- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记5.6.2 pKₐ
pKₐ
- The range of values of Ka is very large and for weak acids, the values themselves are very small numbers
Table of Ka values
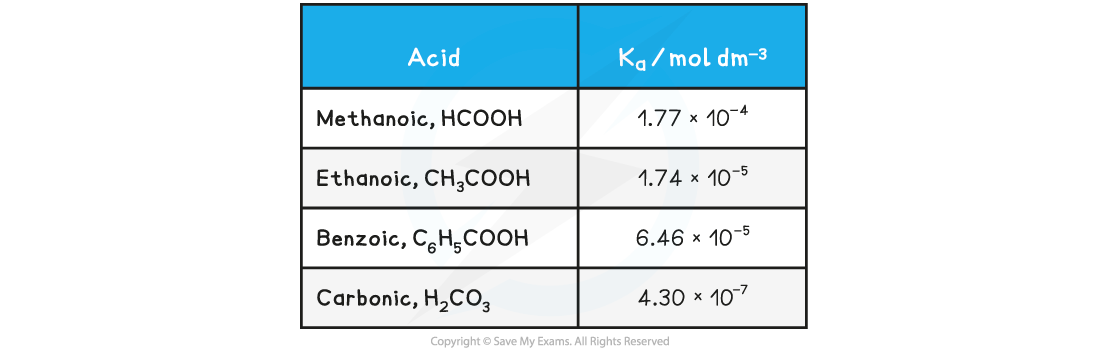
- For this reason it is easier to work with another term called pKa
- The pKa is the negative log of the Ka value, so the concept is analogous to converting [H+] into pH values
pKa = -logKa
- Looking at the pKa values for the same acids:
Table of pKa values
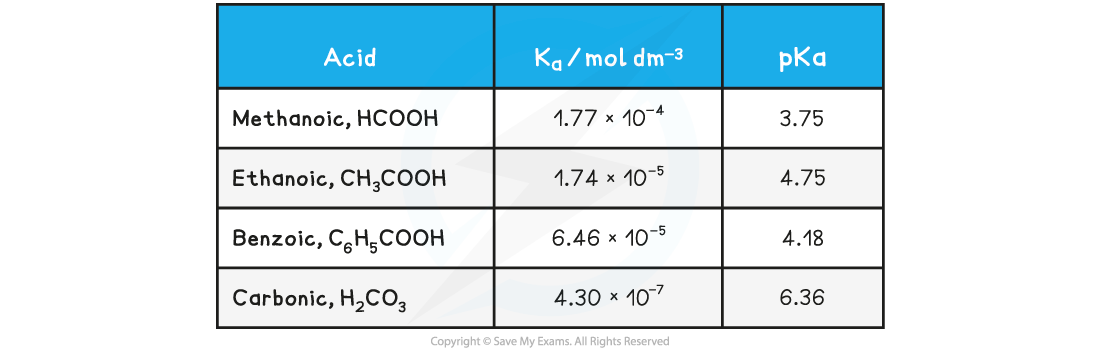
- The range of pKa values for most weak acids lies between 3 and 7
Worked Example
Finding Ka and pKaAt 298 K, a solution of 0.100 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1.32 x 10-3 mol dm-3.Calculate the Ka & pKa of the acid.
Answer
Step 1: Write down the equation for the partial dissociation of ethanoic acid
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression to find Ka
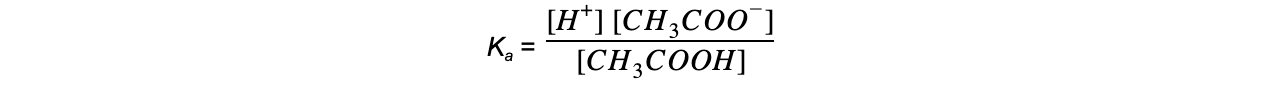
Step 3: Simplify the expression
The ratio of H+ to CH3COO- is 1:1
The concentration of H+ and CH3COO- is, therefore, the same
The equilibrium expression can be simplified to:
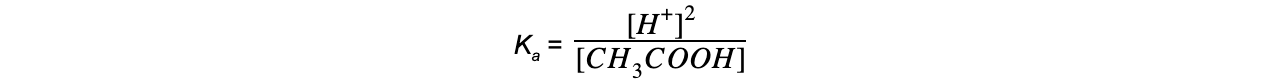
Step 4: Substitute the values into the expression to find Ka
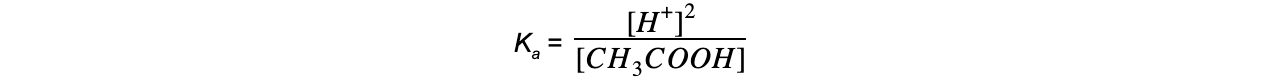
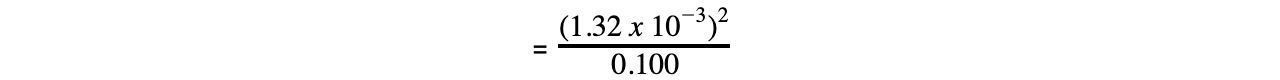
= 1.74 x 10-5
Step 5: Determine the units of Ka
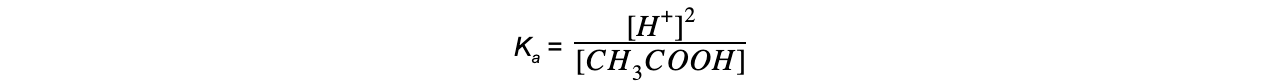
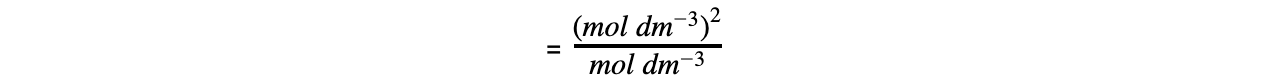
= mol dm-3
The value of Ka is therefore 1.74 x 10-5 mol dm-3
Step 6: Find pKa
pKa = - log10Ka
= - log10 (1.74 x 10-5)
= 4.76
Kₐ from pH
How are Ka values found?
- If we neutralise a weak acid with a strong base such sodium hydroxide the equation for the reaction is:
HA (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq) → A- (aq) + H2O (l)
- When half of the acid has been neutralised the concentration of [HA] is equal to the concentration of [A-]
- Since the acid is poorly dissociated it is assumed all the A- comes from the product rather than HA dissociating
- This simplifies the expression to

- In practice, to find Ka the pH of a weak acid is measured as it is neutralised by a strong base and a graph is plotted for pH versus volume of base added
- This type of graph is known as a pH titration curve
- A vertical tie-line is drawn to the curve at half the volume of base needed for neutralisation
- At this point pKa = pH, so by reading off the pH value from the y-axis, you find the Ka of the acid
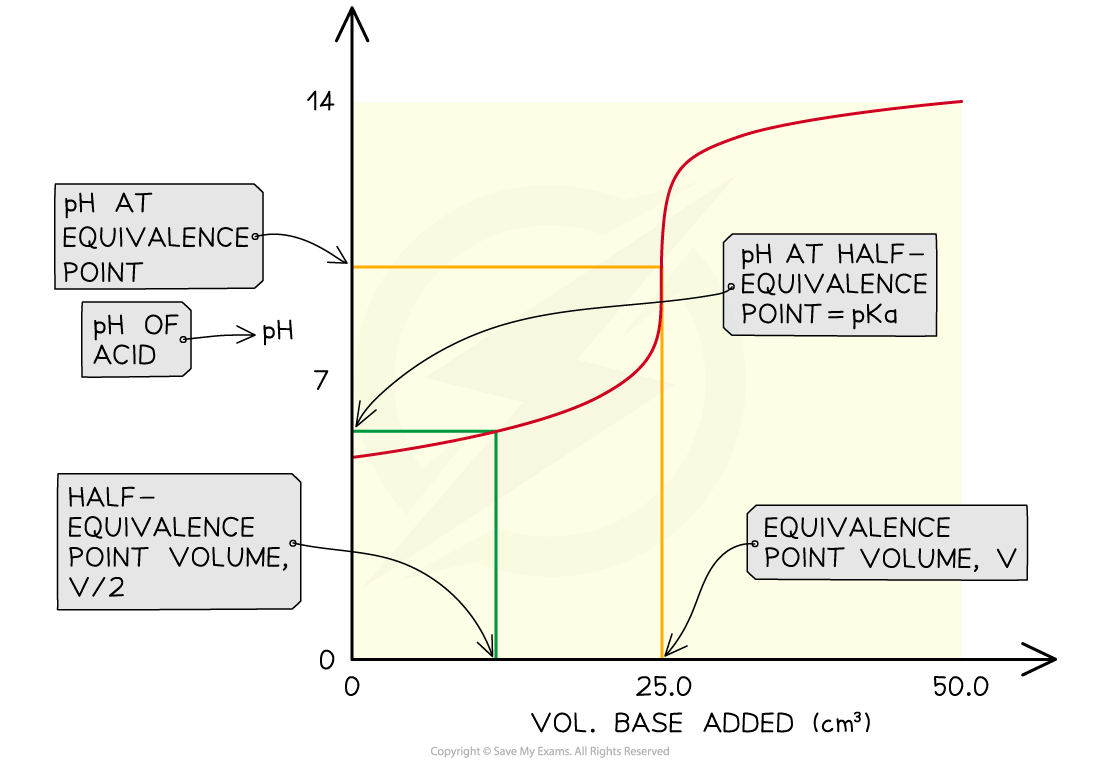
Finding the Ka of a weak acid from a pH titration curve
Exam Tip
You can regard the symbol p as meaning -log10 of a value. You don't need to include the 10 as 'log' means log base 10. If a natural logarithm (base e) is required it is given the symbol ln.Other uses of p include pOH and pKw . The latter gives a useful shortcut in problem solving:
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.00 x 10-14 mol2 dm-6 at 298 K-logKw = -log[H+] + (-log[OH-]) = -log(1.00 x 10-14)
pKw = pH + pOH = 14.00
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








