- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记6.2.7 Catalysis
Catalysis
- Catalysts play an important part in industry allowing reactions to be carried out more quickly and at lower temperatures
- There are two types of catalysts, heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts
- Transition elements and their compounds are often used as catalysts
- A heterogenous catalyst is in a different physical state (phase) from the reactants
- The reaction occurs at active sites on the surface of the catalyst
- For example, vanadium(V) oxide, V2O5, is a solid catalyst used in the Contact process for making sulfuric acid
- Another example is the use of solid iron, Fe, in the Haber process for making ammonia
- A homogeneous catalyst is in the same physical state (phase) as the reactants
- An example of a homogeneous catalyst is the role of iron(II) ions, Fe2+, in the reaction between iodide ions, I-, and peroxydisulfate ions, S2O82-
- Transition elements are often used as catalysts due to their ability to form ions with more than one stable oxidation state, and the fact that they contain vacant d orbitals
Vacant d-orbitals
- Transition elements and their ions have vacant d-orbitals which are energetically accessible
- The orbitals are not too high in energy
- This means that attractions can be formed between the transition element and pairs of electrons on small molecules such as hydrogen
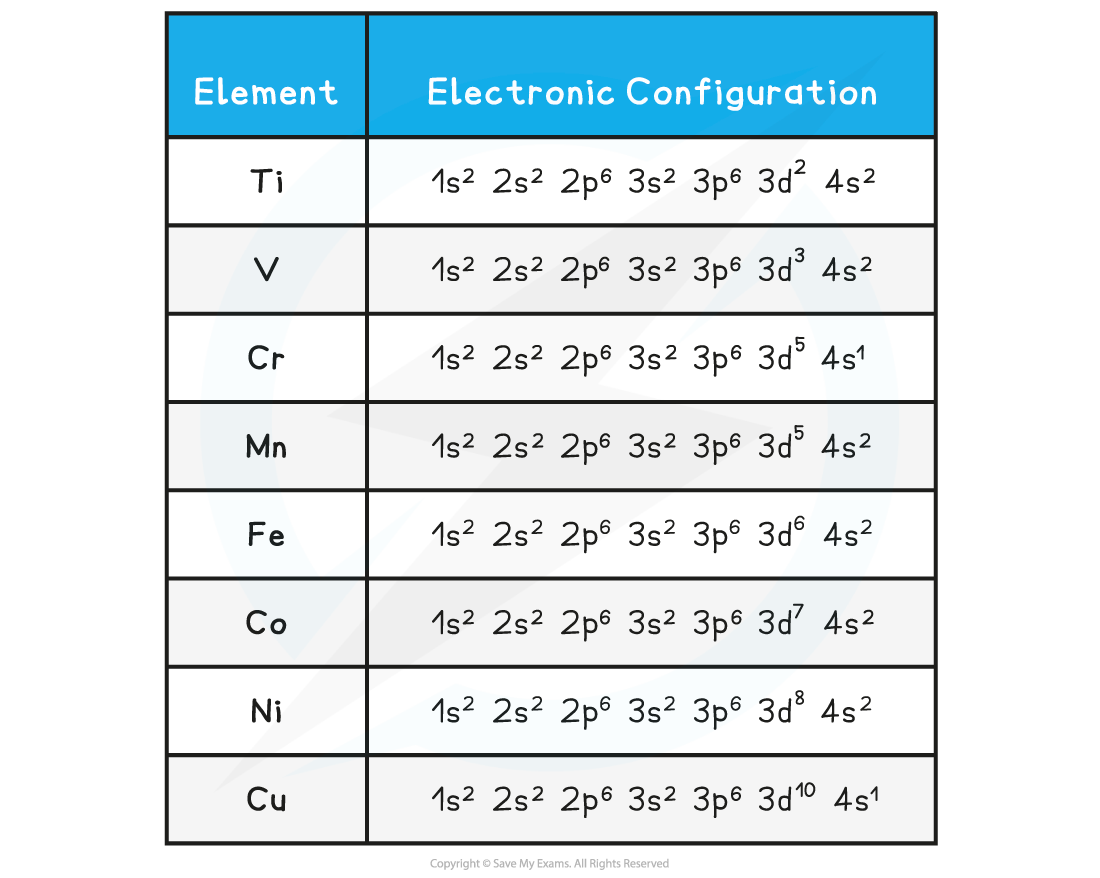
- The table below shows the electron configuration of the transition elements
- The empty d-orbitals can be filled by donated pairs of electrons
Electronic configuration of transition elements table
Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Some of the transition metals are precious metals so they can be very expensive
- In order to minimise the cost and maximise the efficiency of the catalyst the following measures can be taken:
- Increasing the surface area of the catalyst
- Coating an inert surface medium with the catalyst to avoid using large amounts of the catalyst
- This is achieved by spreading the catalyst over a hollow matrix such as a honeycomb-like structure
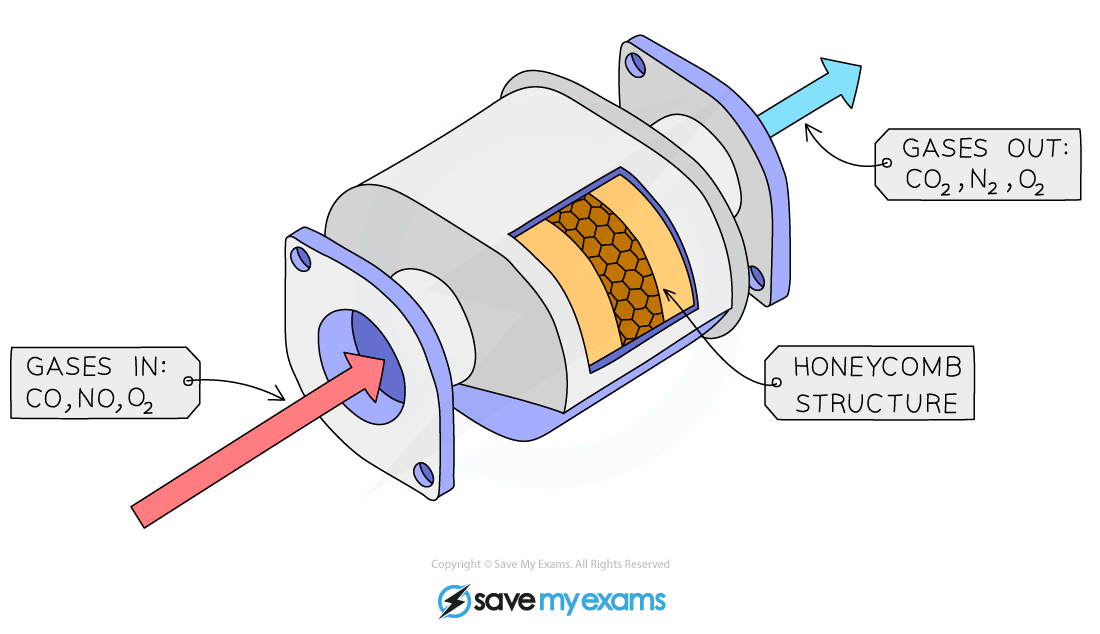
Diagram of a catalyst on an inert support medium in a vehicle catalytic converter
- Catalytic converters are used in car exhaust boxes to reduce air pollution. They usually consist of a mixture of finely divided platinum and rhodium supported on a ceramic base
The Contact Process
- The manufacture of sulfuric acid is a very important piece of industrial chemistry that makes use of heterogeneous catalysis
- The first step of the process is roasting sulfur in air to produce sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
- The second step is an equilibrium reaction which is catalysed by vanadium(V) oxide, V2O5,
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
- The vanadium(V) oxide catalyst converts sulfur dioxide into sulfur trioxide and is reduced to vanadium(IV) oxide
SO2 (g) + V2O5 (s) → V2O4 + SO3 (g)
- The vanadium(V) oxide is then re-generated by reaction with oxygen, fulfilling its role as a catalyst
O2 (g) + 2V2O4 (s) → 2V2O5 (s)
- This reaction shows that a variable oxidation state can also be utilised in heterogenous catalysis
The Haber Process
- The industrial production of ammonia takes place using the Haber process
- The main reaction is:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)
- Iron pellets are used as the catalyst to provide a large surface area
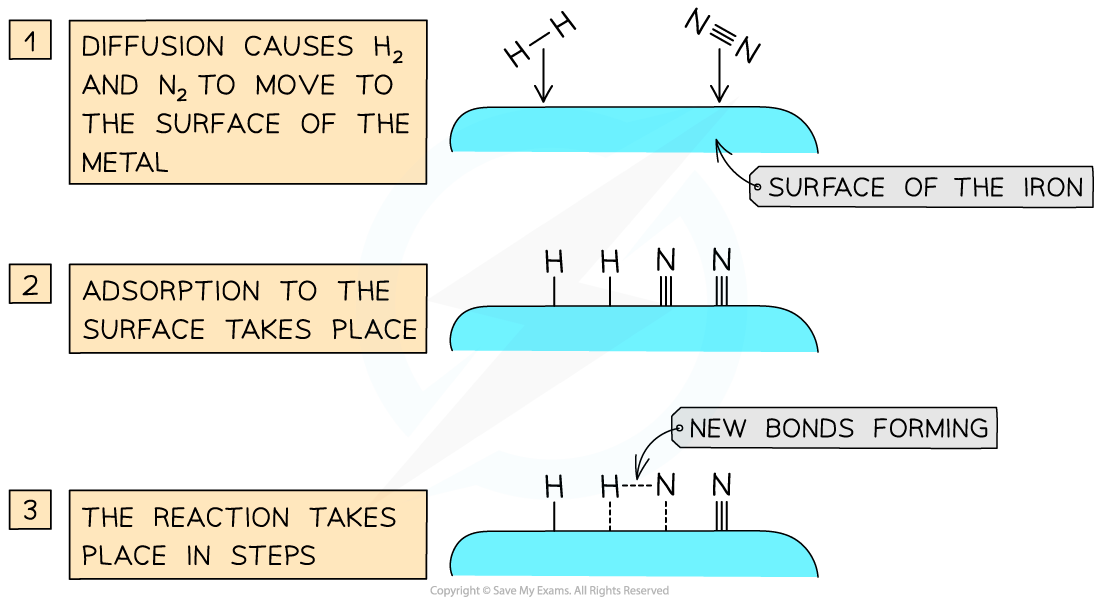
- In the reaction the surface of the iron attracts electrons in the hydrogen and nitrogen and these molecules for temporary loose attachments to the surface. This is called adsorption
Heterogeneous catalysis takes place at active sites on the surface of the transition metal catalyst
Limitations of heterogeneous catalysts
- The operating conditions of car exhausts as well as industrial reactions means that catalysts do not last forever
- Tiny quantities of impurities gradually become lodged on the surface of the catalyst binding with the active sites and preventing further catalytic reaction. This is know as 'poisoning' of the catalyst
- Other heavy metal impurities such as lead can do this, which is one of the reasons why lead additives were phased out of petrol a number of years ago (the other reason was environmental); catalytic converters in cars would soon fail with leaded petrol
- As the catalyst has a very thin coating on the ceramic support it will be gradually be lost over time and so the efficiency of the catalytic converter will be reduced
- Catalytic converters do not work very well at low temperatures and need about 15 minutes of the engine running and warming up the exhaust box before they are effective, so short journeys do almost nothing for pollution reduction
Homogeneous Catalysis
Variable oxidation states - the key to homogeneous catalysis
- Transition element ions can adopt more than one stable oxidation state
- This means that they can accept and lose electrons easily to go from one oxidation state to another
- They can therefore catalyse redox reactions, by acting as both oxidising agents and reducing agents
- For example, iron (Fe) is often used as a catalyst due to its ability to form Fe(II) and Fe(III) ions, acting as an oxidising agent and a reducing agent
- When Fe(II) acts as a reducing agent, it will reduce another species and become oxidised itself
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e-
- The Fe3+ formed in the catalytic cycle, can then also act as an oxidising agent by oxidising another species and getting reduced itself to reform the Fe2+ ion
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+
- Iron(II) ions catalyse the reaction between iodide ions, I-, and peroxodisulfate ions, S2O82-
- The overall reaction is quite slow because the repulsion of two negative ions coming together hinders the reaction
S2O82- + 2I- → I2 + 2SO42-
- The reaction is quite slow even though it is energetically favourable. Both ions are negatively charged, so they are unlikely to make successful collisions with one another. However, if iron(II) ions are added to the reaction, the rate is much quicker. Starch is often added to this reaction, which will form a blue-black colour showing the formation of iodine
- The addition of iron(II) ions reduces the peroxodisulfate to sulfate ions and produces iron(III) in the process
S2O82- + 2Fe2+ → 2SO42- + 2Fe3+
- The iron(III) ions will oxidise iodide ions to iodine and then are reduced once again to iron(II)
2I- + 2Fe3+ → I2 + 2Fe2+
- The iron(II) produced can then go on to reduce more peroxodisulfate so fulfils its role as a catalyst
- A catalyst provides a reaction pathway of lower energy which can be illustrated graphically:
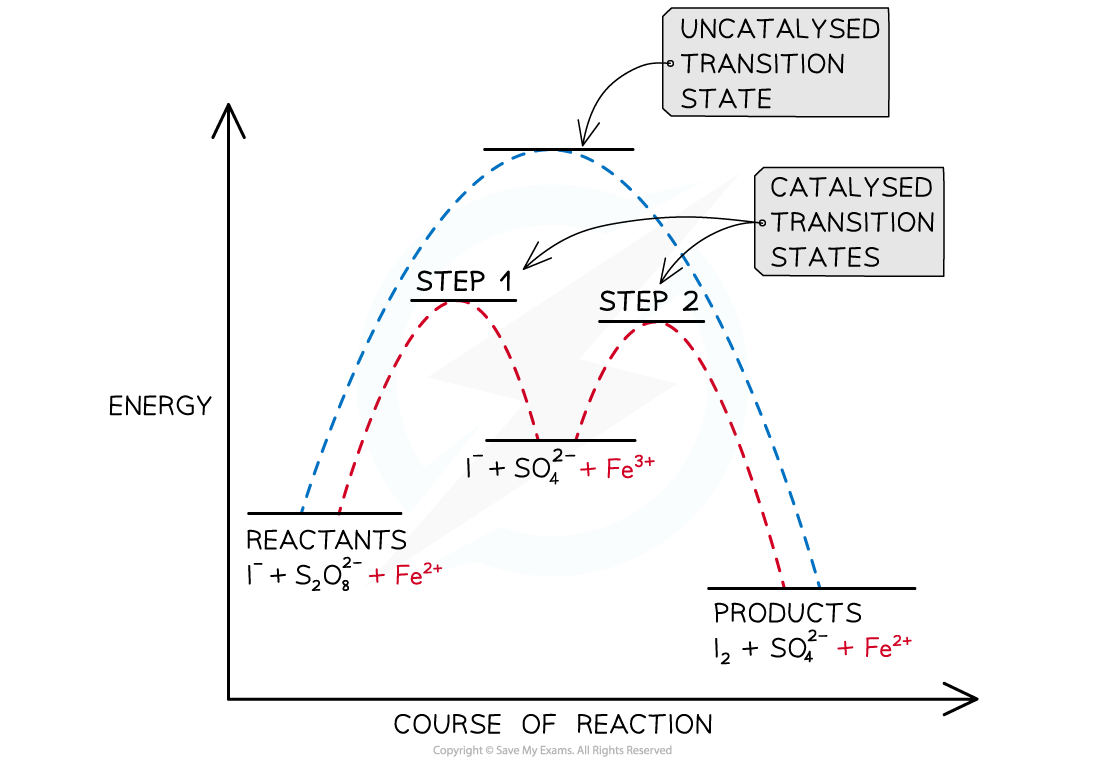
An energy profile showing the alternative reaction pathway provided by iron(II) catalyst in the reaction between iodide ions and peroxodisulfate ions
Autocatalysis
- Autocatalysis the term used to describe a reaction which is speeded up by a product which acts as a catalyst for the reaction
- If you plot a rate graph of concentration versus time it has an usual shape
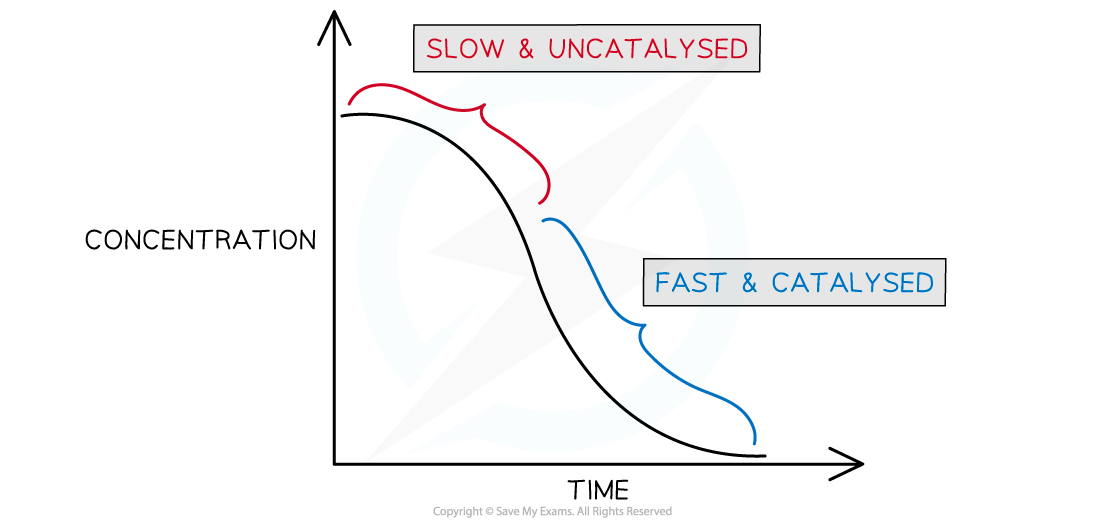
Concentration versus time for an autocatalytic reaction
- The gradient becomes steeper during the course of the reaction which tells you the rate is speeding up, not slowing down over time as the reactants become used up
- An example of an autocatalysed reaction takes place between manganate(VII) ions and oxalate (ethandioate) ions
- The overall equation can be deduced from the half equations

- You can see that one of the products is manganese(II) ions - this is the catalyst
- As more manganese(II) is formed the reaction speeds up
- Like to the role of iron(II) in the previous section, manganese(II) ions take part in a redox cycle between two different oxidation states (+2 → +3 → +2)
4Mn2+ (aq) + MnO4– (aq) + 8H+ (aq) → 5Mn3+ (aq) + 4H2O (aq)
2Mn3+ (aq) + C2O42- (aq) → 2CO2 (g) + 2Mn2+ (aq)
- The manganese(II) is not present in the beginning of the reaction, but as it is formed is speeds up the reaction and is re-generated during the redox cycle
- This reaction is easily followed on a colorimeter as the rate at which the purple manganate(VII) ion is consumed accelerates with time
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1