- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记7.2.2 Gene Pools & Allele Frequency
Gene Pools & Allele Frequency
Gene pools
- The phenotype of an organism is dependent on its genotype and the environmental influence on the organism
- Members of the same species will have the same genes, of which there may exist different alleles (alternate versions of genes)
- A gene pool is the collection of genes within an interbreeding population at a particular time
- As these genes can have different alleles, a gene pool can also be thought of as the sum of all the alleles of the genes of a population (of a single species) at a particular time
Allele frequency
- How often different alleles occur in the gene pool of a population is known as the allele frequency
- The gene pool (or allele frequencies) in a species population can change over time due to processes such as natural selection
- When the gene pool (or allele frequencies) within a species population changes sufficiently over time, the characteristics of the species population will also change
- Over time, these changes can become so great that a new species forms
Apparatus & Techniques: Collecting Data about the Frequency of a Phenotype
- The frequency of a phenotype is simply the number of individuals in a population that have a specific, observable trait (a particular phenotypic characteristic)
- Many organisms have traits that show more than one phenotype (e.g. shell colour in banded snails can be pink or yellow and flower colour in pea plants can be purple or white)
- Phenotype frequencies can be calculated by counting the number of times a particular phenotype appears in a population (or sample of a population) and dividing this by the total number of individuals in the population (or the sample)
- Phenotype frequencies are normally given as a percentage of the total population
Phenotype frequency = (total individuals with phenotype ÷ total individuals in population) × 100
Worked Example
In a population of 9 pea plants, 7 of the plants have purple flowers, whilst 2 have white flowers. Calculate the phenotype frequencies of purple and white flowers. Give your answers as percentages.
Two phenotypes of pea plant flowers
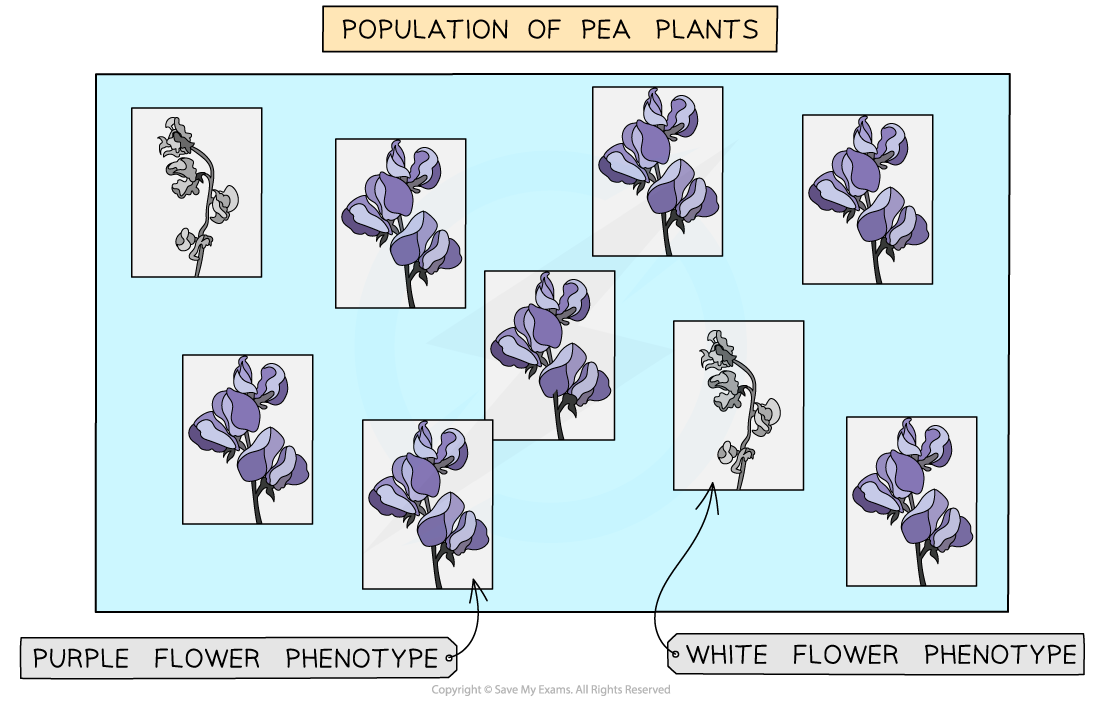
Step 1: Calculate the phenotype frequency of purple flowers
Phenotype frequency = (total individuals with phenotype ÷ total individuals in population) × 100
= (7 ÷ 9) × 100
= 0.78 × 100
= 78%
Step 2: Calculate the phenotype frequency of white flowers
Phenotype frequency = (total individuals with phenotype ÷ total individuals in population) × 100
= (2 ÷ 9) × 100
= 0.22 × 100
= 22%
Worked Example
In banded snails (Cepaea nemoralis), shell colour is controlled by two alleles of a single gene. The pink allele (Cᴾ) is dominant over the yellow allele (Cʸ). Out of a sample of individuals collected, 275 snails have the genotype CᴾCᴾ, 150 have the genotype CᴾCʸ, and 75 have the genotype CʸCʸ. Calculate the relative phenotype frequencies of the banded snails collected.
Two phenotypes of banded snails
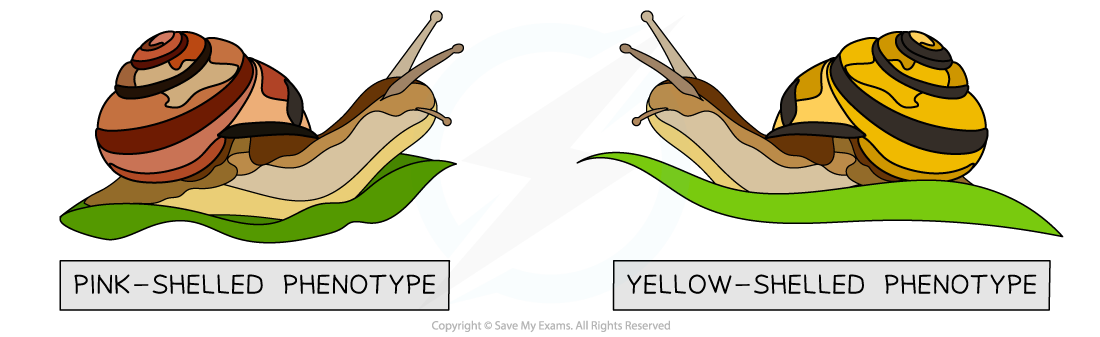
Step 1: Calculate the total number of snails in the sample
= 275 + 150 + 75
= 500
Step 2: Calculate the total number of pink-shelled snails (genotypes: CᴾCᴾ and CᴾCʸ)
= 275 + 150
425
Step 3: Calculate the phenotype frequency of pink-shelled snails
Phenotype frequency = (total individuals with phenotype ÷ total individuals in population) × 100
= (425 ÷ 500) × 100
= 0.85 × 100
= 85%
Step 4: Calculate the phenotype frequency of yellow-shelled snails
Phenotype frequency = (total individuals with phenotype ÷ total individuals in population) × 100
= (75 ÷ 500) × 100
= 0.15 × 100
= 15%
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









