- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.6.4 Calorimetry
Calorimetry
Measuring enthalpy changes
- Calorimetry is the measurement enthalpy changes in chemical reactions
- A simple calorimeter can be made from a polystyrene drinking cup, a vacuum flask or metal can
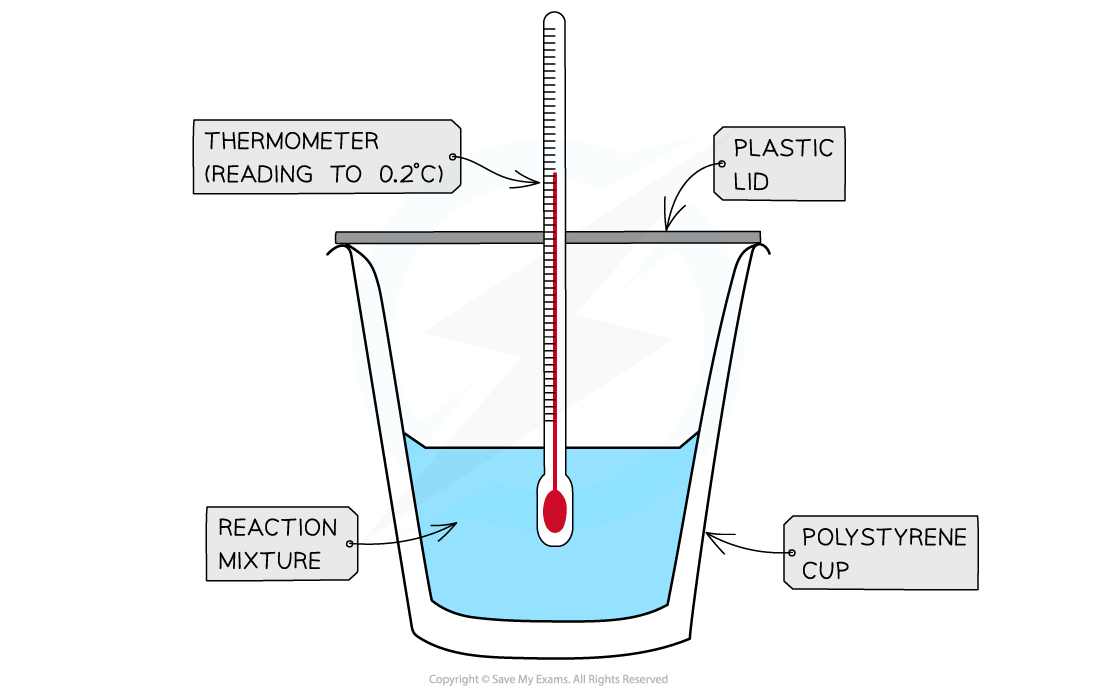
A polystyrene cup can act as a calorimeter to find enthalpy changes in a chemical reaction
- The energy needed to increase the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 oC is called the specific heat capacity (c) of the liquid
- The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 oC-1
- The energy transferred as heat can be calculated by:
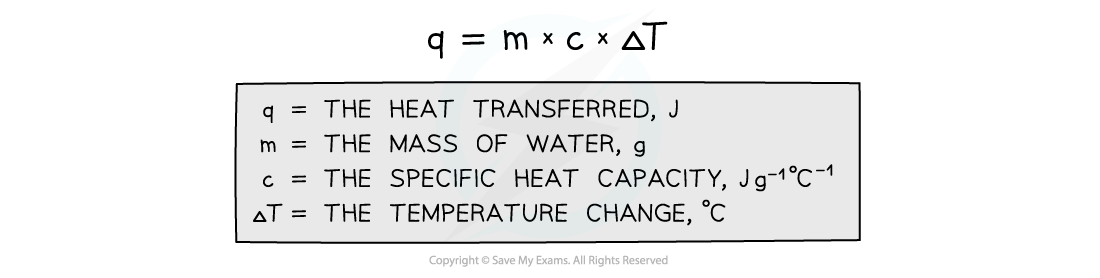
Equation for calculating energy transferred in a calorimeter
Worked Example
Specific heat capacity calculationsIn a calorimetry experiment 2.50 g of methane is burnt in excess oxygen. 30% of the energy released during the combustion is absorbed by 500 g of water, the temperature of which rises from 25 °C to 68 °CThe specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1°C−1 What is the total energy released per gram of methane burnt?
Answer
Step 1: q = m x c x ΔT
m (of water) = 500 g
c (of water) = 4.18 J g-1 °C-1
ΔT (of water) = 68 oC - 25 oC
= 43 oC
Step 2: q = 500 x 4.18 x 43
= 89 870 J
Step 3: This is only 30% of the total energy released by methane
Total energy x 0.3 = 89 870 J
Total energy = 299 567 J
Step 4: This is released by 2.50 g of methane
Energy released by 1.00 g of methane = 299 567 ÷ 2.50
= 119 827 J = 120 000 J
= 120 kJ g-1
Exam Tip
When new bonds are formed the amount of energy released is equal to the amount of energy absorbed when the same bonds are broken.For example:O2 (g) → 2O (g) E (O=O) = +498 kJ mol-12O (g) → O2 (g) E (O=O) = -498 kJ mol-1 Aqueous solutions of acid, alkalis and salts are assumed to be largely water so you can just use the m and c values of water when calculating the energy transferred. To calculate any changes in enthalpy per mole of a reactant or product the following relationship can be used: When there is a rise in temperature, the value for ΔH becomes negative suggesting that the reaction is exothermic and when the temperature falls, the value for ΔH becomes positive suggesting that the reaction is endothermic.
When there is a rise in temperature, the value for ΔH becomes negative suggesting that the reaction is exothermic and when the temperature falls, the value for ΔH becomes positive suggesting that the reaction is endothermic.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








