- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.7.4 Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate
Temperature & Rate of Reaction
Temperature & Rate of Reaction
- Increasing the temperature of the reaction mixture increases the rate of reaction in the following two ways:
- At higher temperatures, the particles are moving faster, so collide more frequently. A higher number of collisions in total mean a higher number of successful collisions
- At higher temperatures, a higher proportion of the molecules have the activation energy or more. This means that a higher proportion of collisions are successful
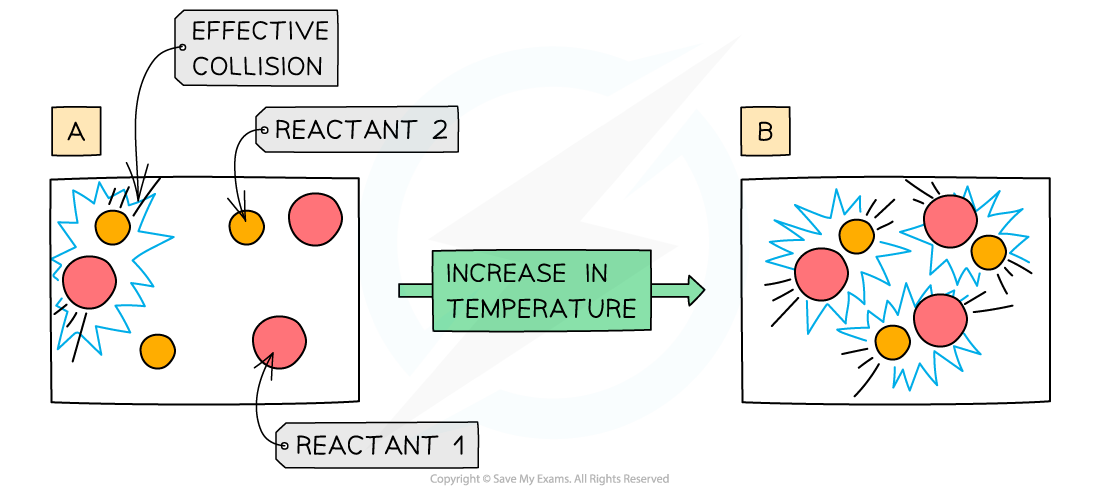
An increase in temperature causes an increase in the kinetic energy of the particles. The number of collisions increases and the proportion of successful collisions increases
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








