- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.6.7 Bond Enthalpies
Bond Enthalpies
- The amount of energy required to break one mole of a specific covalent bond in the gas phase is called the bond dissociation energy
- Bond dissociation energy (E) is usually just simplified to bond energy or bond enthalpy
- In symbols, the type of bond broken is written in brackets after E
- Eg. E (H-H) is the bond energy of a mole of single bonds between two hydrogen atoms
Average bond energy
- Bond energies are affected by other atoms in the molecule (the environment)
- Therefore, an average of a number of the same type of bond but in different environments is calculated
- This bond energy is known as the average bond energy
- Since bond energies cannot be determined directly, enthalpy cycles are used to calculate the average bond energy
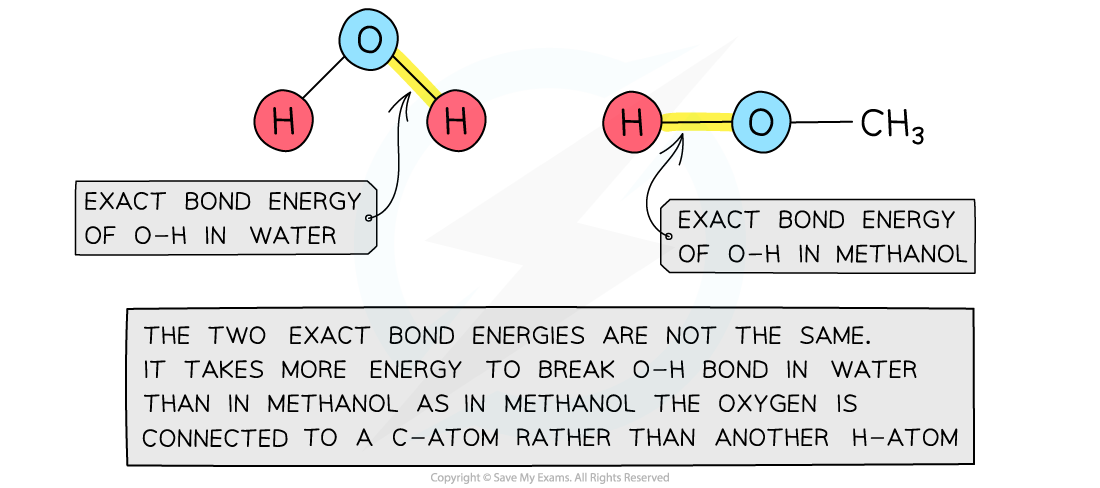
Bond energies are affected by other atoms in the molecule, so average bond enthalpies are listed in data tables
Calculating enthalpy change from bond energies
- Bond energies are used to find the ΔHrꝋ of a reaction when this cannot be done experimentally
- The formula is:

The formula for calculating the standard enthalpy change of reaction using bond energies
Worked Example
Calculating the enthalpy change in the Haber processCalculate the change in enthalpy of reaction for the Haber process, producing ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)
The relevant bond energies are given in the table below: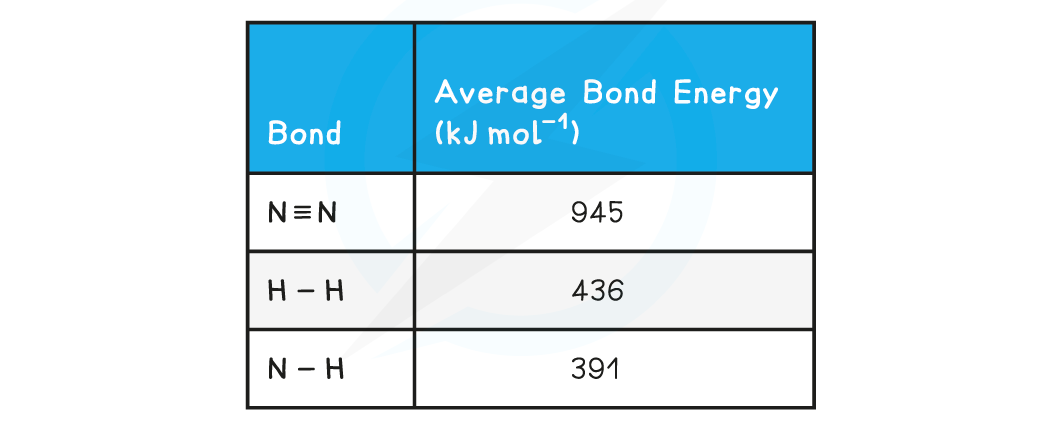
Answer
Step 1: Use the equation to work out the bonds broken and formed and set out the calculation as a balance sheet as shown below:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)

Note! Values for bonds broken are positive (endothermic) and values for bonds formed are negative (exothermic)
Step 2: Calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction
ΔHrꝋ = enthalpy change for bonds broken + enthalpy change for bonds formed
= (+2253 kJ mol-1) + (-2346 kJ mol-1)
= -93 kJ mol-1
Worked Example
Calculating the enthalpy of combustion using bond enthalpiesThe complete combustion of ethyne, C2H2, is shown in the equation below: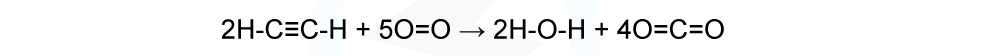 Using the average bond enthalpies given in the table, what is the enthalpy of combustion of ethyne?
Using the average bond enthalpies given in the table, what is the enthalpy of combustion of ethyne?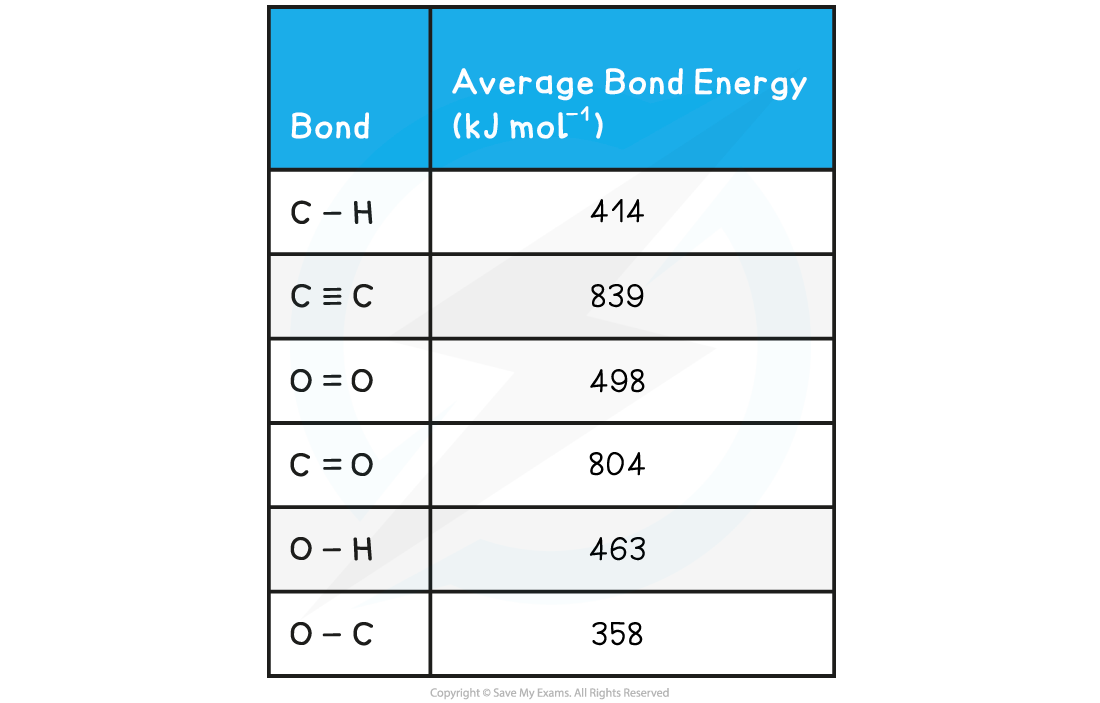
Answer
Step 1: The enthalpy of combustion is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance reacts in excess oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide
The chemical reaction should be therefore simplified such that only one mole of ethyne reacts in excess oxygen:
H-C≡C-H + 2 ½ O=O → H-O-H + 2O=C=O
Step 2: Set out the calculation as a balance sheet as shown below:
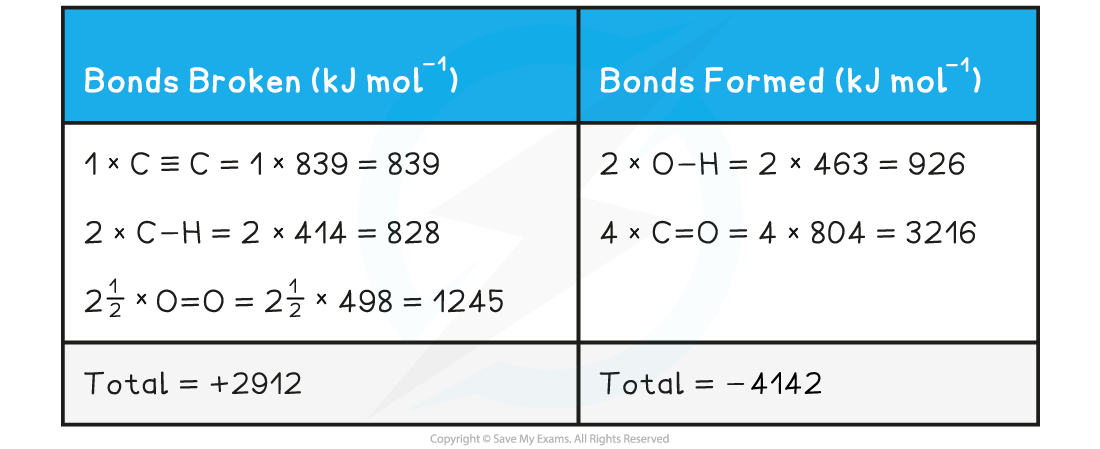
ΔHrꝋ = enthalpy change for bonds broken + enthalpy change for bonds formed
= (+2912 kJ mol-1) + (- 4142 kJ mol-1)
= -1230 kJ mol-1
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








