- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记 6.2.2 Ligand Exchange
Ligand Exchange
- Ligand exchange (or ligand substitution) is when one ligand in a complex is replaced by another
- Ligand exchange forms a new complex that is more stable than the original one
- The ligands in the original complex can be partially or entirely substituted by others
- The complex ion can change its charge or remain the same depending on the ligand involved
- There are no changes in coordination number, or the geometry of the complex, if the ligands are of a similar size
- But, if the ligands are of a different size, for example water ligands and chloride ligands, then a change in coordination number and the geometry of the complex will occur
Complete substitution without change in coordination number in cobalt(II) complexes
- The [Co(H2O)6]2+(aq) complex ion is pink in colour
- If excess concentrated ammonia solution is added to [Co(H2O)6]2+, a brown solution will be formed
- Complete ligand substitution of the water ligands by ammonia ligands has occurred
[Co(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + 6NH3 (aq) → [Co(NH3)6 ]2+ (s) + 6H2O (l)
pink solution brown solution
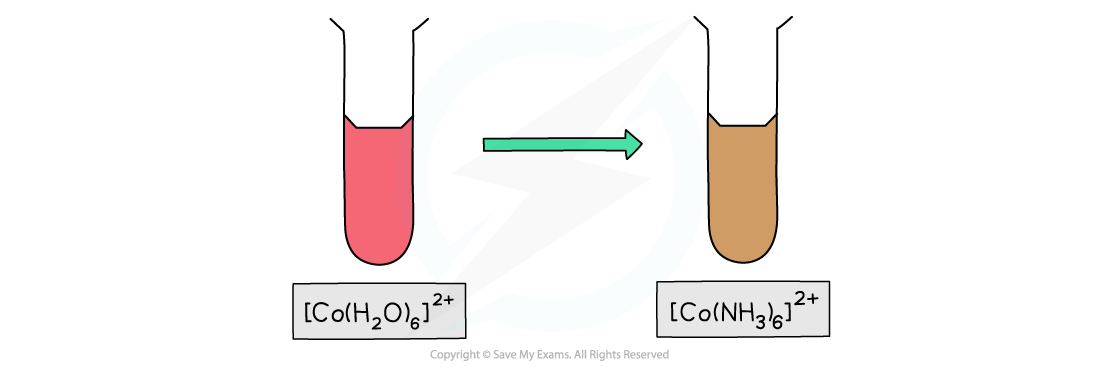
Aqueous cobalt(II) changes to a brown solution on addition of excess ammonia solution
- The ammonia ligands make the cobalt(II) ion so unstable that it readily gets oxidised in air to cobalt(III), [Co(NH3)6]3+
- Upon dropwise addition of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution to [Co(H2O)6]2+(aq), a blue precipitate is formed
- Partial ligand substitution of two water ligands by two hydroxide (OH-) ligands has occurred
[Co(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) → Co(OH)2(H2O)4 (s) + 2H2O (l)
pink solution blue precipitate
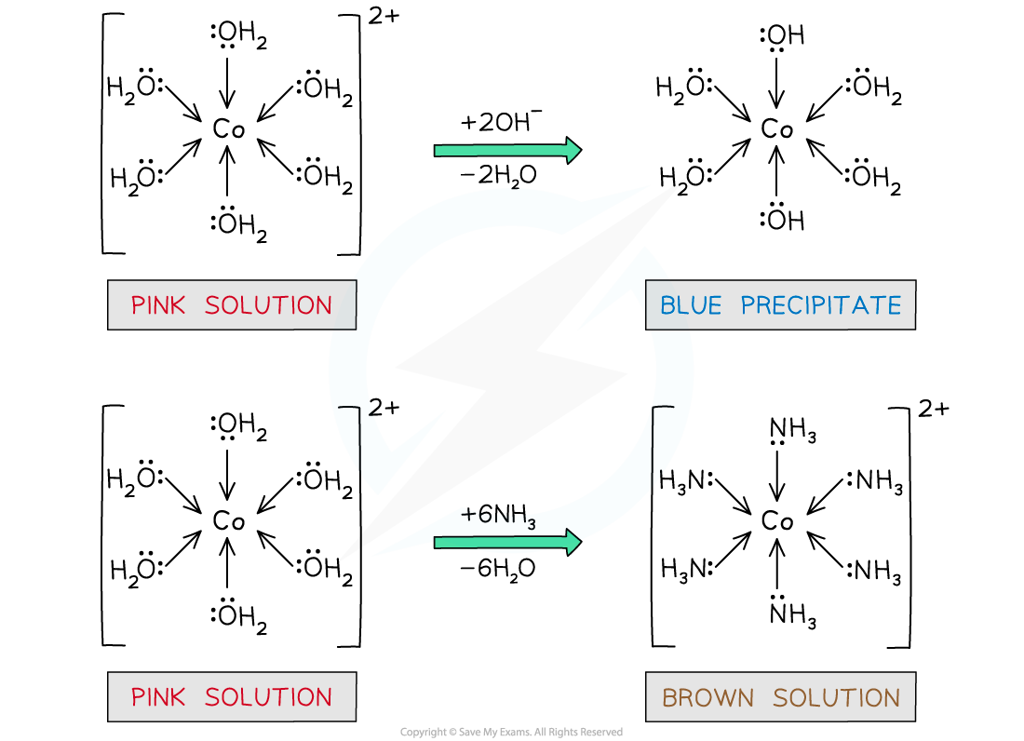
Water ligands are exchanged by hydroxide and ammonia ligands in the cobalt(II) complex
Incomplete Ligand Substitution
- Ligand substitution maybe incomplete if the energetics of the reaction and stability of the product are not favourable
- Copper(II)ions illustrate this behaviour with ammonia
- Different sized ligands can also lead to incomplete substitution
Incomplete substitution in copper(II) complexes
- When a transition element ion is in solution, the most common arrangement is a hexaaqua complex ion (i.e. it has six water ligands attached to it)
- For example, Cu2+(aq) is [Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq)
- The [Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq) complex ion is pale blue in colour
- Upon dropwise addition of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution, a light blue precipitate is formed
- Partial ligand substitution of two water ligands by two hydroxide ligands has occurred
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) → Cu(OH)2(H2O)4 (s) + 2H2O (l)
blue solution blue precipitate
- Upon addition of excess concentrated ammonia (NH3) solution, the pale blue precipitate dissolves to form a deep blue solution
- Again, partial ligand substitution has occurred
Cu(OH)2(H2O)4 (s) + 4NH3 (aq) → [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2 ]2+ (aq) + 2H2O (l) + 2OH- (aq)
light blue precipitate deep blue solution
- If you were to add concentrated ammonia (NH3) solution dropwise to the [Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq), rather than sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution, the same light blue precipitate would form
- Again, the pale blue precipitate will dissolve to form a deep blue solution, if excess ammonia solution is then added
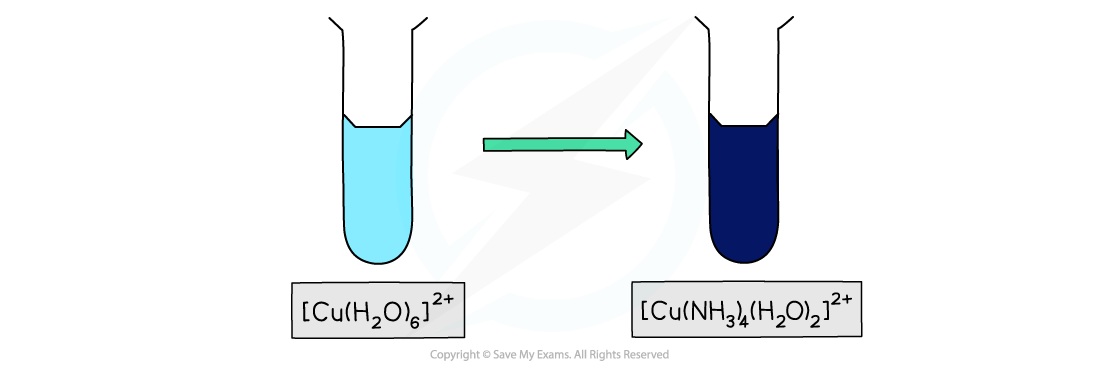
Addition of excess aqueous ammonia to the aqueous copper(II) ion results in a gorgeous deep blue complex
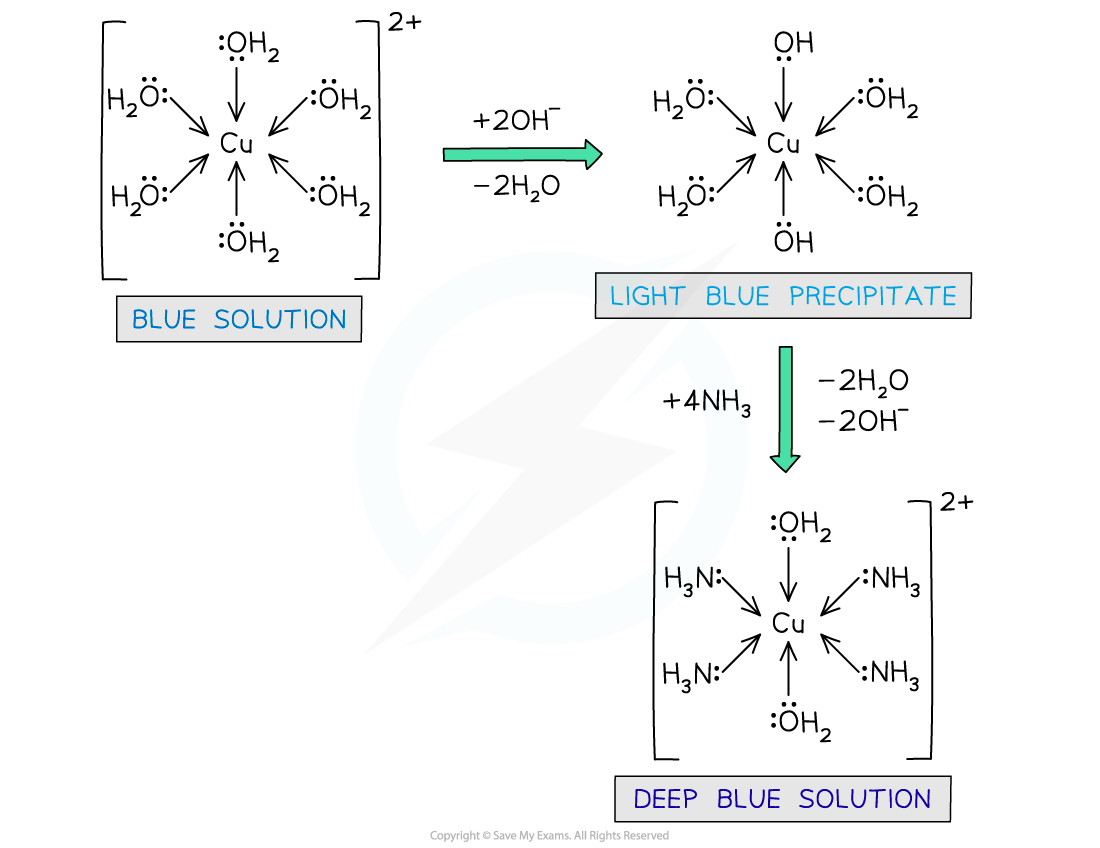
Water ligands are exchanged by hydroxide and ammonia ligands in the copper(II) complex
Change in co-ordination number
- The water ligands in [Cu(H2O)6]2+ can also be substituted by chloride ligands, upon addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- The complete substitution of the water ligands causes the blue solution to turn yellow
[Cu(H2O)6 ]2+ (aq) + 4Cl- (aq) → [CuCl4 ]2- (aq) + 6H2O (l)
light blue solution yellow solution
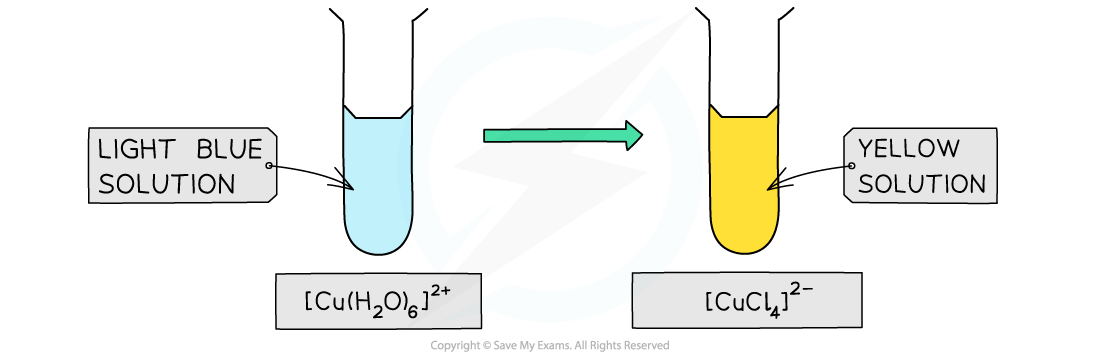
The colour changes from light blue to a yellow-green when copper(II) is treated with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The green appearance is due to the presence of unreacted aqueous copper(II) ions
- The coordination number has changed from 6 to 4, because the chloride ligands are larger than the water ligands, so only 4 will fit around the central metal ion
- This is a reversible reaction, and some of the [Cu(H2O)6]2+ complex ion will still be present in the solution
- The mixture of blue and yellow solutions in the reaction mixture will give it a green colour
- Adding water to the solution will cause the chloride ligands to be displaced by the water molecules, and the [Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq) ion and blue solution will return
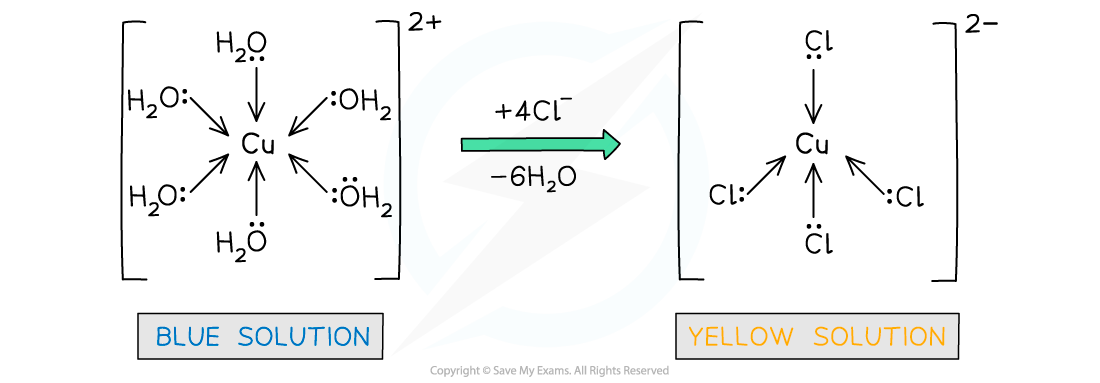
Water ligands are exchanged by chloride ligands in the copper(II) complex
Incomplete substitution in cobalt(II) complexes
- The water ligands in [Co[H2O)6]2+ can also be substituted by chloride ligands, upon addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid
- The complete substitution of the water ligands causes the pink solution to turn blue
[Co(H2O)6 ]2+ (aq) + 4Cl- (aq) → [CoCl4 ]2- (aq) + 6H2O (l)
pink solution blue solution
- Like with [Cu(H2O)6]2+ above, the coordination number has changed from 6 to 4, because the chloride ligands are larger than the water ligands, so only 4 will fit around the central metal ion
- Adding water to the solution will cause the chloride ligands to be displaced by the water molecules, and the [Co(H2O)6]2+ (aq) ion and pink solution will return
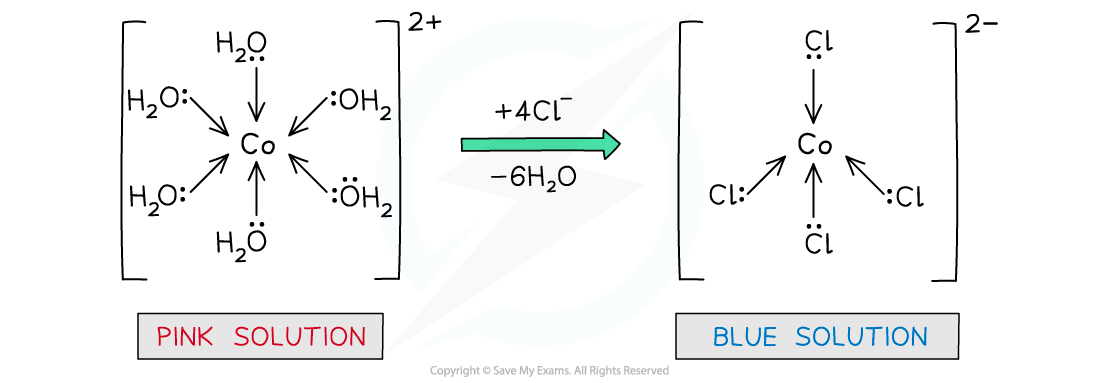
Water ligands are exchanged by chloride ligands in the cobalt(II) complex
The Haem Complex
- Haemoglobin is one of nature's complexes using a transition metal ion
- The haem molecule is a complex with iron(II) at its centre
- Oxygen atoms form a dative covalent bond with the Fe(II) which enables oxygen molecules to be transported around the body in the blood
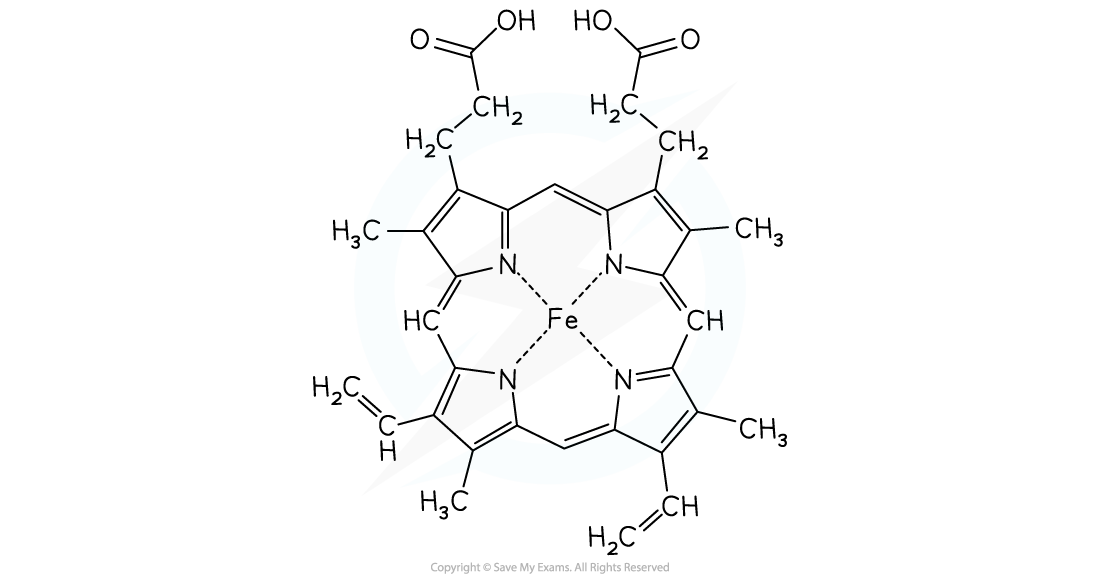
The haem molecule with iron(II) at its centre
- Oxygen molecules are not very good ligands and bond weakly to the iron(II)
- The weak bonds allows them to break off easily and be transported into cells
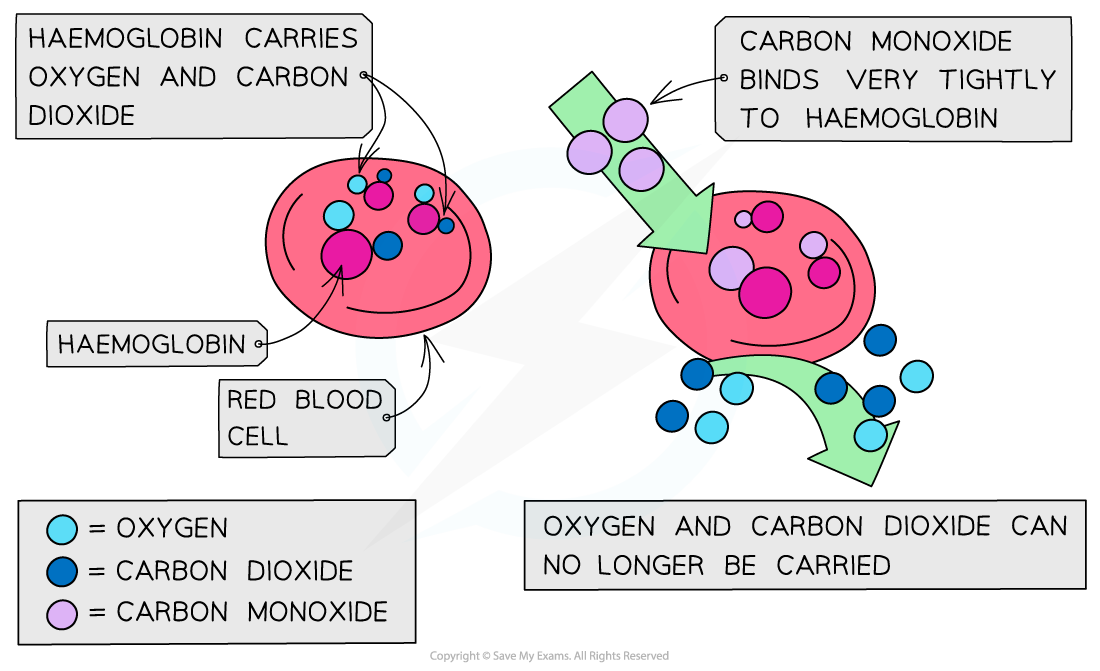
- Carbon monoxide is toxic because it is a better ligand than oxygen and binds strongly and irreversibly to the iron(II) preventing oxygen from being carried to the cells
- If oxygen attached to the haemoglobin (oxyhaemoglobin) is replaced by carbon monoxide (carboxyhaemoglobin), a darker red colour is produced in the haem complex
- A sign of carbon monoxide poisoning
- The condition anaemia occurs when a person does not have enough haemoglobin in their blood due to a loss of blood or deficiency in iron
- Deficiency in iron can be restored by taking iron sulfate tables in the diet
The Chelate Effect
- The replacement of monodentate ligands with bidentate and multidentate ligands in complex ions is called the chelate effect
- It is an energetically favourable reaction, meaning that ΔGꝋ is negative
- The driving force behind the reaction is entropy
- The Gibbs equation reminds us of the link between enthalpy and entropy:
ΔGꝋ = ΔHreactionꝋ – TΔSsystemꝋ
- Reactions in solution between aqueous ions usually come with relatively small enthalpy changes
- However, the entropy changes are always positive in chelation because the reactions produce a net increase in the number of particles
- A small enthalpy change and relative large positive entropy change generally ensures that the overall free energy change is negative
- For example, when EDTA chelates with aqueous cobalt(II) two reactants becomes seven product species
[Co(H2O)6 ]2+ (aq) + EDTA4- (aq) → [CoEDTA]2- (aq) + 6H2O(l)
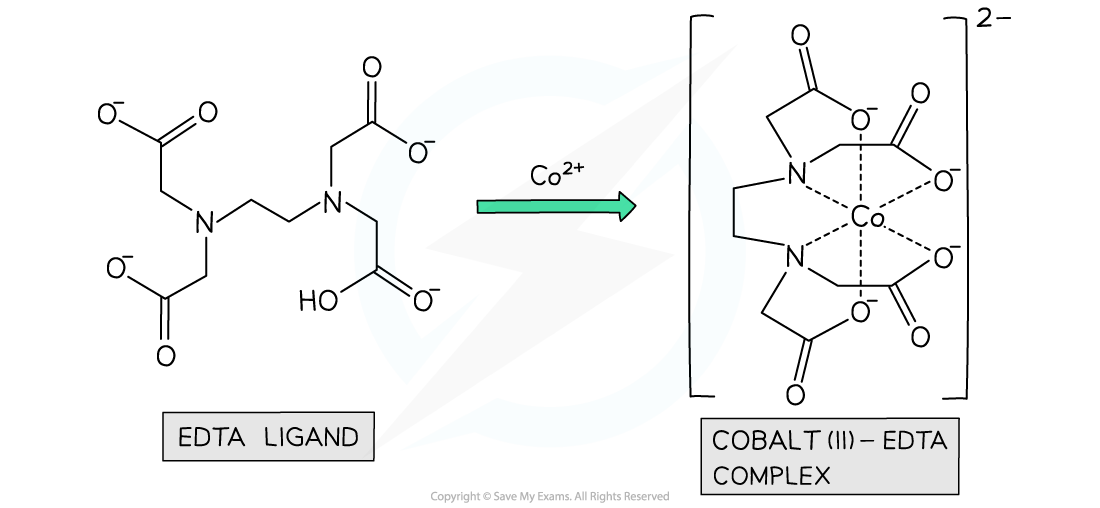
The ligand EDTA readily chelates with aqueous transition metal ions in an energetically favourable reaction
Exam Tip
Make sure you can explain the chelate effect in terms of the balance between entropy and enthalpy changes.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









