- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.3.4 The Ideal Gas Equation
The Ideal Gas Equation
Kinetic theory of gases
- The kinetic theory of gases states that molecules in gases are constantly moving
- The theory makes the following assumptions:
- That gas molecules are moving very fast and randomly
- That molecules hardly have any volume
- That gas molecules do not attract or repel each other (no intermolecular forces)
- No kinetic energy is lost when the gas molecules collide with each other (elastic collisions)
- The temperature of the gas is related to the average kinetic energy of the molecules
- Gases that follow the kinetic theory of gases are called ideal gases
- However, in reality gases do not fit this description exactly but may come very close and are called real gases
Ideal gases
- The volume that an ideal gas occupies depends on:
- Its pressure
- Its temperature
- When a gas is heated (at constant pressure) the particles gain more kinetic energy and undergo more frequent collisions with the container wall
- To keep the pressure constant, the molecules must get further apart and therefore the volume increases
- The volume is therefore directly proportional to the temperature (at constant pressure)
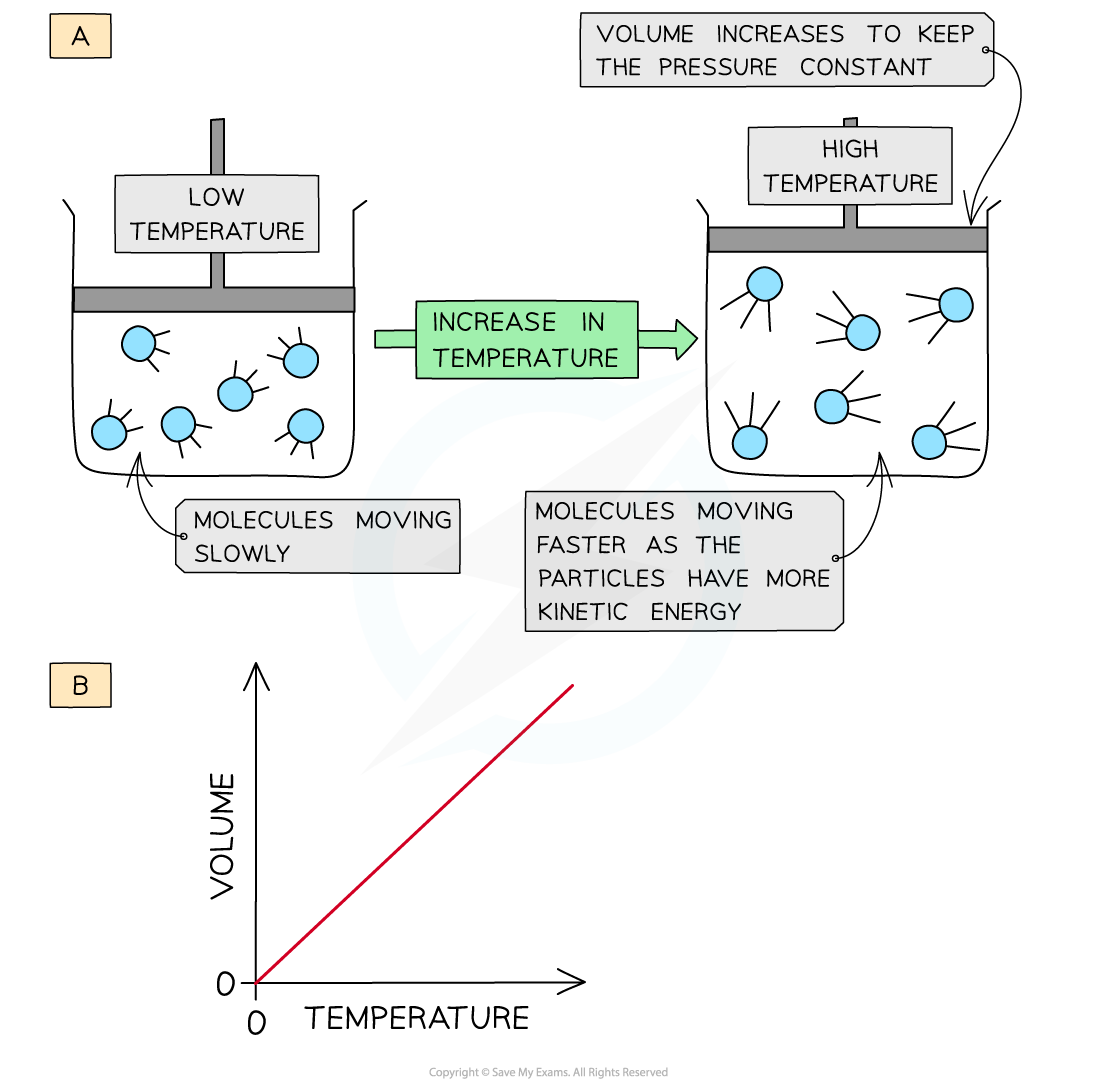
The volume of a gas increases upon heating to keep a constant pressure (a); volume is directly proportional to the temperature (b)
Limitations of the ideal gas law
- At very low temperatures and high pressures real gases do not obey the kinetic theory as under these conditions:
- Molecules are close to each other
- There are instantaneous dipole- induced dipole or permanent dipole- permanent dipole forces between the molecules
- These attractive forces pull the molecules away from the container wall
- The volume of the molecules is not negligible
- Real gases therefore do not obey the following kinetic theory assumptions at low temperatures and high pressures:
- There is zero attraction between molecules (due to attractive forces, the pressure is lower than expected for an ideal gas)
- The volume of the gas molecules can be ignored (volume of the gas is smaller than expected for an ideal gas)
Ideal gas equation
- The ideal gas equation shows the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature and number of moles of gas of an ideal gas:
PV = nRT
P = pressure (pascals, Pa)
V = volume (m3)
n = number of moles of gas (mol)
R = gas constant (8.31 J K-1 mol-1)
T = temperature (kelvin, K)
Worked Example
Calculating the volume of a gas
Calculate the volume occupied by 0.781 mol of oxygen at a pressure of 220 kPa and a temperature of 21 °C
Answer
Step 1: Rearrange the ideal gas equation to find volume of gas
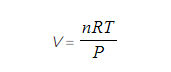
Step 2: Calculate the volume the oxygen gas occupies
-
- P = 220 kPa = 220 000 Pa
- n = 0.781 mol
- R = 8.31 J K-1 mol-1
- T = 21 oC = 294 K
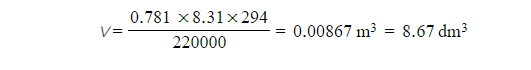
Worked Example
Calculating the molar mass of a gas
A flask of volume 1000 cm3 contains 6.39 g of a gas. The pressure in the flask was 300 kPa and the temperature was 23 °C.
Calculate the relative molecular mass of the gas.
Answer
Step 1: Rearrange the ideal gas equation to find the number of moles of gas
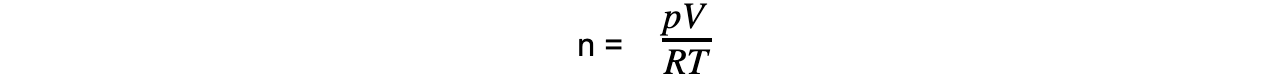
Step 2: Calculate the number of moles of gas
p = 300 kPa = 300 000 Pa
V = 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3 = 0.001 m3
R = 8.31 J K-1 mol-1
T = 23 oC = 296 K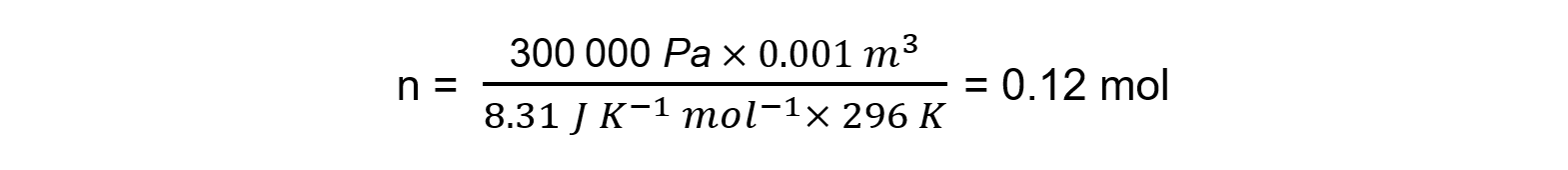
Step 3: Calculate the molar mass using the number of moles of gas
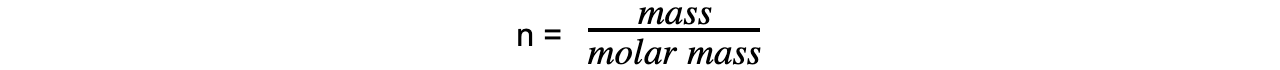
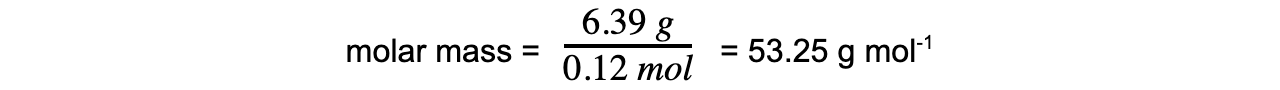
Exam Tip
To calculate the temperature in Kelvin, add 273 to the Celsius temperature - e.g. 100 oC is 373 Kelvin.
You must be able to rearrange the ideal gas equation to work out all parts of it.
The units are incredibly important in this equation - make sure you know what units you should use, and do the necessary conversions when doing your calculations!
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









