- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记7.7.2 Proteins
Proteins
- Each amino acid contains an amine (-NH2) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) group
- The -NH2 group of one amino acid can react with the -COOH group of another amino acid in a condensation reaction to form a dipeptide
- The new amide bond between two amino acids is also called a peptide link or peptide bond
- Since this is a condensation reaction, a small molecule (in this case H2O) is eliminated
- The dipeptide still contains an -NH2 and -COOH group at each end of the molecule which can again participate in a condensation reaction to form a tripeptide
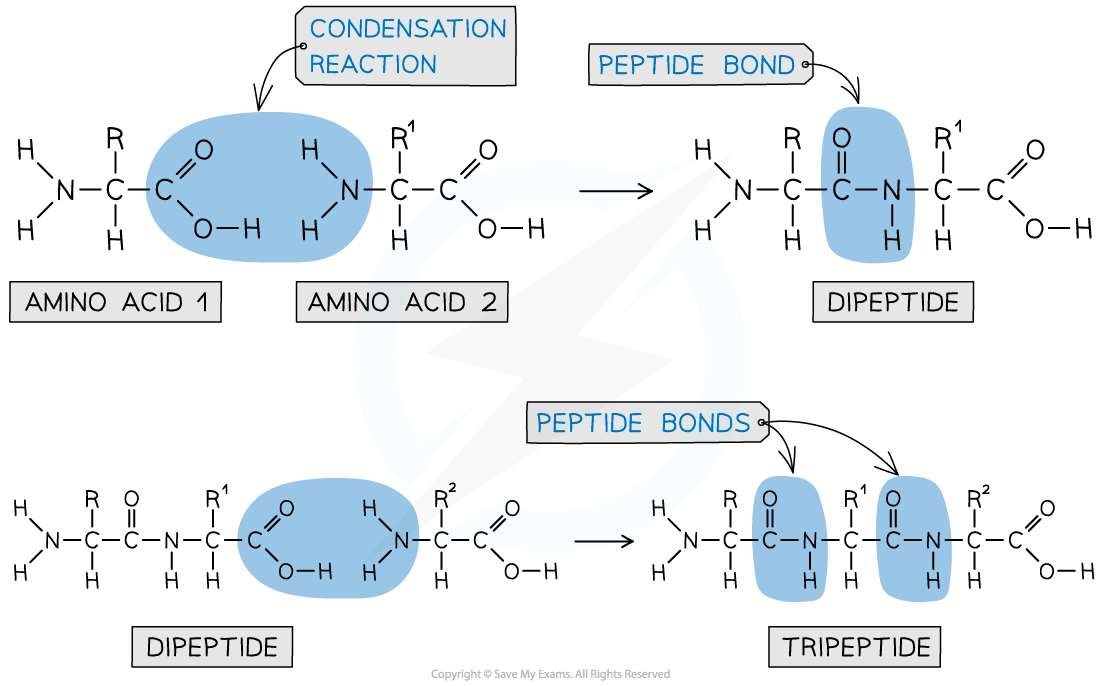
A peptide bond is an amide bond between two amino acids
- A polypeptide is formed when many amino acids join together to form a long chain of molecules
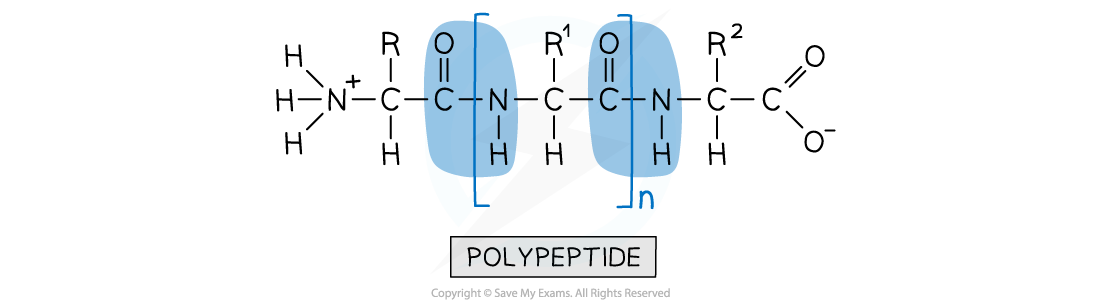
A polypeptide is a long chain of amino acid molecules joined together
The structure of proteins
- There are four levels of structure in proteins, three are related to a single polypeptide chain and the fourth level relates to a protein that has two or more polypeptide chains
- Polypeptide or protein molecules can have anywhere from 3 amino acids (Glutathione) to more than 34,000 amino acids (Titan) bonded together in chains
Primary
- The sequence of amino acids bonded by covalent peptide bonds is the primary structure of a protein
- The primary structure is specific for each protein (one alteration in the sequence of amino acids can affect the function of the protein)
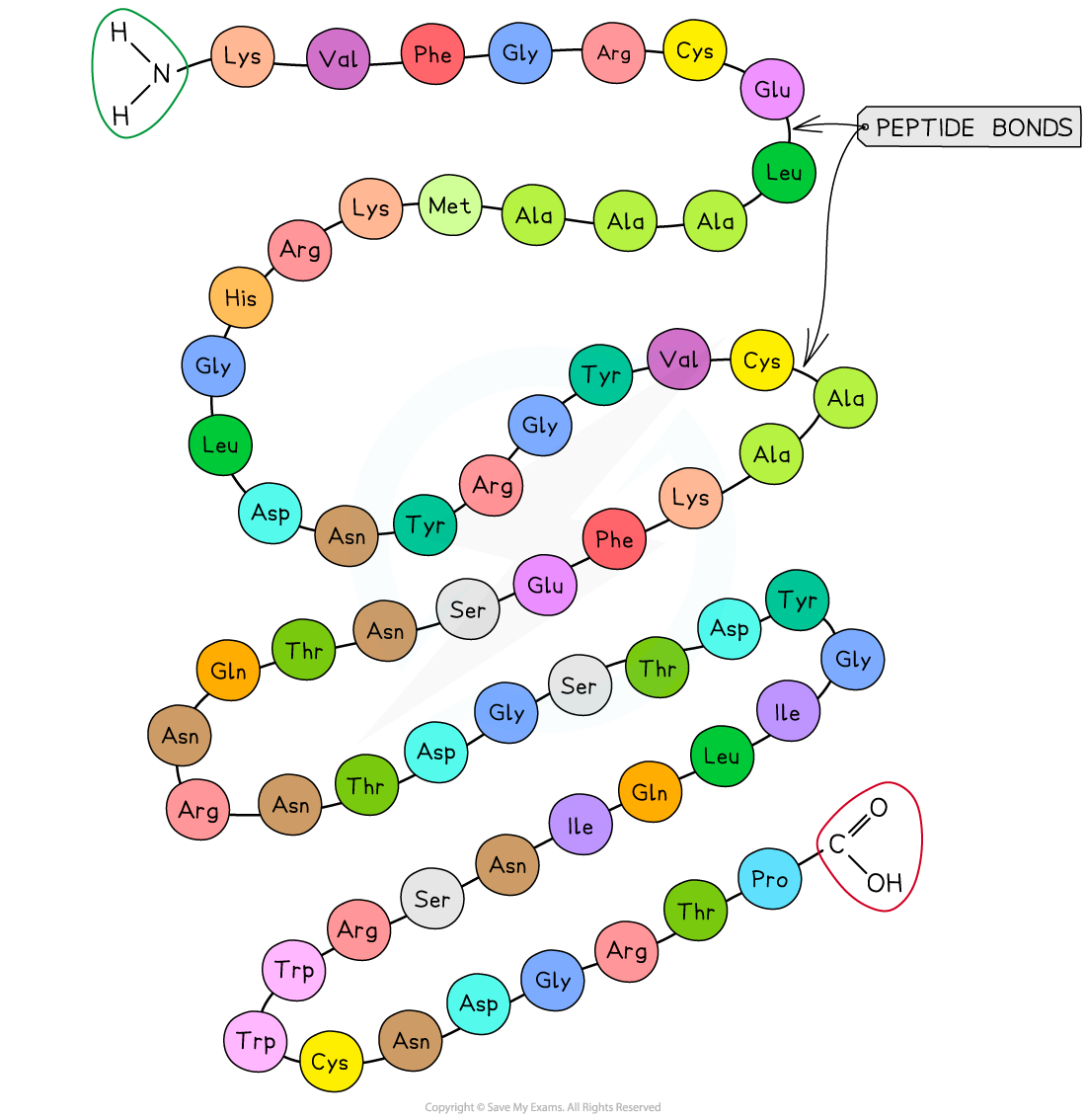
The primary structure of a protein. The three-letter abbreviations indicate the specific amino acid (there are 20 commonly found in cells of living organisms)
Secondary
- The secondary structure of a protein occurs when the weak negatively charged nitrogen and oxygen atoms interact with the weak positively charged hydrogen atoms to form hydrogen bonds
- There are two shapes that can form within proteins due to the hydrogen bonds:
- α-helix
- β-pleated sheet
- The α-helix shape occurs when the hydrogen bonds form between every fourth peptide bond (between the oxygen of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the amine group)
- The β-pleated sheet shape forms when the protein folds so that two parts of the polypeptide chain are parallel to each other enabling hydrogen bonds to form between parallel peptide bonds
- Most fibrous proteins have secondary structures (e.g. collagen and keratin)
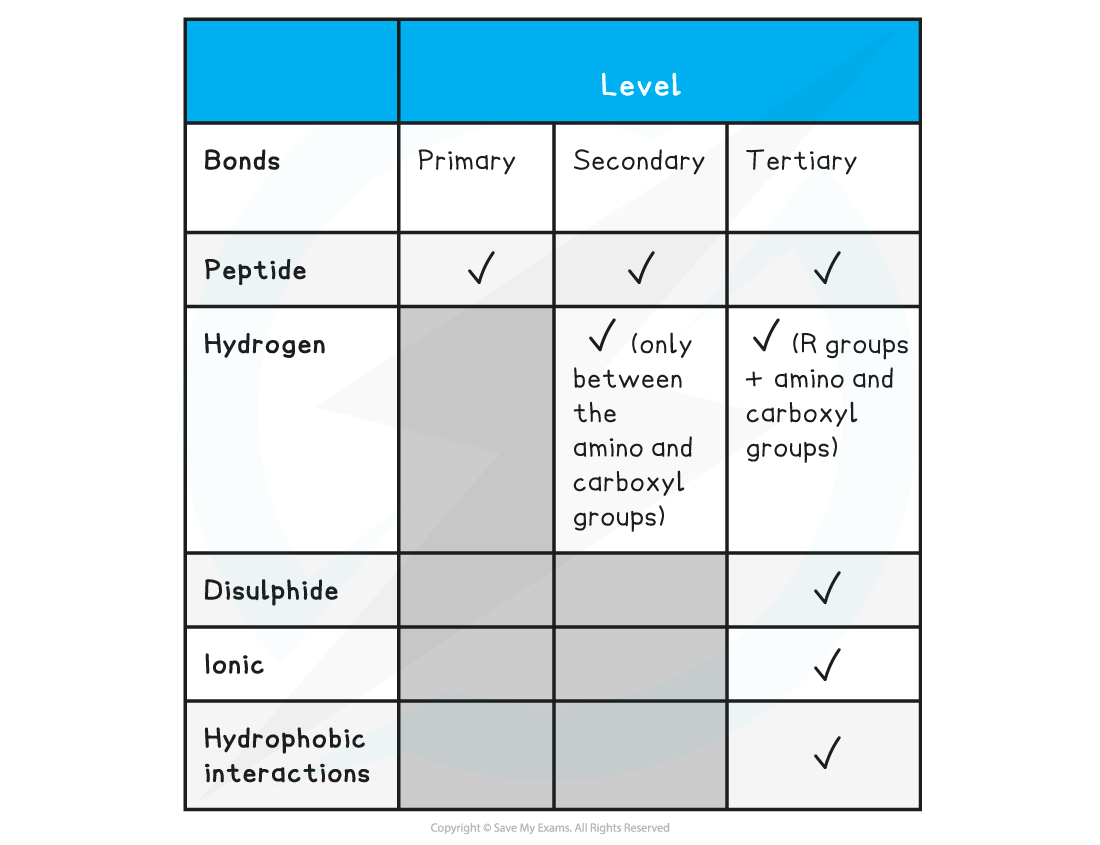
- The secondary structure only relates to hydrogen bonds forming between the amino group and the carboxyl group (the ‘protein backbone’)
- The hydrogen bonds can be broken by high temperatures and pH changes
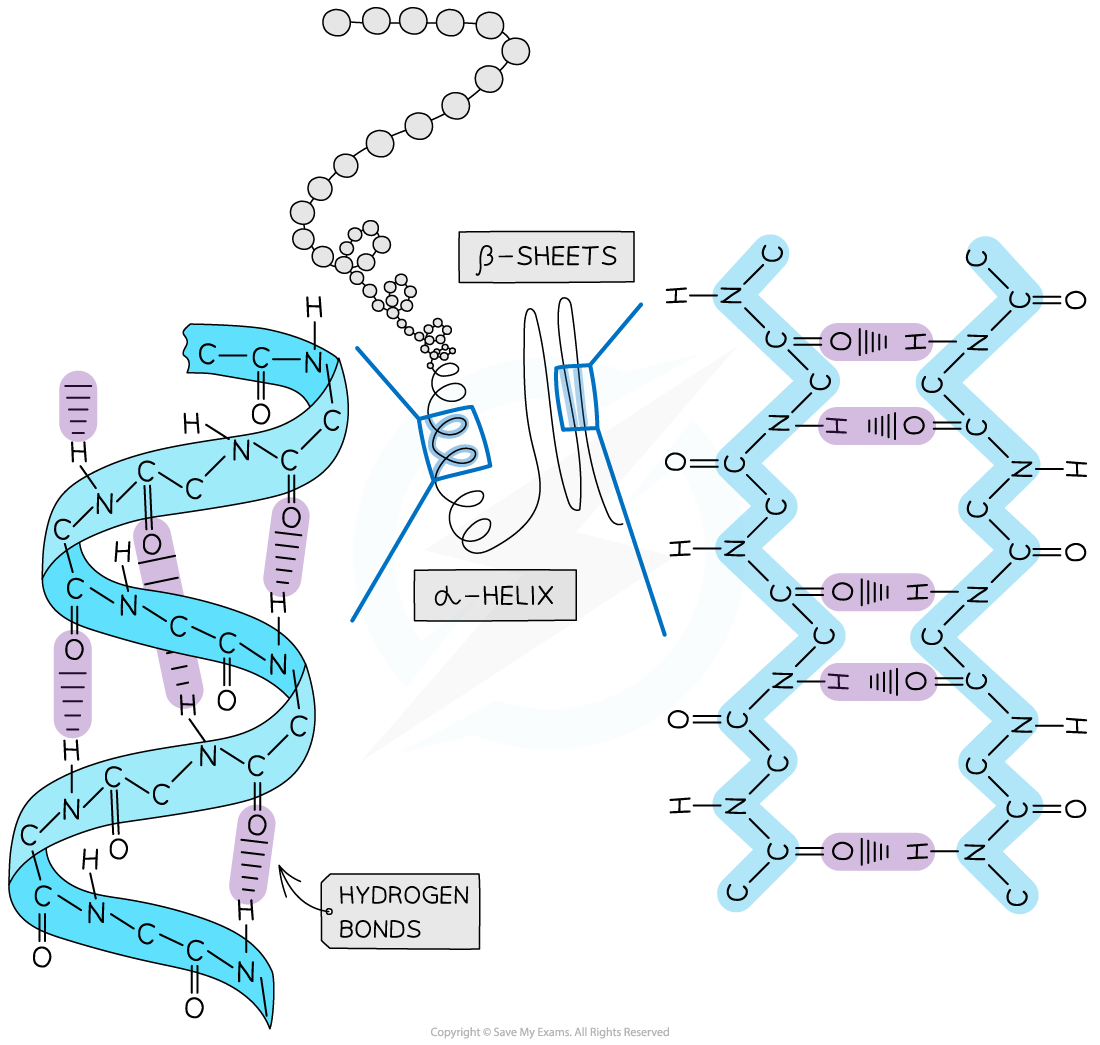
The secondary structure of a protein with the α-helix and β-pleated sheet shapes highlighted. The magnified regions illustrate how the hydrogen bonds form between the peptide bonds
Tertiary
- Further conformational change of the secondary structure leads to additional bonds forming between the R groups (side chains)
- The additional bonds are:
- Hydrogen (these are between R groups)
- Disulphide (only occurs between cysteine amino acids)
- Ionic (occurs between charged R groups)
- Weak hydrophobic interactions (between non-polar R groups)
- This structure is common in globular proteins
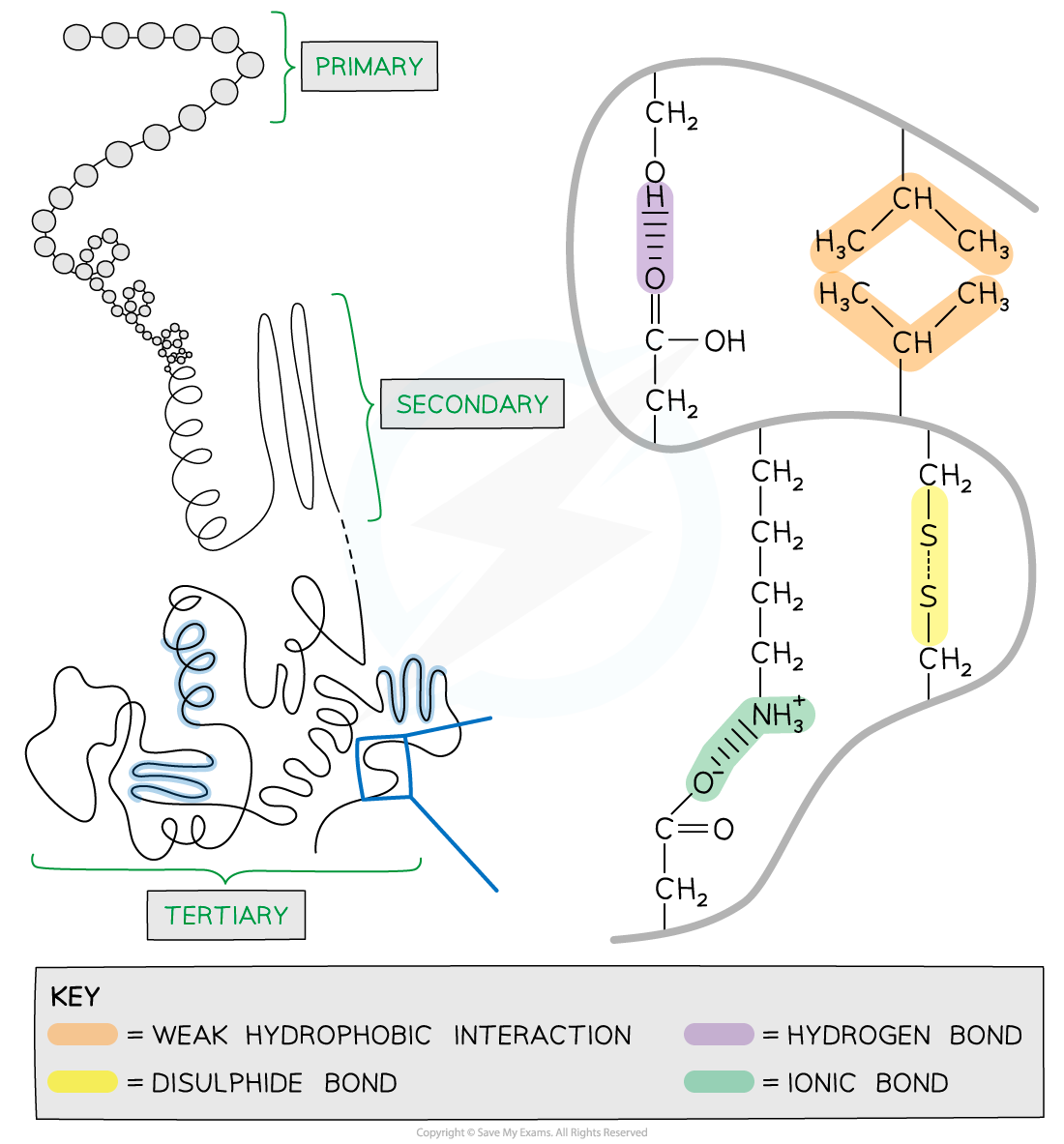
The tertiary structure of a protein with hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds and hydrophobic interactions formed between the R groups of the amino acids
Summary of the types of bonding in peptides Table
Exam Tip
You should be able to draw the peptide formed by the joining of up to three amino acids.
Hydrolysis of Proteins
- Hydrolysis of proteins is the reverse reaction of condensation in which the peptide link is broken and water added, hence the term hydrolysis
- During hydrolysis reactions polypeptides are broken down to amino acids when the addition of water breaks the peptide bonds
- The condensation and hydrolysis of a dipeptide is shown here for reference, but the reaction is identical with a protein chain
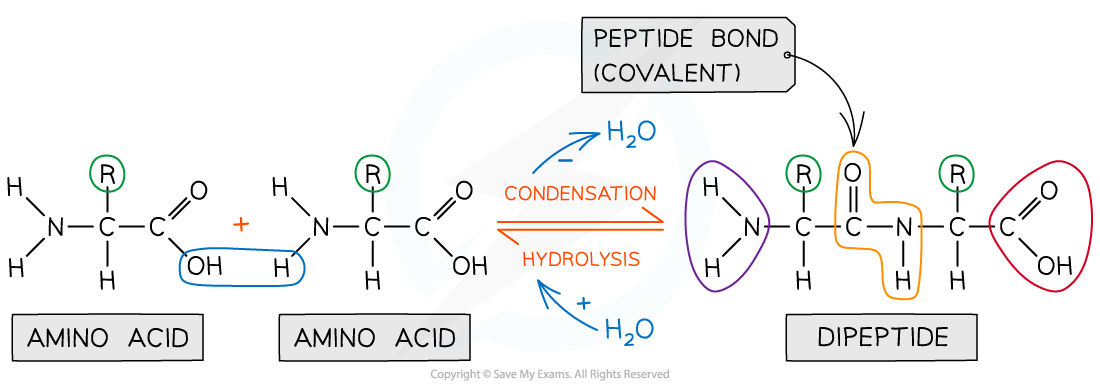
Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction
- The hydrolysis reaction can be carried out by chemical means or using enzymes
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid is the reagent used and the mixture is boiled for many hours as the reaction is slow
- With enzyme the reaction occurs at room temperature
Identifying Amino Acids
- After hydrolysis, the amino acid components from polypeptides can be identified by using the technique of thin layer chromatography (TLC)
- This technique is described in more detail in a later section
- Although the amino acids have the same basic structure the R group changes the overall polarity of the molecule so the amino acids will rise up the TLC at different rates
- Since amino acids are colourless the TLC plate has to either be sprayed with a locating agent such as ninhydrin which stains the amino acids, or the plate must be illuminated under a UV light
- A TLC plate can be used to calculate Rf values for compounds
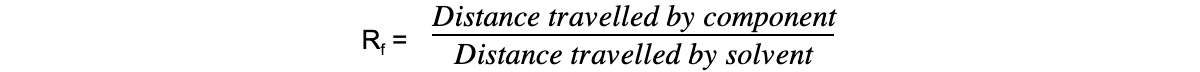 These values can be used alongside other analytical data to deduce composition of mixtures
These values can be used alongside other analytical data to deduce composition of mixtures- The Rf value (retention factor) can be determined and use to identify a specific amino acid
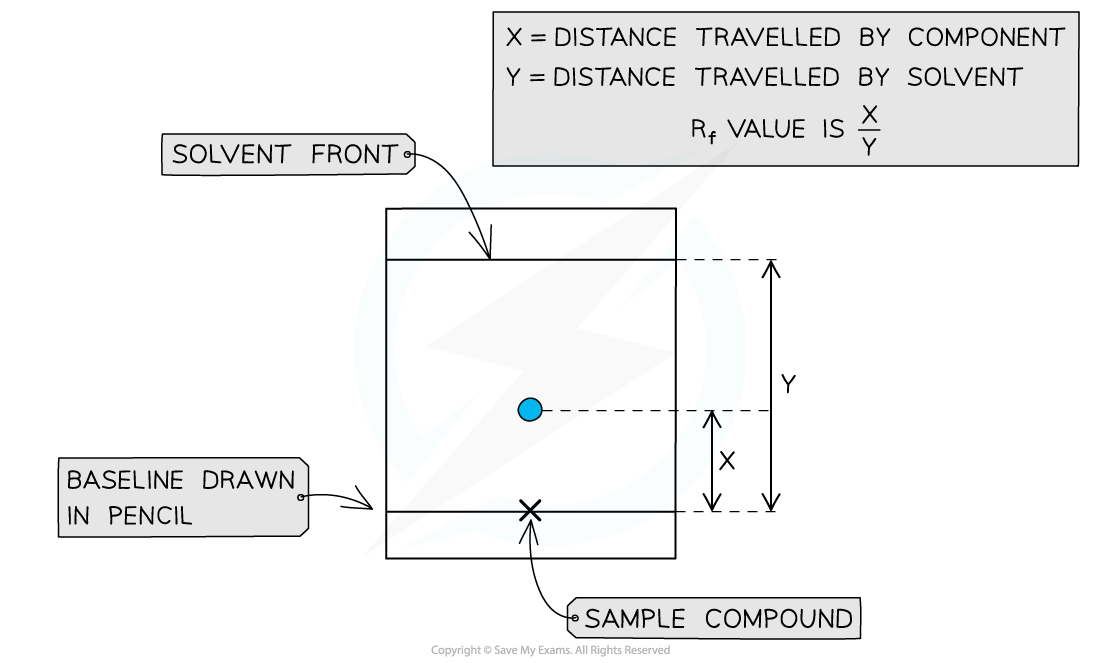
Rf values can be calculated by taking 2 measurements from the TLC plate
- Sometimes amino acids have very similar values in the same solvent, so a further technique of two dimensional TLC can be used
- In this technique the same plate is run through two different solvents
- A square TLC plate is used and run through the first solvent, then the plate is turned through 90o and run through the second solvent
- Two Rf values are determined allowing greater confidence in identifying the amino acids
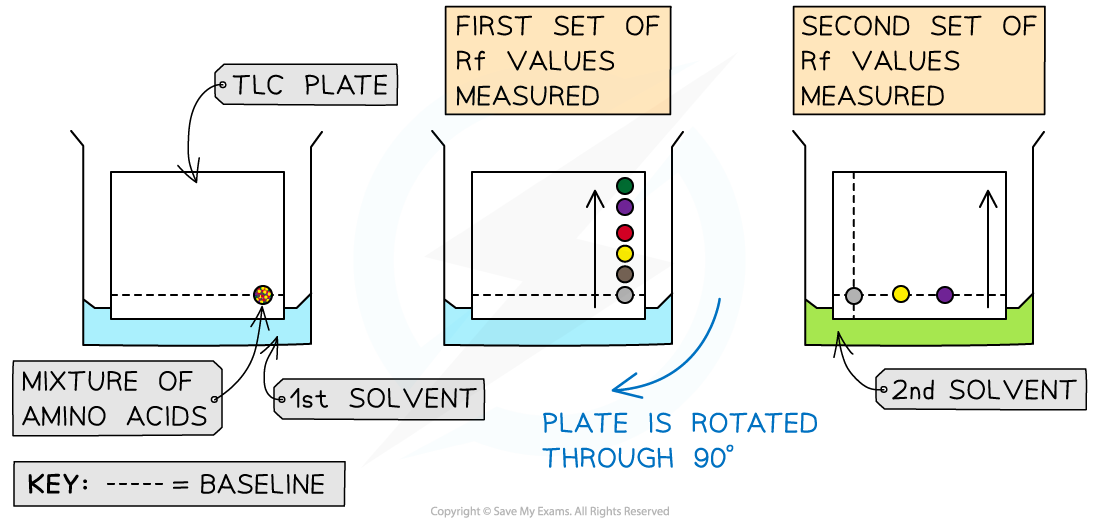
Two dimensional TLC allows greater confidence in identifying amino acids
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








