- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记5.2.8 Rate Determining Step
Rate Determining Step
Rate-determining step & intermediates
- A chemical reaction can only go as fast as the slowest part of the reaction
- So, the rate-determining step is the slowest step in the reaction
- If a reactant appears in the rate-determining step, then the concentration of that reactant will also appear in the rate equation
- For example, the rate equation for the reaction below is rate = k [CH3Br] [OH-]
CH3Br + OH- → CH3OH + Br-
-
- This suggests that both CH3Br and OH- take part in the slow rate-determining step
- This reaction is a bimolecular reaction
- Unimolecular: one species involved in the rate-determining step
- Bimolecular: two species involved in the rate-determining step
- The intermediate is derived from substances that react together to form it in the rate-determining step
- For example, for the reaction above the intermediate would consist of CH3Br and OH-

The intermediate is formed from the species that are involved in the rate-determining step (and thus appear in the rate equation)
Predicting the reaction mechanism
- The overall reaction equation and rate equation can be used to predict a possible reaction mechanism of a reaction
- This shows the individual reaction steps which are taking place
- For example, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) react to form nitrogen monoxide (NO) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
- The overall reaction equation is:
NO2 (g) + CO (g) → NO (g) + CO2 (g)
-
- The rate equation is:
Rate = k [NO2]2
- From the rate equation it can be concluded that the reaction is zero order with respect to CO (g) and second order with respect to NO2 (g)
- This means that there are two molecules of NO2 (g) involved in the rate-determining step and zero molecules of CO (g)
- A possible reaction mechanism could therefore be:
Step 1:
2NO2 (g) → NO (g) + NO3 (g) slow (rate-determining step)
Step 2:
NO3 (g) + CO (g) → NO2 (g) + CO2 (g) fast
Overall:
2NO2 (g) + NO3 (g) + CO (g) → NO (g) + NO3 (g) + NO2 (g) + CO2 (g)
= NO2 (g) + CO (g) → NO (g) + CO2 (g)
Predicting the reaction order & deducing the rate equation
- The order of a reactant and thus the rate equation can be deduced from a reaction mechanism if the rate-determining step is known
- For example, the reaction of nitrogen oxide (NO) with hydrogen (H2) to form nitrogen (N2) and water
2NO (g) + 2H2 (g) → N2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
- The reaction mechanism for this reaction is:
Step 1:
NO (g) + NO (g) → N2O2 (g) fast
Step 2:
N2O2 (g) + H2 (g) → H2O (l) + N2O (g) slow (rate-determining step)
Step 3:
N2O (g) + H2 (g) → N2 (g) + H2O (l) fast
- The second step in this reaction mechanism is the rate-determining step
- The rate-determining step consists of:
- N2O2 which is formed from the reaction of two NO molecules
- One H2 molecule
- The reaction is, therefore, second order with respect to NO and first order with respect to H2
- So, the rate equation becomes:
Rate = k [NO]2 [H2]
- The reaction is, therefore, third order overall
Identifying the rate-determining step
- The rate-determining step can be identified from a rate equation given that the reaction mechanism is known
- For example, propane (CH3CH2CH3) undergoes bromination under alkaline solutions
- The overall reaction is:
CH3CH2CH3 + Br2 + OH- → CH3CH2CH2Br + H2O + Br-
- The reaction mechanism is:

Reaction mechanism for the bromination of propane under alkaline conditions
- The rate equation is:
Rate = k [CH3CH2CH3] [OH-]
- From the rate equation, it can be deduced that only CH3CH2CH3 and OH- are involved in the rate-determining step and not bromine (Br2)
- CH3CH2CH3 and OH- are only involved in the first step of the reaction mechanism, therefore the rate-determining step is:
- CH3CH2CH3 + OH- → CH3CH2CH2- + H2O
Identifying intermediates & catalyst
- When a rate equation includes a species that is not part of the chemical reaction equation then this species is a catalyst
- For example, the halogenation of butanone under acidic conditions
- The reaction mechanism is:

- The reaction mechanism is:
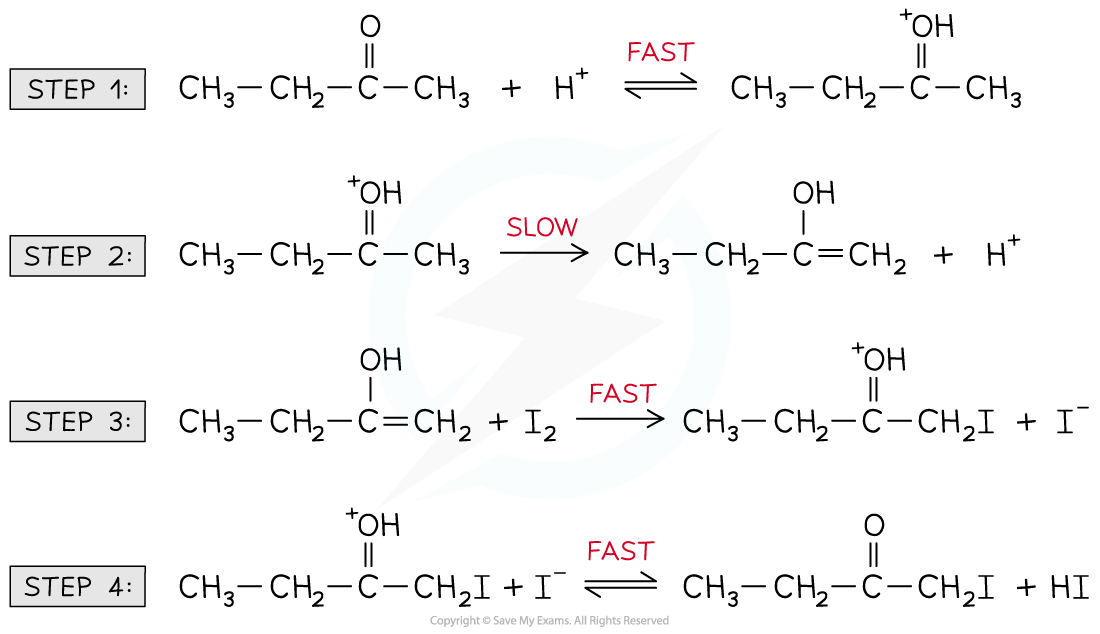
Reaction mechanism of the halogenation of butanone under acidic conditions
- The rate equation is:
Rate = k [CH3CH2COCH3] [H+]
- The H+ is not a reactant in the chemical reaction equation but does appear in the rate equation
- H+ must, therefore, be a catalyst
- Furthermore, the rate equation suggest that CH3CH2COCH3 and H+ must be involved in the rate-determining (slowest) step
- The CH3CH2COCH3 and H+ appear in the rate-determining step in the form of an intermediate (which is a combination of the two species)

Intermediate is formed in the rate-determining step from the reaction of CH3CH2COCH3 and H+
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








