- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.1.3 Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
- Mass Spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique
- It is the most useful instrument for accurate determination of the relative atomic mass of an element, based on the abundance and mass of each of its isotopes
- It is also used to find the relative molecular mass of molecules
- As a sample passes through the mass spectrometer, a spectrum is produced of mass / charge ratio against abundance
- The spectrum can be used to find the relative isotopic abundance, atomic and molecular mass and the structure of a compound
- The peak with the highest mass is the molecular ion peak, M+, and the peak which has the largest abundance (tallest peak) is called the base peak
- There are several types of mass spectrometer, but all of them are based on an ionised sample being accelerated through the mass spectrum, and being separated based on the ratio of their charge to their mass
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
- This is a common form of mass spectrometry, where all particles of the sample to be analysed are ionised to form 1+ ions
- These 1+ ions are then accelerated to high speeds, deflected through the spectrometer and then arrive at the detector
- As they hit the detector, the mass spectrum graph is produced
- The whole of the apparatus is kept under a high vacuum to prevent any ions that are produced from colliding with molecules in the air
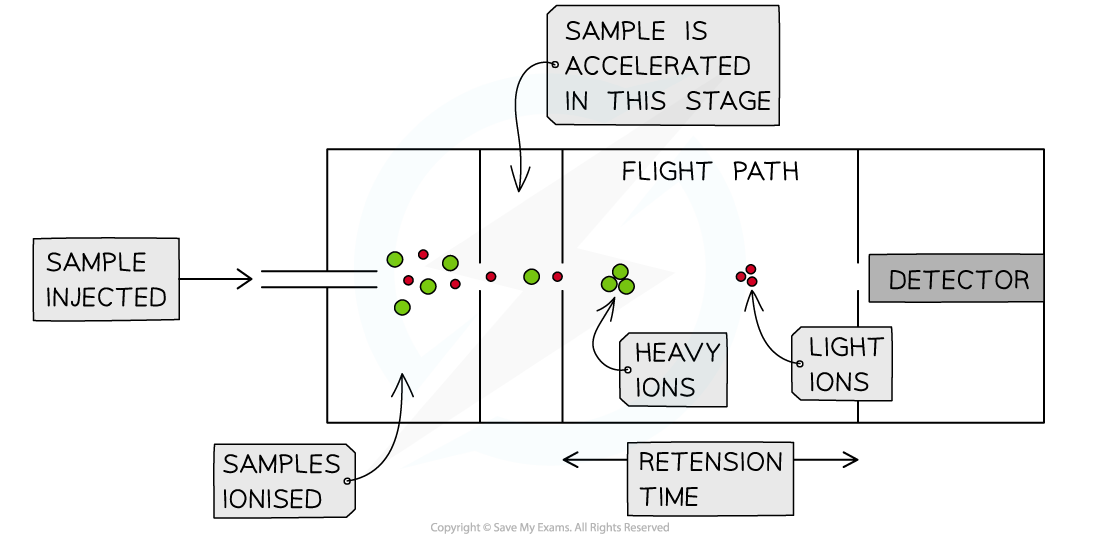
Inside the time of flight mass spectrometer
- There are 4 key stages in time of flight mass spectrometry:
- Ionisation
- Acceleration
- Ion drift
- Detection
Stage 1: Ionisation
- There are two key ways in which the sample could be ionised:
- Electron Impact (or electron ionisation)
- Electrospray Ionisation
Electron Impact Ionisation
- This method of ionisation is used for elements and substances which have a lower molecular mass
- The sample is vaporised and then bombarded with high energy electrons
- The electrons are 'fired' from an electron gun
- The electron gun is a hot wire filament which emits electrons as a current runs through it
- As the sample is bombarded by these electrons, an electron is knocked off each particle, forming a 1+ ion
X (g) → X+ (g) + e-
- The 1+ ions which have been formed are called molecular ions, or M+ ions
- These are then attracted towards a negatively charged plate
- This accelerates them through the mass spectrometer
- The molecular ion can be broken down further, or fragmented
- The fragments are also accelerated through the sample and hit the detector, causing different peaks to show on the mass spectrum which is produced
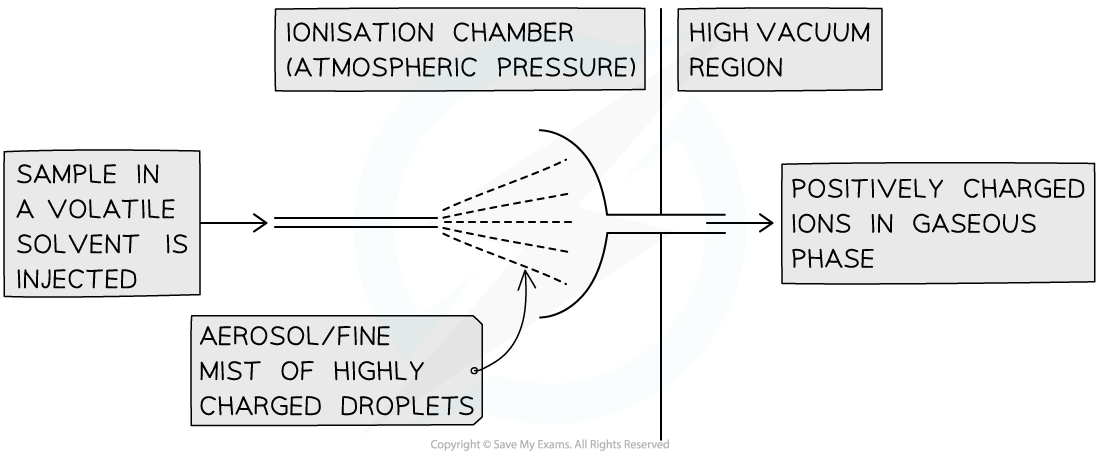
Electrospray Ionisation
- This method is used for substances which have a higher molecular mass
- Unlike with electron impact ionisation, fragmentation is unlikely to happen
- This is often called a soft ionisation technique
- For this method, the sample is dissolved in a volatile solvent
- The solvent is injected into the mass spectrometer using a hypodermic needle
- This produces a fine mist or aerosol
- The needle is attached to a high voltage power supply, so as the sample is injected, the particles are ionised by gaining a proton from the solvent
X (g) + H+ → XH+ (g)
- The solvent evaporates and the XH+ ions are attracted towards a negatively charged plate
- This accelerates them through the mass spectrometer
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer
Stage 2: Acceleration
- The 1+ ions formed from either ionisation method are accelerated using an electric field
- They are all accelerated to have the same kinetic energy
- This is important for you to remember when completing calculations
- Since all 1+ ions will have the same kinetic energy, their velocity will depend on their mass
- Lighter ions will move faster and heavier ions will move slower
Stage 3: Ion Drift (in the flight tube)
- The 1+ ions will pass through a hole in the negatively charged plate and move into a flight tube
- This is where the name 'Time of Flight' comes from
- The time of flight of each 1+ ion in this tube depends on their velocity
- Again, this is important to remember when completing calculations
Stage 4: Detection
- Once they have pass through the mass spectrometer, the 1+ ions will hit a negatively charged 'detector' plate
- As they hit this electric plate, they gain an electron
- This gaining of an electron discharges the ion, and causes a current to be produced
- This size of the current is proportional to the abundance of those ions hitting the plate and gaining an electron
- The detector plate is connected to a computer, which produces the mass spectrum
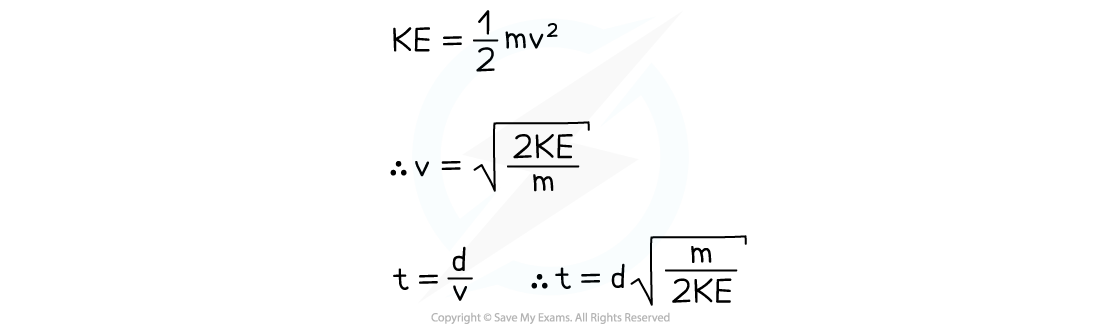
Key Equations for Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
where
KE = kinetic energy of the particles (J)
m = mass of the particles (kg)
v = velocity of the particles (ms-1)
t = time of flight of the particles (s)
d = the length of the flight tube (m)
Exam Tip
Remember: all particles in the mass spectrometer are accelerated to the same kinetic energy. The time of flight is proportional to the square root of the mass of the ions, showing that the lighter the ion the faster it will pass through and the quicker it will hit the detector. The heavier the ion, the slower it will travel and the longer it will take to hit the detector.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









