- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.2.3 Balanced Equations
Deducing Formulae of Compounds
- Ionic compounds are formed from a metal and a non-metal bonded together
- Ionic compounds are electrically neutral; the positive charges equal the negative charges
Charges on positive ions
- All metals form positive ions
- There are also some non-metal positive ions, such as ammonium, NH4+, and hydrogen, H+
- The metals in Group 1, Group 2 and Group 3 (13) have a charge of 1+ and 2+ and 3+ respectively
- The charge on the ions of the transition elements can vary which is why Roman numerals are often used to indicate their charge
- Roman numerals are used in some compounds formed from transition elements to show the charge (or oxidation state) of metal ions
- E.g. in copper (II) oxide, the copper ion has a charge of 2+ whereas in copper (I) nitrate, the copper has a charge of 1+
Non-metal ions
- The non-metals in group 15 to 17 have a negative charge and have the suffix ‘ide’
- E.g. nitride, chloride, bromide, iodide
- Elements in group 17 gain 1 electron so have a 1- charge, eg. Br-
- Elements in group 16 gain 2 electrons so have a 2- charge, eg. O2-
- Elements in group 15 gain 3 electrons so have a 3- charge, eg. N3-
- There are also polyatomic negative ions, which are negative ions made up of more than one type of atom
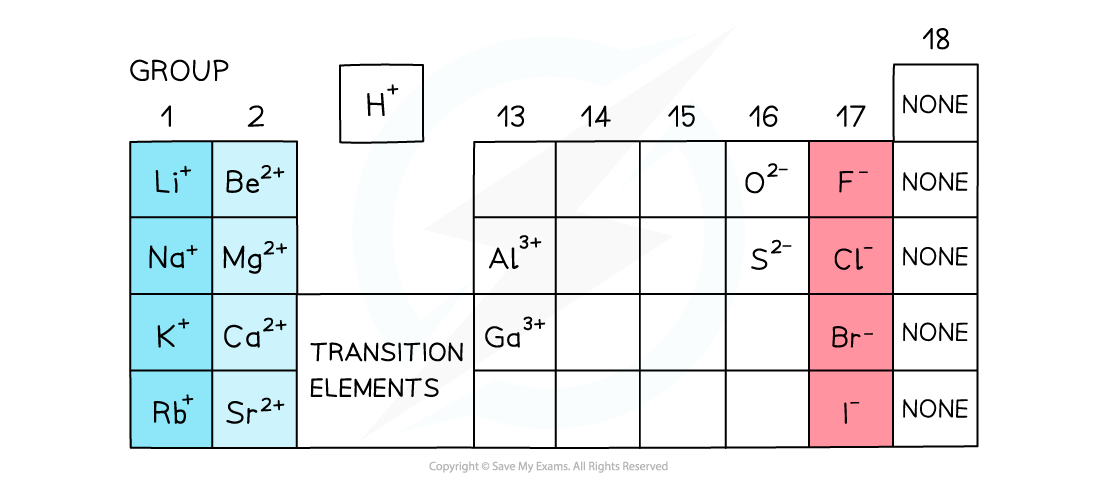
The charges of simple ions depend on their position in the Periodic Table
Formulae of Ionic Compounds Table
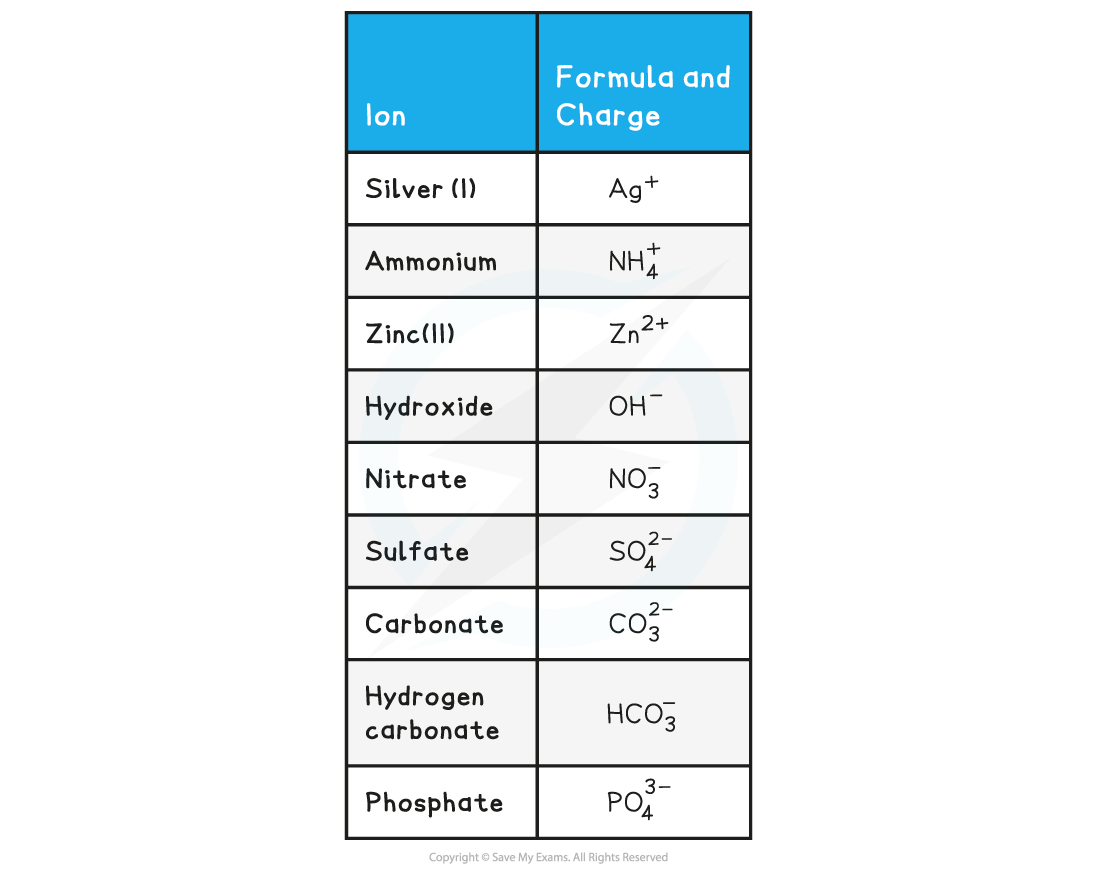
Worked Example
Formulae
Determine the formulae of the following ionic compounds
- Magnesium chloride
- Iron(III) oxide
- Aluminium nitrate
Answer
Answer 1: Magnesium chloride
-
- Magnesium is in Group 2 so has a charge of 2+
- Chlorine is in group 17 so has a charge of 1-
- Magnesium needs two chloride ions for each magnesium ion to be balanced so the formula is MgCl2
Answer 2: Iron (III) oxide
-
- The Roman numeral states that iron has a charge of 3+
- Oxygen is in group 16 so has a charge of 2-
- The charges need to be equal so 2 iron ions to 3 oxide ions will balance electrically, so the formula is Fe2O3
Answer 3: Aluminum nitrate
-
- Aluminium is in group 13 so has a charge of 3+
- Nitrate is a polyatomic ion and has a charge of 1-
- The polyatomic ion needs to be placed in a bracket if more than 1 is needed
- The formula of aluminium nitrate is Al(NO3)3
Exam Tip
Remember: Polyatomic ions are ions that contain more than one type of element, such as OH-
Balancing Equations
- A symbol equation is a shorthand way of describing a chemical reaction using chemical symbols to show the number and type of each atom in the reactants and products
- A word equation is a longer way of describing a chemical reaction using only words to show the reactants and products
Balancing equations
- During chemical reactions, atoms cannot be created or destroyed
- The number of each atom on each side of the reaction must therefore be the same
- E.g. the reaction needs to be balanced
- When balancing equations remember:
- Not to change any of the formulae
- To put the numbers used to balance the equation in front of the formulae
- To balance firstly the carbon, then the hydrogen and finally the oxygen in combustion reactions of organic compounds
- When balancing equations follow the following the steps:
- Write the formulae of the reactants and products
- Count the numbers of atoms in each reactant and product
- Balance the atoms one at a time until all the atoms are balanced
- Use appropriate state symbols in the equation
- The physical state of reactants and products in a chemical reaction is specified by using state symbols
- (s) solid
- (l) liquid
- (g) gas
- (aq) aqueous
Ionic Equations
Ionic equations
- In aqueous solutions ionic compounds dissociate into their ions
- Many chemical reactions in aqueous solutions involve ionic compounds, however only some of the ions in solution take part in the reactions
- The ions that do not take part in the reaction are called spectator ions
- An ionic equation shows only the ions or other particles taking part in a reaction, and not the spectator ions
Worked Example
Balance the following equation:
magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
Answer:
Step 1: Write out the symbol equation showing reactants and products
Mg + O2 → MgO
Step 2: Count the numbers of atoms in each reactant and product
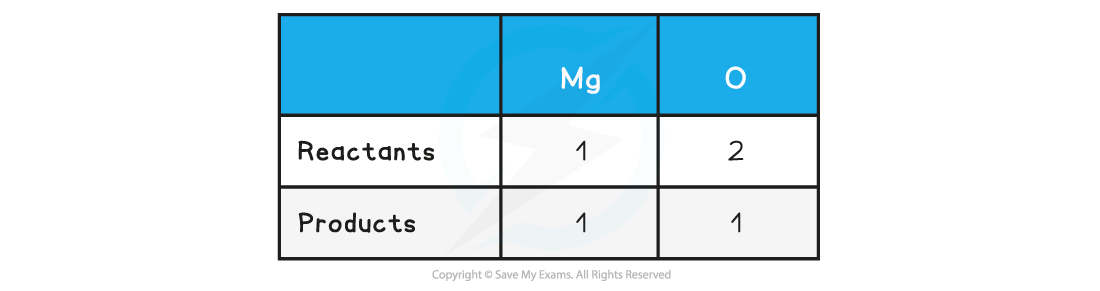
Step 3: Balance the atoms one at a time until all the atoms are balanced
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
This is now showing that 2 moles of magnesium react with 1 mole of oxygen to form 2 moles of magnesium oxide
Step 4: Use appropriate state symbols in the fully balanced equation
2Mg (s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO (s)
Worked Example
1. Balance the following equation
zinc + copper(II) sulfate → zinc sulfate + copper
2. Write down the ionic equation for the above reaction
Answer 1:
Step 1: To balance the equation, write out the symbol equation showing reactants and products
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Step 2: Count the numbers of atoms in each reactant and product. The equation is already balanced
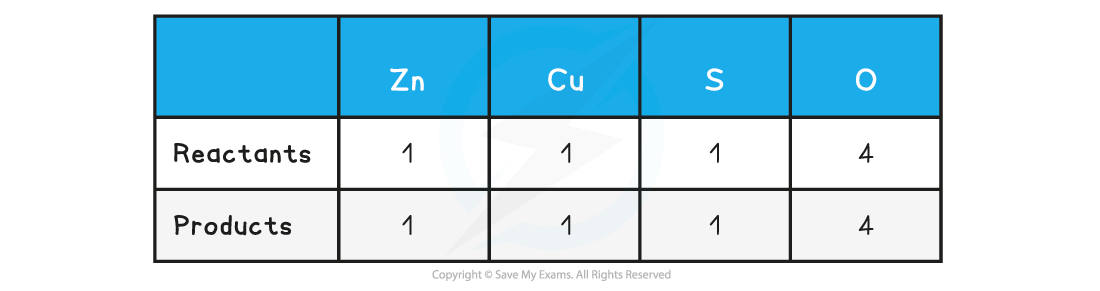
Step 3: Use appropriate state symbols in the equation
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Answer 2:
Step 1: The full chemical equation for the reaction is
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Step 2: Break down reactants into their respective ions
Zn (s) + Cu2+ + SO42- (aq) → Zn2++ SO42- (aq) + Cu (s)
Step 3: Cancel the spectator ions on both sides to give the ionic equation
Zn (s) + Cu2+ + SO42- (aq) → Zn2++ SO42- (aq) + Cu (s)
Zn (s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









