- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记6.2.5 Variable Oxidation States
Variable Oxidation States
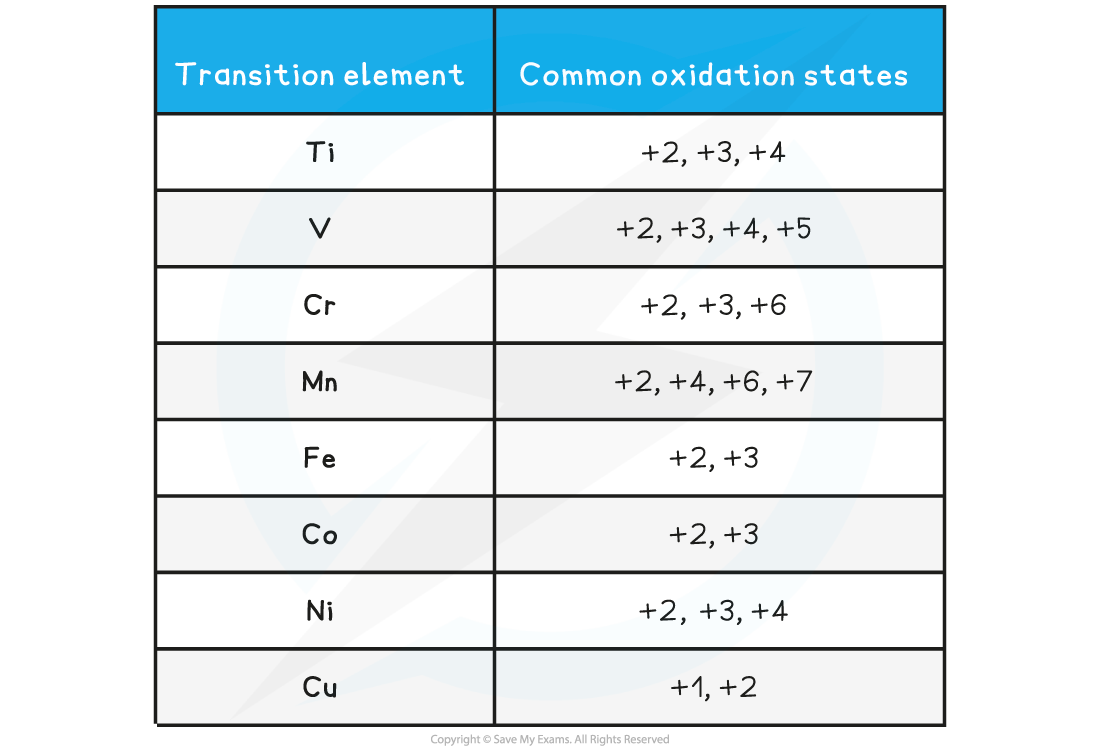
- The table below shows the most common oxidation states of a few transition metals
Oxidation states of transition elements table
- When transition elements forms ions they lose electrons from the 4s subshell first
- This is because when the orbitals are occupied, the repulsion between electrons pushes the 4s into a higher energy state so that it now becomes slightly higher in energy than the 3d subshell
- The 4s is now the outer shell and loses electrons first
- The loss of the 4s electrons means that +2 is common oxidation state in transition metals
- The reason why the transition metals have variable oxidation states all comes down to energy
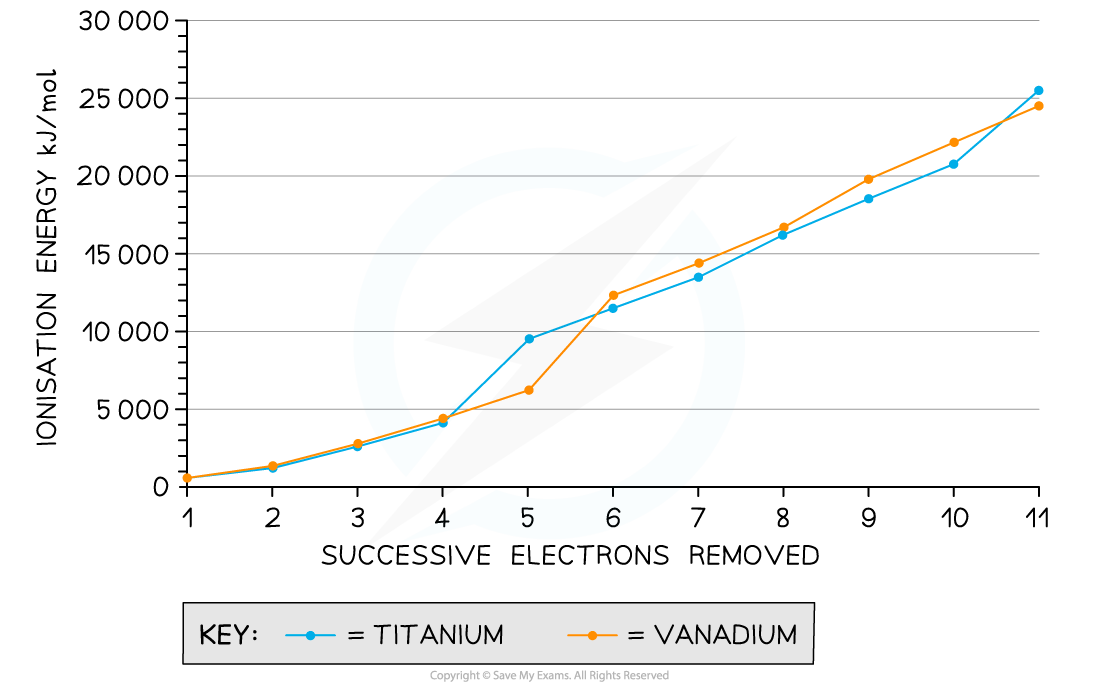
Ionisation energies for the removal of successive electrons in titanium and vanadium
- We can see from the graph that the first few ionisation energies are relatively small and relatively close together
- This means that the energy difference associated with removing a small number of electrons enables transition metals to vary their oxidation state with ease
Redox Potential & Oxidation State
Influence of pH
- The redox potential for a transition metal ion changing from a higher to a lower oxidation state is influenced by pH and by the ligand
- When aqueous transition metal ions undergo a change in oxidation state, the reactions frequently involve hydrogen ions
- By analysing the reaction equations we can see the redox processes taking place
- The reduction of manganese in the manganate(VII) ion takes place readily in acidic solutions
MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e- ⇌ Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l) Eꝋ = +1.51 V
- The manganese changes from +7 to +2
- The positive value of Eꝋ indicates the equilibrium position is well over to the right
- An excess of acid drops the pH and provides the hydrogen ions to ensure this reaction usually goes to completion
- However, in a neutral solution the reduction is limited to the +4 oxidation state for the manganese
MnO4- (aq) + 2H2O (l) + 3e- ⇌ MnO2 (s) + 4OH- (aq) Eꝋ = +0.59 V
- Notice that the value of Eꝋ has changed as a result of changing the pH of the solution
Changing the ligand
- Changing the ligand also influences the redox potential
- If you compare the aqueous nickel(II) ion with the hexaamminenickel(II) ion, the Eꝋ becomes more negative when ammonia ligands replace water ligands
[Ni(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + 2e- ⇌ Ni(s) + 6H2O (l) Eꝋ = -0.26
[Ni(NH3)6]2+ (aq) + 2e− ⇌ Ni(s) + 6NH3 (aq) Eꝋ = -0.49
- Ammonia is a stronger ligand than water meaning that it binds better to the nickel(II) ion
- The position of the second equilibrium is slightly more to the left than the first one (hence the more negative Eꝋ value)
Oxidation states of Vanadium
- The variation in oxidation states of transition metal ions is illustrated by the reaction of zinc with ammonium vanadate(V) (also known as ammonium metavanadate) under acidic conditions
- Vanadium had four common oxidation states, from +2 to +5
- Zinc is a reducing agent that is capable to reducing vanadium(V) to vanadium(II) in a sequence of steps accompanied by vibrant colour changes
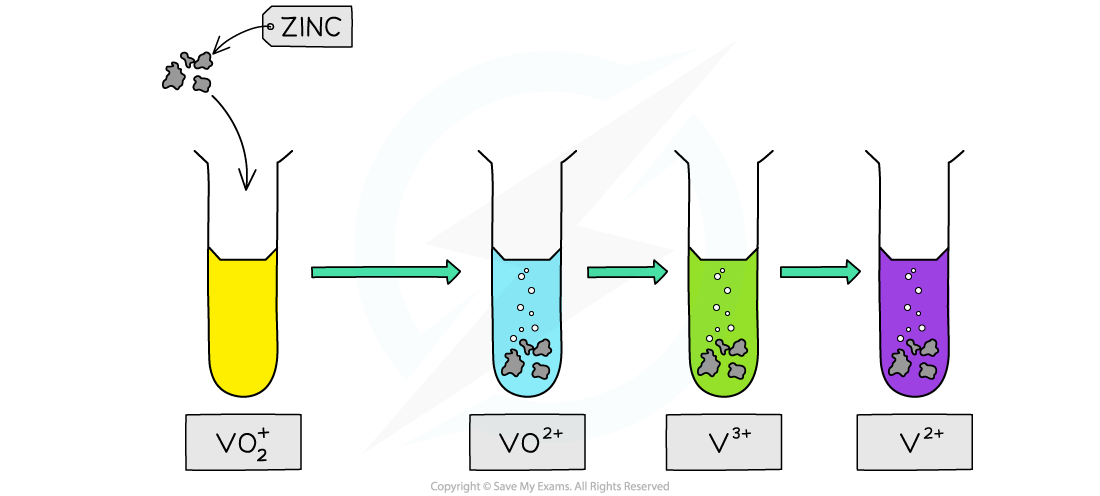
The reducing of vanadate(V) ions by zinc in acidic conditions is one of the most colourful reactions in chemistry
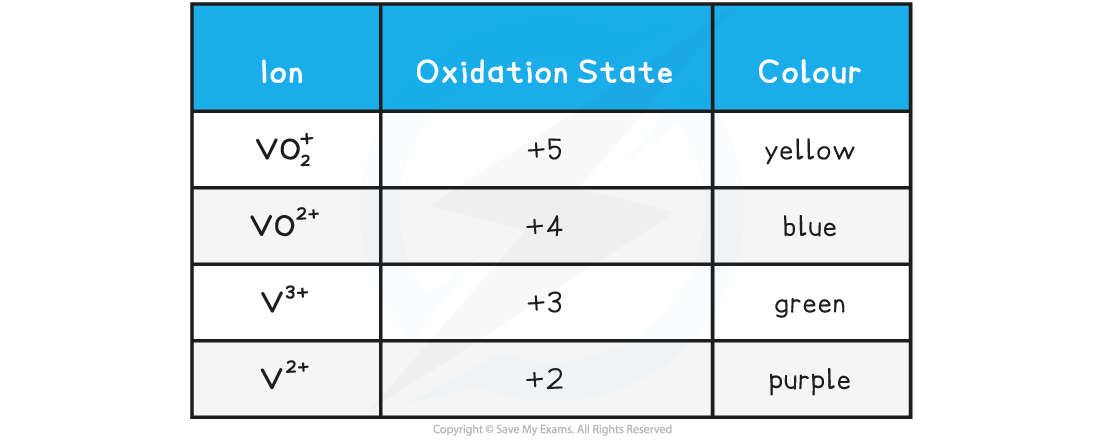
The colours of the different ions of vanadium are:
Vanadium ions and oxidation states table
- The first step in the reduction
2VO2+ (aq) + 4H+(aq) + Zn(s) → 2VO2+ (aq) + 2H2O(l) + Zn2+ (aq)
- The second step:
2VO2+ (aq) + 4H+(aq) + Zn(s) → 2V3+ (aq) + 2H2O(l) + Zn2+ (aq)
- The third step:
2V3+ (aq) + Zn(s) → 2V2+ (aq) + Zn2+ (aq)
- By carefully selecting suitable reducing agents you can stop the reduction of vanadium(V) at different states
Worked Example
Use the table of redox potentials to deduce the final oxidation state when a) tin and b) thiosulfate ions are used to reduce vanadium(V).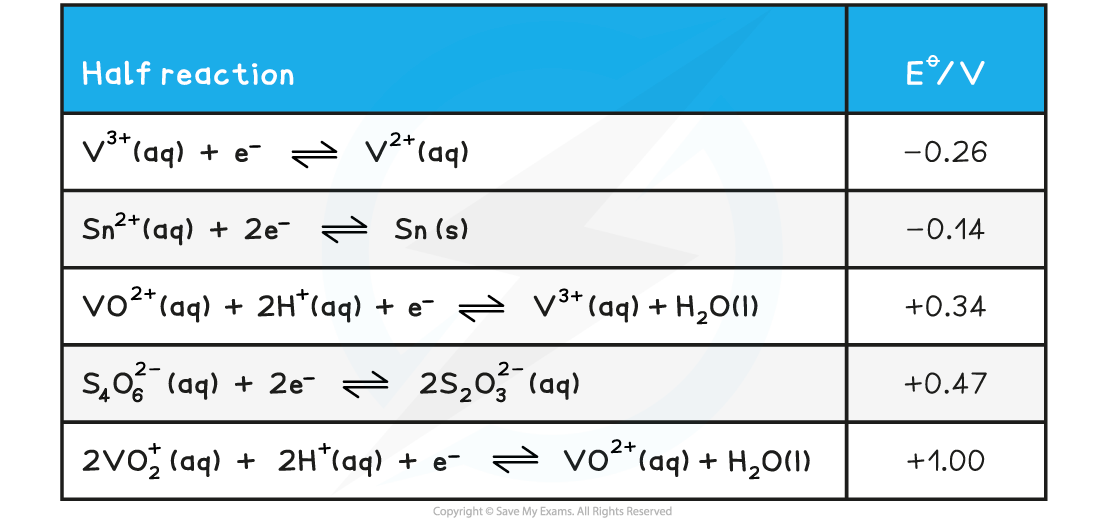
Answer
a) The reaction with tin:
-
- Vanadium(V) is present as the ion VO2+
- For a feasible reaction to take place Eꝋcell (or the emf) must be positive
- To act as a reducing agent tin, Sn , must provide electrons and the half equation will go backwards
2Sn ⇌ Sn2+ + 2e-
-
- For this to be the case the tin half reaction potential must be more negative than the reaction containing the vanadium species
- Only a reaction from vanadium(V) to vanadium(III) will give a positive emf
4VO2+ + 4H+ + Sn ⇌ 2VO2+ + 2H2O + Sn2+ Eꝋcell = 1.00-(-0.14) = +1.14 V
2VO2+ + 4H+ + Sn ⇌ 2V3+ + 2H2O + Sn2+ Eꝋcell = 0.34-(-0.14) = +0.48 V
2V3+ + Sn ⇌ 2V2+ + Sn2+ Eꝋcell = -0.26-(-0.14) = -0.12 V
Therefore the final oxidation state is +3 (as the final Eꝋcell is -0.12 V which is negative meaning this reaction is not feasible)
b) The reaction with thiosulfate ions
-
- To act as a reducing agent thiosulfate ions, S2O32- , must provide electrons and the half equation will go backwards
2S2O32- ⇌ S4O62- (aq) + 2e-
-
- For this to be the case the thiosulfate half reaction potential must be more negative than the reaction containing the vanadium species
- Only a reaction from vanadium(V) to vanadium(IV) will give a positive emf
4VO2+ + 4H+ + 2S2O32- ⇌ 2VO2+ + 2H2O + S4O62- Eꝋcell = 1.00-0.47 = +0.53 V
2VO2+ + 4H+ + 2S2O32- ⇌ 2V3+ + 2H2O + S4O62- Eꝋcell = 0.34-0.47 = -0.13 V
2V3+ + 2S2O32- ⇌ 2V2+ + S4O62- Eꝋcell = -0.26-0.47 = -0.73 V
The final oxidation state is therefore +4
Reduction of Tollens' Reagent
- Tollens' reagent contains the transition metal complex ion called diamminesilver(I), [Ag(NH3)2]+
- It is not stable in solution so it prepared when needed by adding sodium hydroxide solution to silver nitrate solution followed concentrated ammonia solution
- The reaction briefly produces a brown precipitate which quickly re-dissolves to form a colourless solution containing the diamminesilver(I) ion
- Tollens' reagent is used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones, but it can also be used to detect reducing sugars such as glucose
- A few drops of an aldehyde are warmed with Tollens' reagent in a water bath
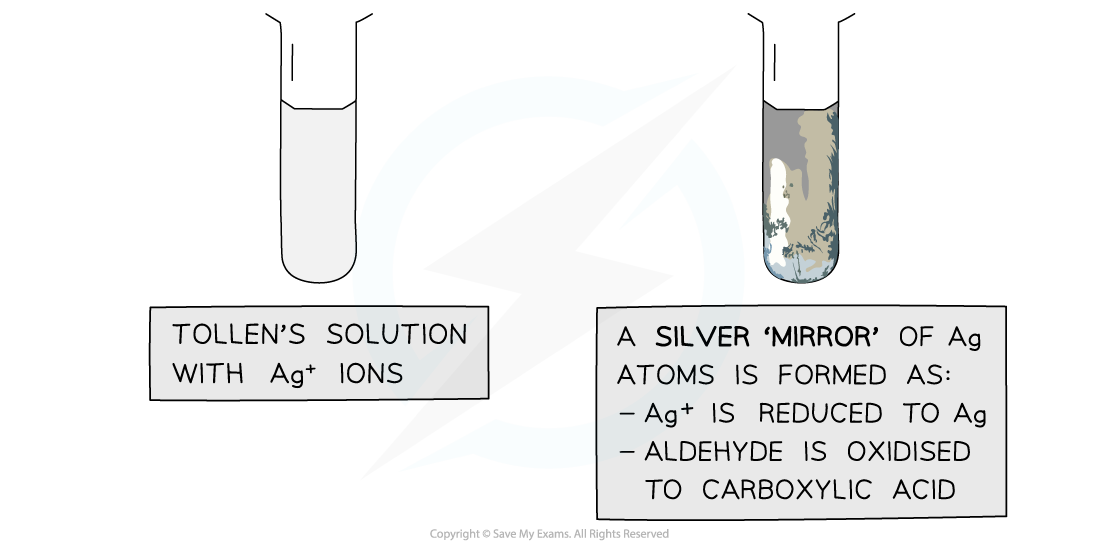
Testing an aldehyde with Tollens' reagent
- Although aldehydes and ketones are very similar chemically, aldehydes are reducing agents and can reduce the silver ion to silver metal
- The result is a striking silver mirror coating on the inside of the test tube, hence it is known as the 'silver mirror' test
- The equation for the reaction is
[Ag(NH3)2]+ +e-→ Ag (s) + 2NH3 (aq)
- Apart from its usefulness in chemistry this reaction was used in the past to create the coating on mirrors with silver
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









