- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.3.3 Reacting Volumes
Volumes & Concentrations of Solutions
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of solute dissolved in a solvent to make 1 dm3 of solution
- The solute is the substance that dissolves in a solvent to form a solution
- The solvent is often water
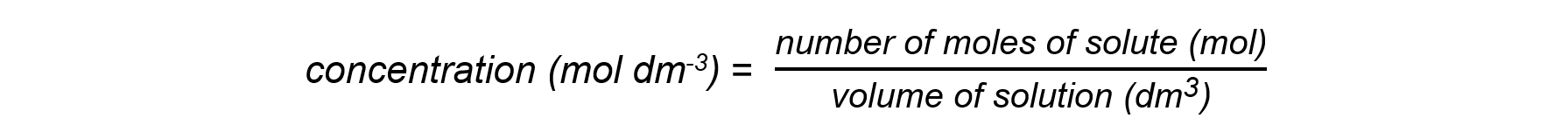
- A concentrated solution is a solution that has a high concentration of solute
- A dilute solution is a solution with a low concentration of solute
- When carrying out calculations involve concentrations in mol dm-3 the following points need to be considered:
- Change mass in grams to moles
- Change cm3 to dm3
- To calculate the mass of a substance present in solution of known concentration and volume:
- Rearrange the concentration equation
number of moles (mol) = concentration (mol dm-3) x volume (dm3)
-
- Multiply the moles of solute by its molar mass
mass of solute (g) = number of moles (mol) x molar mass (g mol-1)
Worked Example
Calculating volume from concentration
Calculate the volume of hydrochloric acid of concentration 1.0 mol dm-3 that is required to react completely with 2.5 g of calcium carbonate
Answer
Step 1: Write the balanced symbol equation
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Step 2: Calculate the amount, in moles, of calcium carbonate that reacts
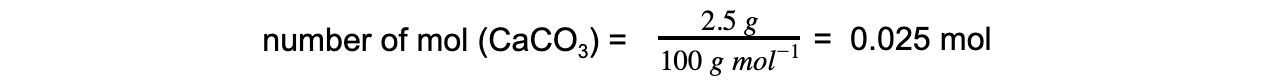
Step 3: Calculate the moles of hydrochloric acid required using the reaction’s stoichiometry
1 mol of CaCO3 requires 2 mol of HCl
So 0.025 mol of CaCO3 requires 0.05 mol of HCl
Step 4: Calculate the volume of HCl required
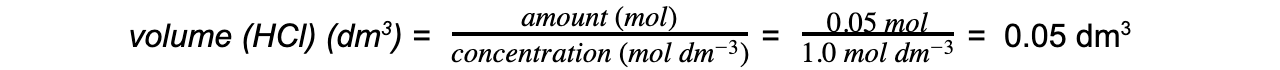
Volume of hydrochloric acid = 0.05 dm3
Worked Example
Neutralisation calculation
25.0 cm3 of 0.050 dm-3 sodium carbonate was completely neutralised by 20.00 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid. Calculate the concentration in mol dm-3 of the hydrochloric acid.
Answer
Step 1: Write the balanced symbol equation
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
Step 2: Calculate the amount, in moles, of sodium carbonate reacted by rearranging the equation for amount of substance (mol) and dividing the volume by 1000 to convert cm3 to dm3
amount (Na2CO3) = 0.025 dm3 x 0.050 mol dm-3 = 0.00125 mol
Step 3: Calculate the moles of hydrochloric acid required using the reaction’s stoichiometry
1 mol of Na2CO3 reacts with 2 mol of HCl, so the molar ratio is 1 : 2
Therefore 0.00125 moles of Na2CO3 react with 0.00250 moles of HCl
Step 4: Calculate the concentration, in mol dm-3, of hydrochloric acid
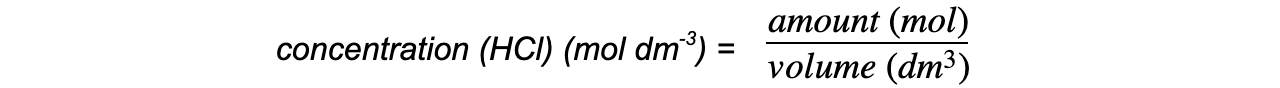
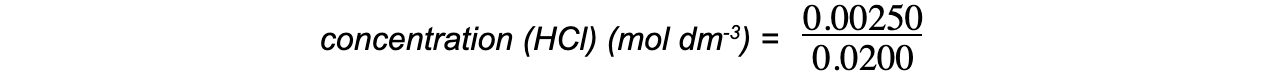
concentration (HCl) (mol dm-3) = 0.125 mol dm-3
Volumes of gases
- Avogadro suggested that ‘equal volumes of gases contain the same number of molecules’ (also called Avogadro’s hypothesis)
- At room temperature (20 degrees Celsius) and pressure (1 atm) one mole of any gas has a volume of 24.0 dm3
- This molar gas volume of 24.0 dm3 mol-1 can be used to find:
- The volume of a given mass or number of moles of gas:
volume of gas (dm3) = amount of gas (mol) x 24 dm3 mol-1
- The mass or number of moles of a given volume of gas:
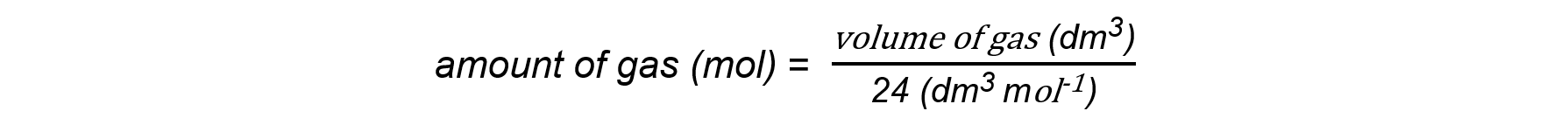
Worked Example
Calculation volume of gas using excess & limiting reagents
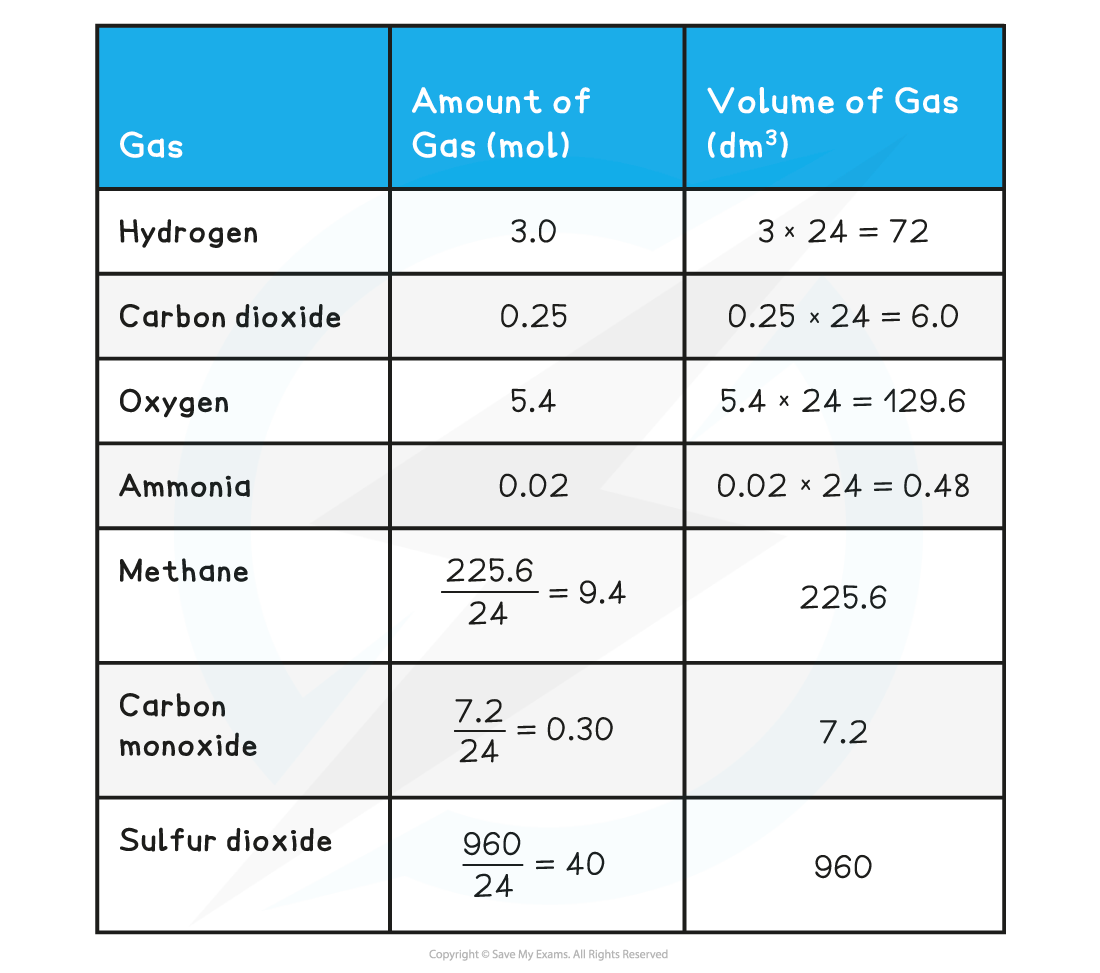
Calculate the volume the following gases occupy:
- Hydrogen (3 mol)
- Carbon dioxide (0.25 mol)
- Oxygen (5.4 mol)
- Ammonia (0.02 mol)
Calculate the moles in the following volumes of gases:
- Methane
- Carbon monoxide
- Sulfur dioxide
Answer
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








