- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.7.2 Measuring Rates of Reaction
Measuring the Rate of a Reaction
Reaction rate
- The rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place and has units mol dm-3 s-1 or mol dm-3 min-1
- The rate of a reaction can be calculated using:

Worked Example
Calculating the rate of reactionCalculate the rate of reaction, in mol dm-3 s-1, if 0.0440 g of ethyl ethanoate, CH3COOC2H5, (M = 88.0 g mol-1) is formed in 1.00 min from a reaction mixture of total volume 400 cm3
Answer
Step 1: Calculate the amount of ethyl ethanoate in moles:
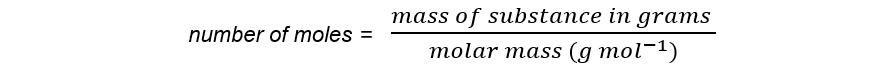
amount of ethyl ethanoate = 0.0440 g ÷ 88.0 g mol-1
= 0.0005 mol
Step 2: Calculate the concentration of the product:
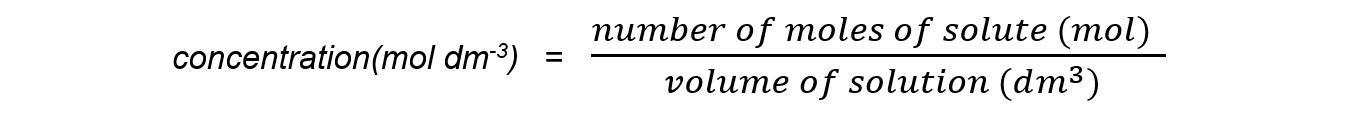
concentration of ethyl ethanoate = 0.0005 mol ÷ 0.400 dm3
= 0.00125 mol dm-3
Step 3: Calculate the rate:
rate of reaction = 0.00125 mol dm-3÷ 60 s
rate of reaction = 2.08 x 10-5 mol dm-3 s-1
Measuring a rate from a graph
- During a reaction, the reactants are used up and changed into products
- This means that as the reaction proceeds, the concentration of the reactants is decreasing and the concentration of the products is increasing
- Because of this, the rate of the reaction is not the same throughout the reaction but changes
- The rate of reaction during the reaction can be calculated from a concentration-time graph
- The isomerisation of cyclopropane to propene is used as an example:

Isomerisation of cyclopropane
- The concentrations of reactant (cyclopropane) and product (propene) over time can be measured by experiment
Concentrations of Cyclopropane & Propene Table
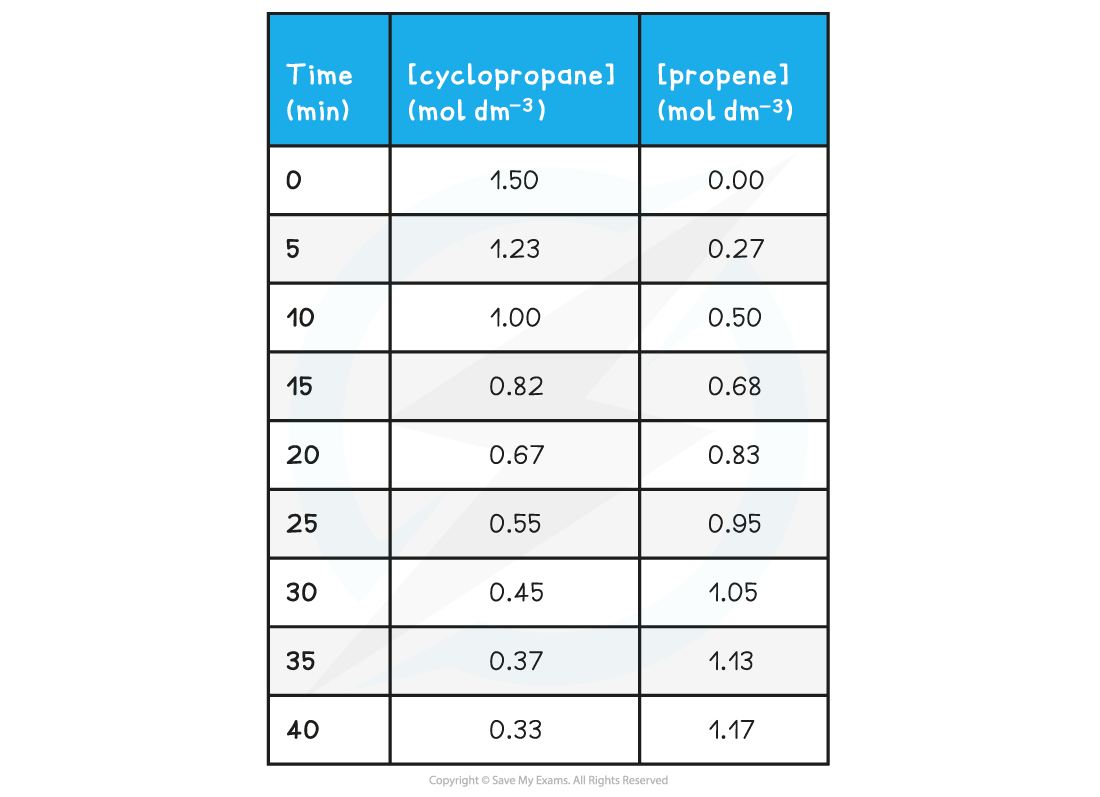
- When taking the measurements, the temperature should be kept constant as a change in temperature will change the rate of reaction
- A concentration-time graph for the concentration of propene as well as cyclopropane can be obtained from the above results
- As an example, the concentration-time graph for propene is shown below:
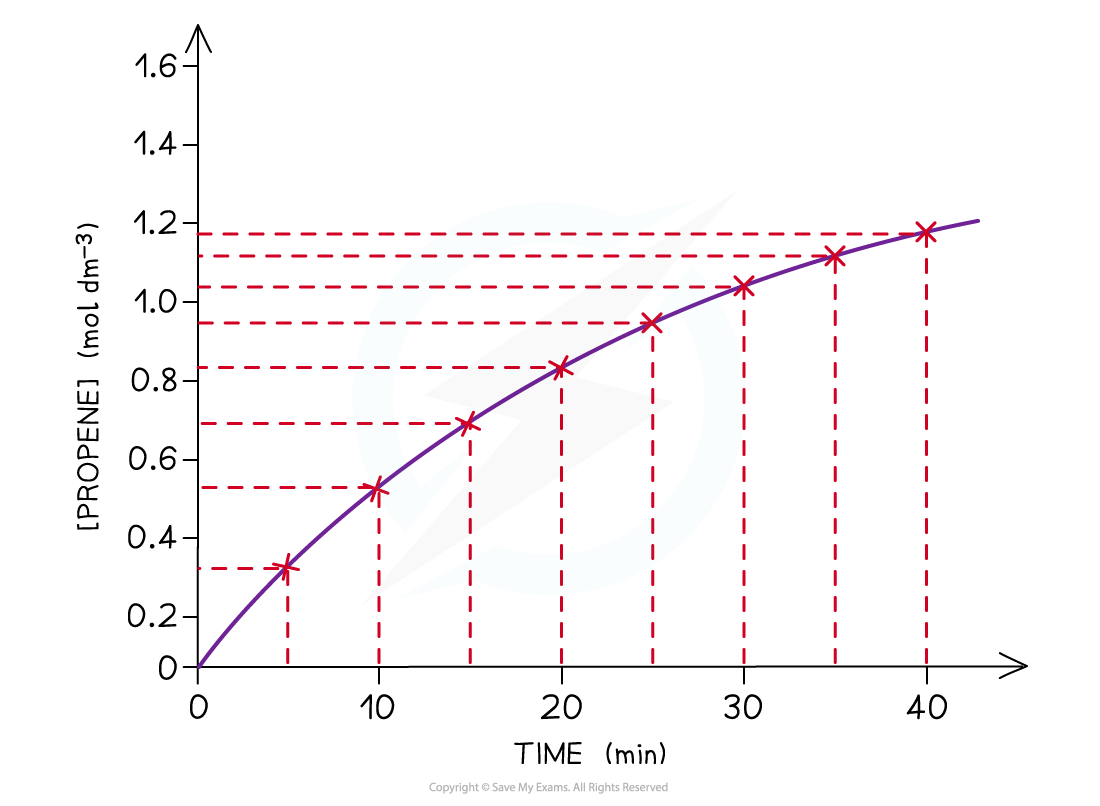
The graph shows that the concentration of propene increases with time
Calculating the rate at the start of a reaction
- At the start of the reaction, the concentration-time curve looks almost linear
- The rate at this point can therefore be found by treating the curve as a linear line and by using:

- Using the graph, the average rate of the reaction over the first 5 minutes for propene is:
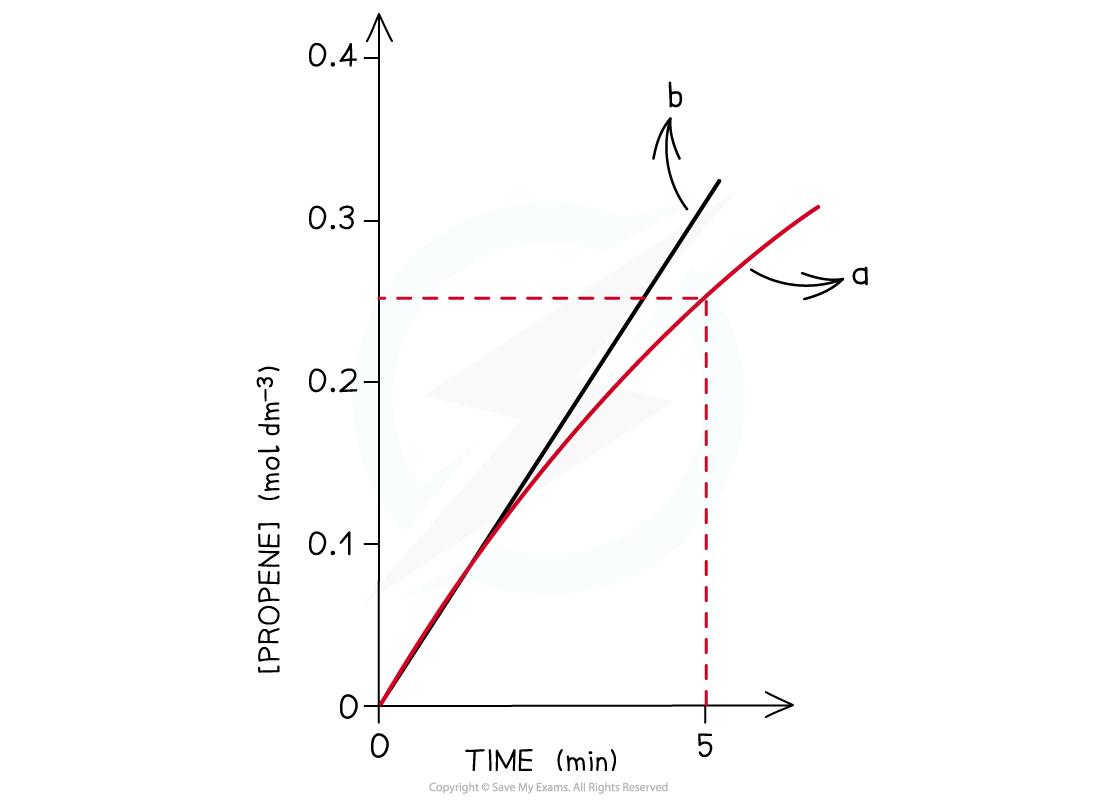
Line a shows the average rate over the first five minutes whereas line b shows the actual initial rate found by drawing a tangent at the start of the curve. The calculated rates are very similar for both methods
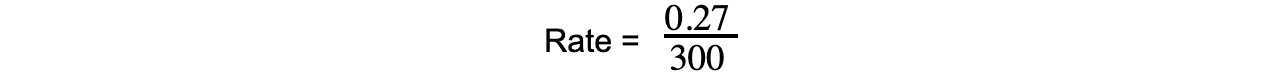
= 0.0009 mol dm-3 s-1
Calculating the rate as the reaction proceeds
- The curve becomes shallower with time which means that the rate decreases with time
- The rate of reaction can be calculated by taking short time intervalsEg. you can calculate the rate of reaction from 15 to 20 mins during which the concentration of propene increases from 0.68 to 0.83 mol dm-3:
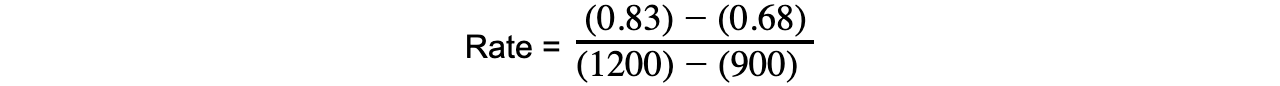
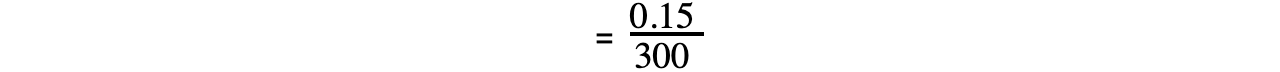
= 0.0005 mol dm-3 s-1
- The smaller the time intervals, the more accurate the reaction rate value is
- It is even more accurate to find the rate of reaction at different concentrations of reactant or product at particular time points
- This can be done by drawing tangents at several points on the graph
- As an example, the rates of reaction at different concentrations of cyclopropane are calculated by drawing the appropriate tangents:
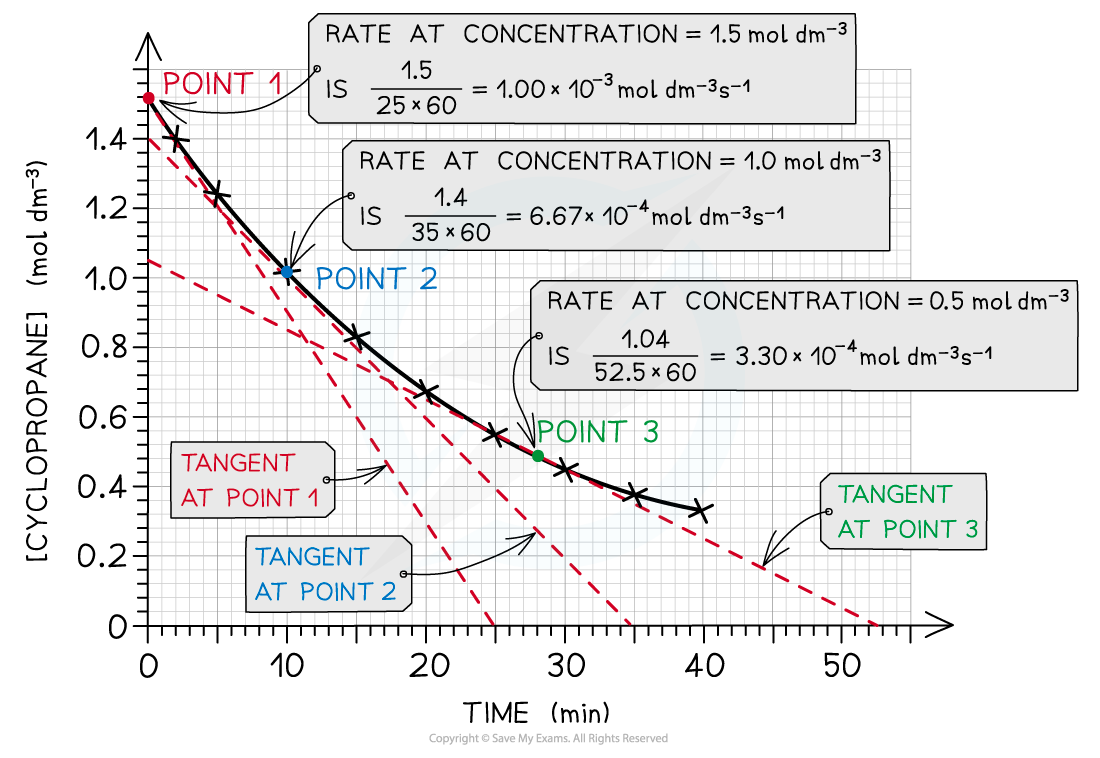
The rate of reaction at three different concentrations of cyclopropane is calculated by drawing tangents at those points in the graph
Rate-concentration graph
- The calculated rates can then be summarised in a table to show how the rate of reaction changes with changing concentration of the reactants or products
Change in rate with Increasing Concentration of Cyclopropane
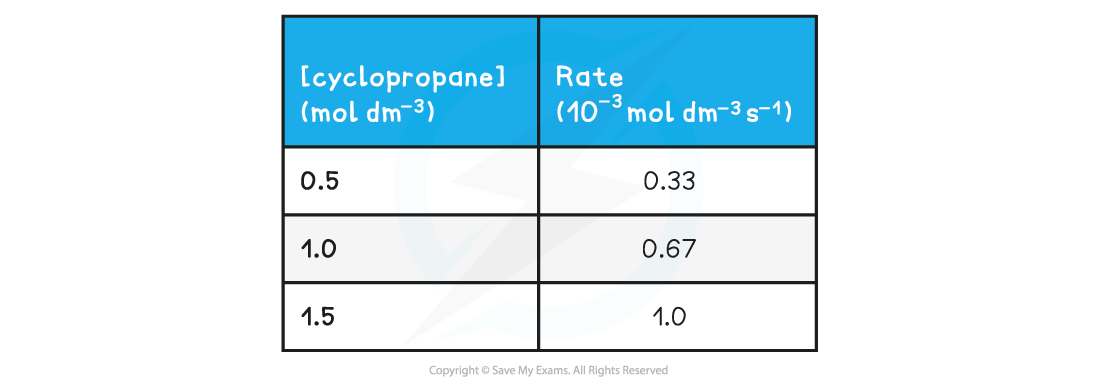
- This data can then be used to plot a rate-concentration graph
- The graph shows that the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of cyclopropane
- If you double the concentration of cyclopropane the rate of reaction will double too
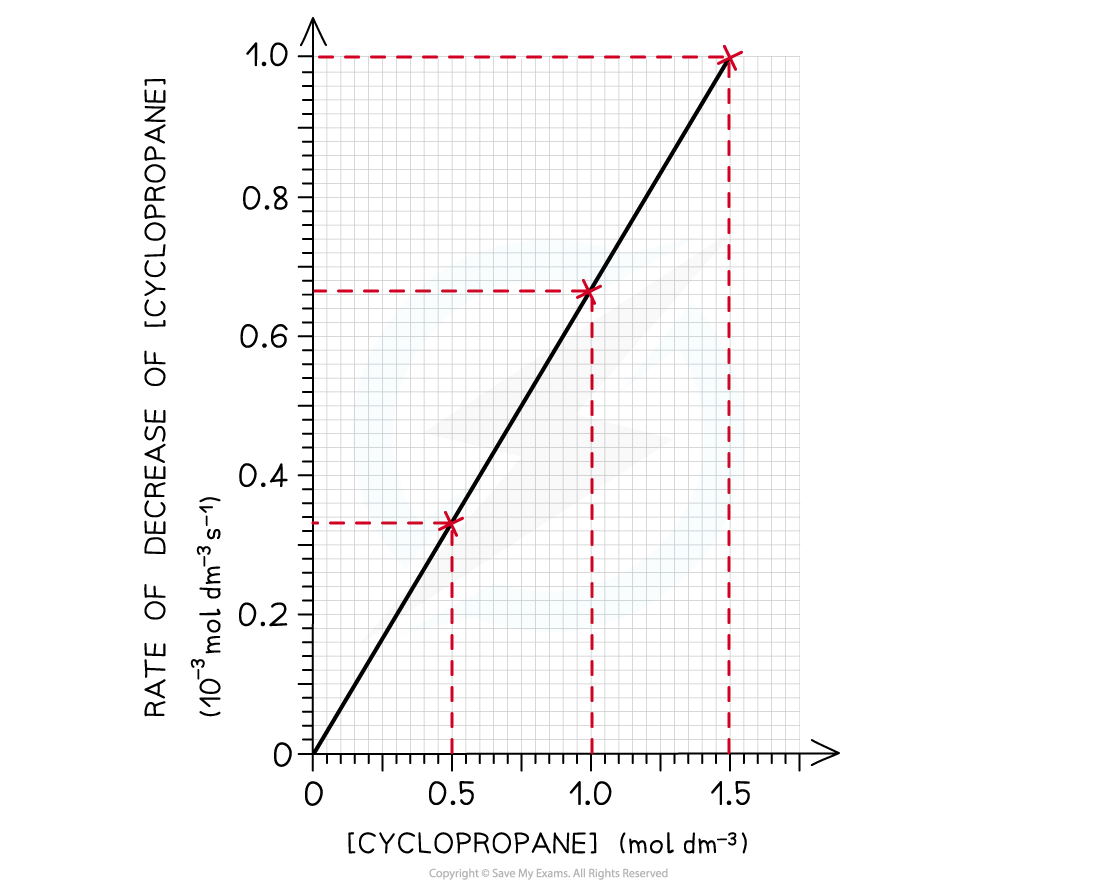
The graph shows a directly proportional correlation between the concentration of cyclopropane and the rate of reaction
Exam Tip
To calculate the rate of reaction you can either use the increase in concentration of products (like in the example above) or the decrease in concentration of reactants.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









