- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记3.4.2 Isomerism in Alkenes
Isomerism in Alkenes
Unsaturated compounds
- In unsaturated compounds, the groups attached to the C=C carbons remain fixed in their position
- This is because free rotation of the bonds about the C=C bond is not possible due to the presence of a π bond
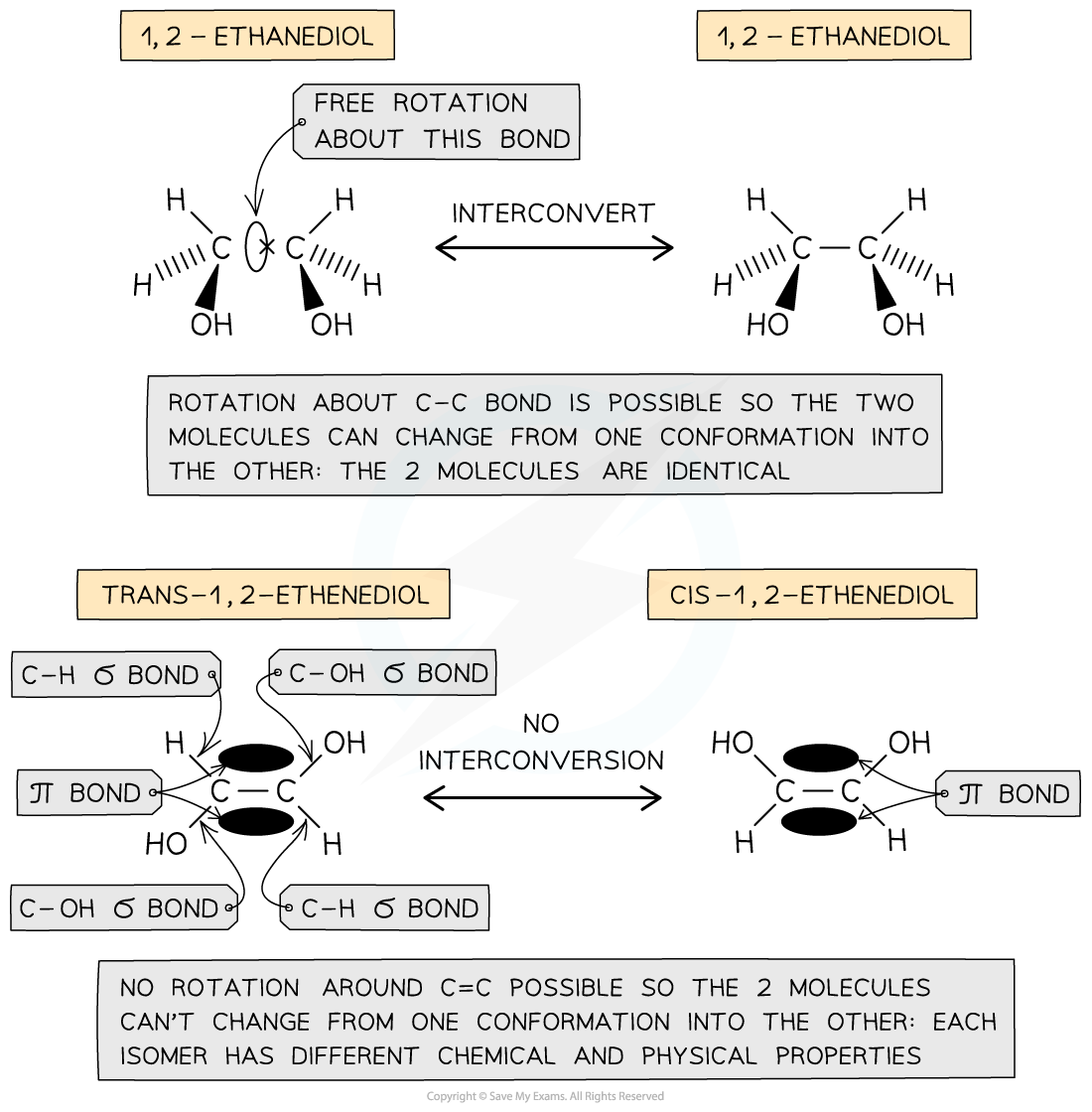
The presence of a π bond in unsaturated compounds restricts rotation about the C=C bond forcing the groups to remain fixed in their position and giving rise to the formation of geometrical isomers
Exam Tip
Geometrical isomerism is also possible in cyclic compounds because there is limited rotation about C-C single bonds that make up the rings. Therefore, the substitutions in cyclic compounds are fixed in their position (to stay either above or below the ring of carbon atoms).
Stability of Cations & Markovnikov's Rule
- Carbocations are positively charged carbon atoms with only three covalent bonds instead of four
- There are three types of carbocations: primary, secondary and tertiary
Inductive effect
- The alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon atoms are ‘electron donating groups’
- This is also known as the inductive effect of alkyl groups
- The inductive effect is illustrated by the use of arrowheads on the bonds
- The alkyl groups push electrons away from themselves towards the positively charged carbon
- This causes the carbocation to become less positively charged
- As a result of this, the charge is spread around the carbocation which makes it energetically more stable
- This means that tertiary carbocations are the most stable as they have three electron-donating alkyl groups which energetically stabilise the carbocation
- Due to the positive charge on the carbon atom, carbocations are electron-loving species (electrophiles)
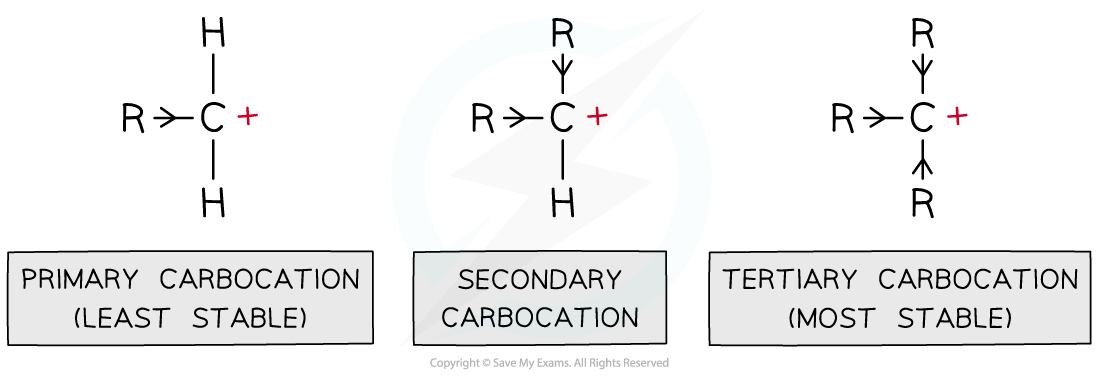
Alkyl groups push electron density towards the carbocation making it energetically more stable; the more alkyl groups the carbocation is bonded to, the more stabilised it is
Markovnikov’s rule
- In addition reactions, an electrophile reacts with the double bond of alkenes
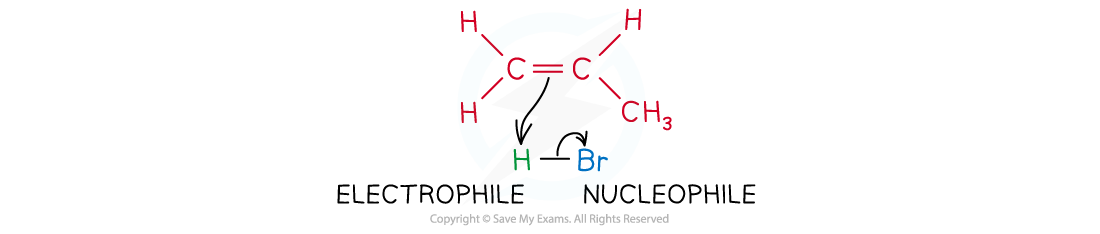
The electrophile reacts with the electron-rich C-C double bond
- The electrophile will add to the carbon to give the most stable carbocation

The most stable carbocation is the major product of the nucleophilic attack on the C-C double bond
- Therefore, the nucleophile will bond to the C-C carbon atom with the highest number of alkyl groups bonded to it
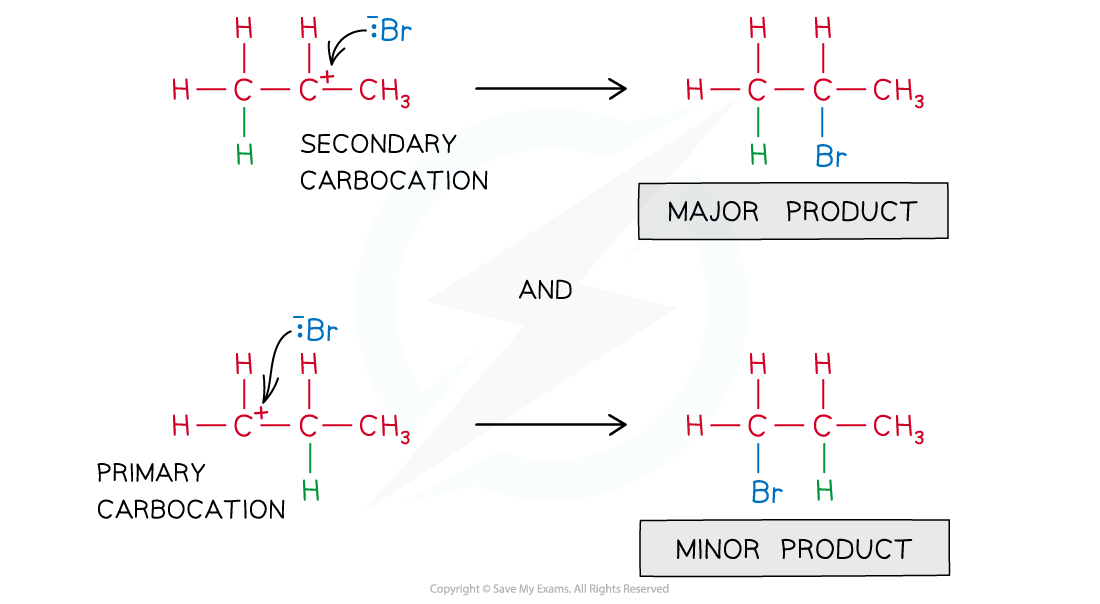
The nucleophile ends up to the most substituted C-C carbon atom
- This is also known as the Markovnikov’s rule which predicts the outcome of addition reactions and states that:
- In an addition reaction of a hydrogen halide (HX) to an alkene, the halogen ends up bonded to the most substituted carbon atom.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









