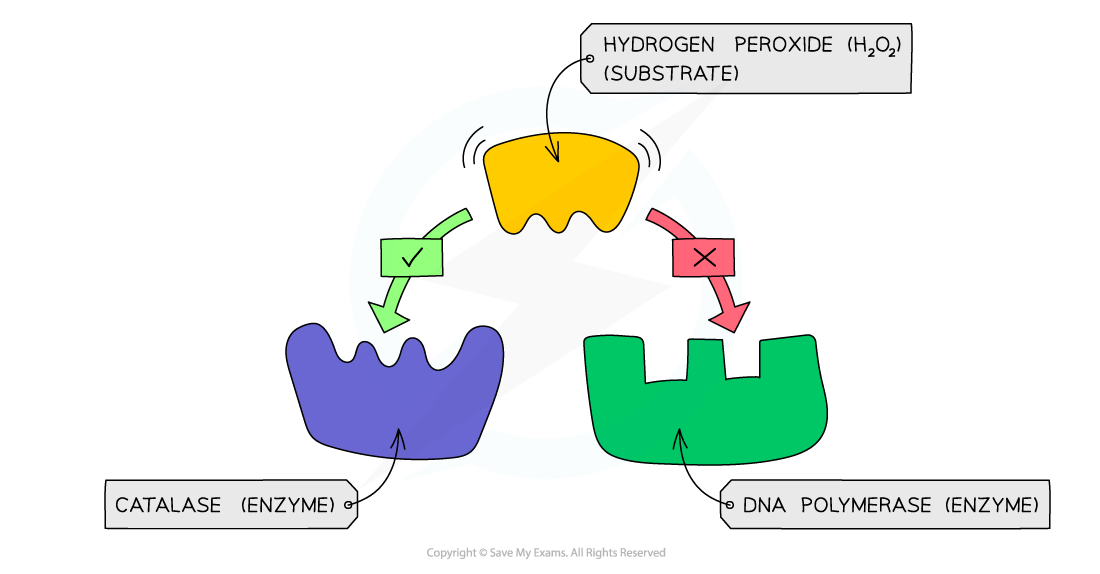
An example of enzyme specificity – the enzyme catalase can bind to its substrate hydrogen peroxide as they are complementary in shape, whereas DNA polymerase is not
Drug-receptor Interactions
- Receptors are proteins found on enzymes, cell membranes or DNA
- Most drugs work by their ability to bind to receptors stopping their normal biological activity and interrupting the development of disease
- Drugs bind to receptors generally using intermolecular forces or ionic bonds
- The stronger the interaction the more effective the drug activity
- Drug-receptor interaction has become very important in drug design
- Computers are widely used to model drug-receptor interactions
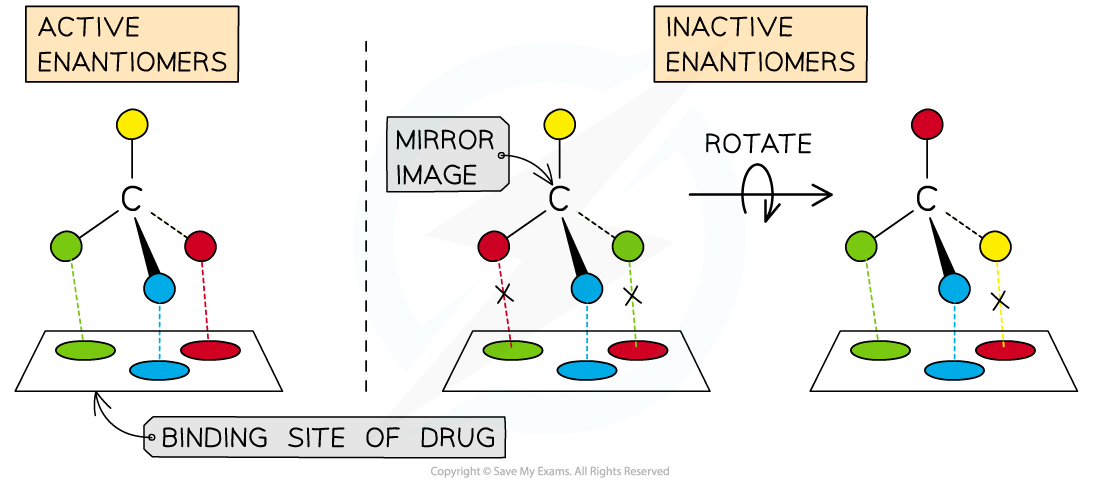
Only the correct orientation of one enantiomer enable the drug to bind to the biomolecule making it stereoselective
- Many naturally occurring organic molecules consist of enantiomers, in which only one enantiomer is biologically active
- Similarly, many drugs have enantiomeric forms in which only one form of the drug is active
- The site where the drug binds to the biomolecule can only accept one orientation; it is said to be stereoselective
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








