- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记7.1.5 Investigating Genetic Ratios
Apparatus & Techniques: Investigating Genetic Ratios
- Known information about genotypes, phenotypes and the process of meiosis can be used to make predictions about the phenotypes of offspring that would result from specific breeding pairs of organisms
- When two individuals sexually reproduce there is an equal chance of either allele from their homologous pair making it into their gametes and subsequently the nucleus of the zygote
- This means there is an equal chance of the zygote inheriting either allele from their parent
- Genetic diagrams are often used to present this information in a clear and precise manner so that predictions can be made
- These diagrams include a characteristic table called a Punnett square
- The predicted genotypes that genetic diagrams produce are all based on chance
- There is no way to predict which gametes will fuse so sometimes the observed or real-life results can differ from the predictions
- Model organisms can be used to investigate the genetic ratios resulting from genetic crosses
- Fast Plant® and Drosophila are commonly used
- They both reproduce at rapid rates due to their short life cycles
- A single gene determines an easily identifiable physical trait in each organism
- This makes them ideal for observation in genetic experiments
- For these experiments, the assumption has been made that gamete fertilisation occurs randomly
Fast Plant®
- A particular type of Fast Plant® is bred from the species Brassica rapa for the purposes of research
- Usually, these plants produce a purple pigment called anthocyanin in their stems
- The dominant allele A results in the production of this pigment
- Some plants however do not produce anthocyanin and so lack the purple colour in their stem
- They are homozygous recessive and so only possess the recessive allele a
- A monohybrid cross can be carried out to study the inheritance of this single pair of alleles. The results can be compared to and explained by the predicted ratios in genetic diagrams
- It is important to include the phenotypes and genotypes of the parents and offspring in a genetic diagram
An example of a monohybrid cross using Fast Plant®
- A homozygous dominant Fast Plant® is crossed with a homozygous recessive Fast Plant®
- The homozygous dominant Fast Plant® produces a purple stem
- It has the genotype AA
- The homozygous recessive Fast Plant® has a green stem
- The allele that causes no anthocyanin to be produced is recessive
- It has the genotype aa
- Gametes contain only one allele from the parent
- In this situation, both parents are homozygous and so they can only produce gametes that contain one type of allele
- All the gametes from the purple plant will contain the allele A and all the gametes from the non-purple plant will contain the allele a
- All of the offspring will be heterozygous, with the genotype Aa
- They will all produce the purple pigment anthocyanin
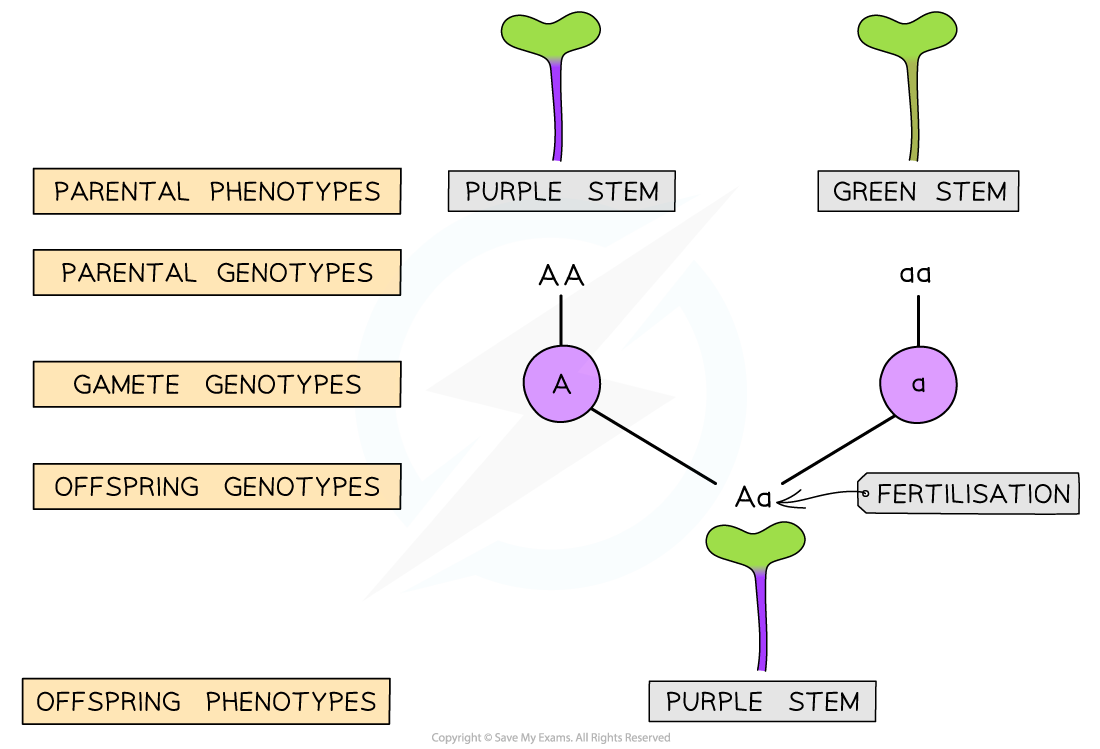
Genetic diagrams follow a specific structure as shown above. As the parents can only produce gametes that contain one type of allele a Punnett square is not needed in this genetic diagram.
- A monohybrid cross can also be used to predict the phenotypes of offspring that would be produced from two heterozygous Fast Plants® interbreeding
- Each parent can produce gametes that contain either allele: A or a
- As a result, the offspring produced can have one of three possible genotypes
- If both parents produce gametes with the dominant allele and they fuse: A + A = AA
- If one parent produces a gamete with the dominant allele and the other parent produces a gamete with the recessive allele and they fuse: A + a = Aa
- If both parents produce gametes with the recessive allele and they fuse: a + a = aa
- A Punnett square can be used within a genetic diagram to help keep track of the different alleles in the parental gametes as well as the genotypes they produce in the offspring
- The resulting genotypes can be used to determine the predicted phenotypes of the offspring
- Offspring with the genotypes AA or Aa will produce purple stems
- Offspring with the genotype aa will produce green stems (due to the lack of anthocyanin)
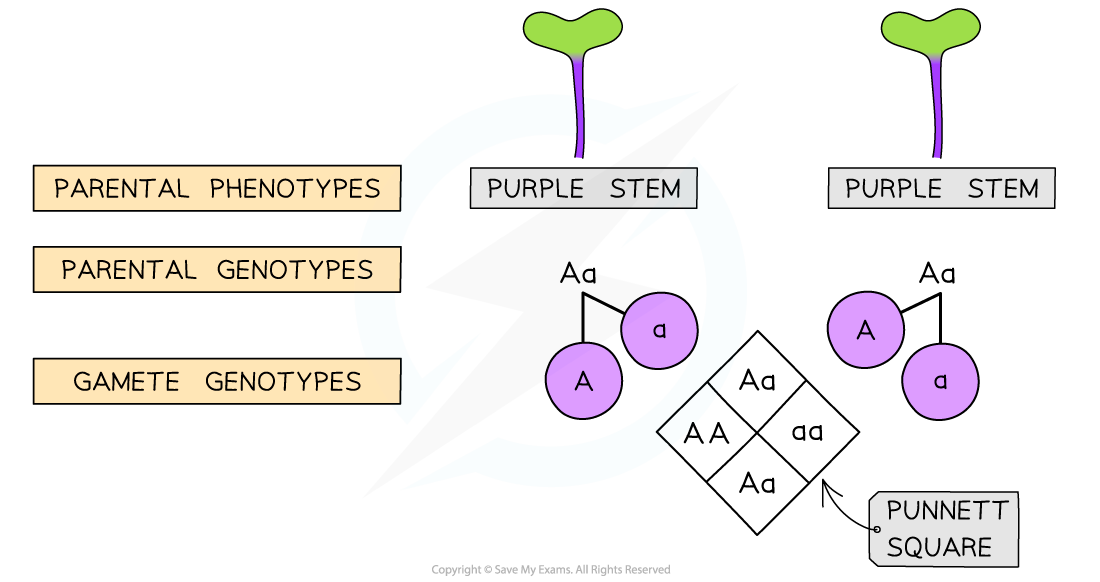
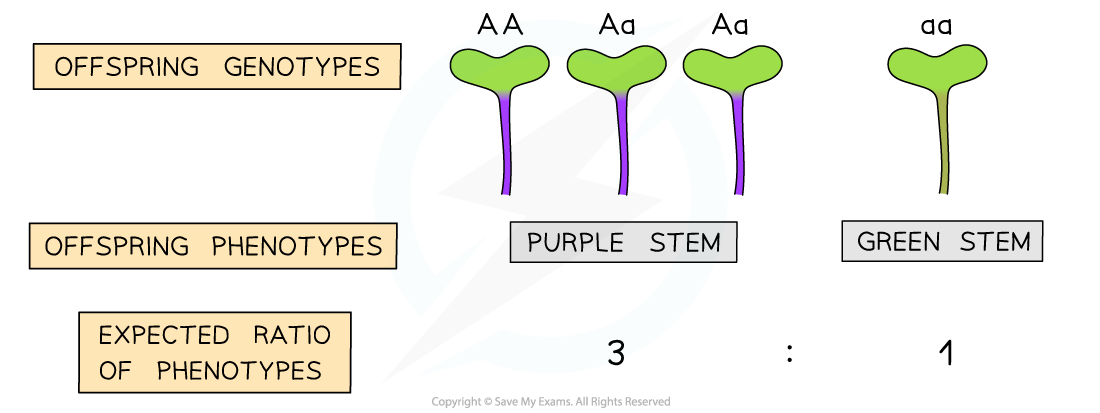
The crossing of two heterozygous individuals results in a predicted phenotype ratio of 3:1
Drosophila
- Small fruit flies from the genus Drosophila have been used in genetic experiments for many years
- Their wing length is controlled by a single gene
- This gene has two alleles
- The dominant allele L produces the long or wild type wing
- The recessive allele l produces the stunted or vestigial wing
- The ratio of phenotypes present in the offspring produced from a monohybrid cross can be explained using genetic diagrams
- Two fruit flies with wild type wings were crossed and around 100 offspring were produced
- Roughly one-quarter or 25% of the offspring displayed the vestigial wing phenotype
- This can be explained by both of the parents being heterozygous, Ll
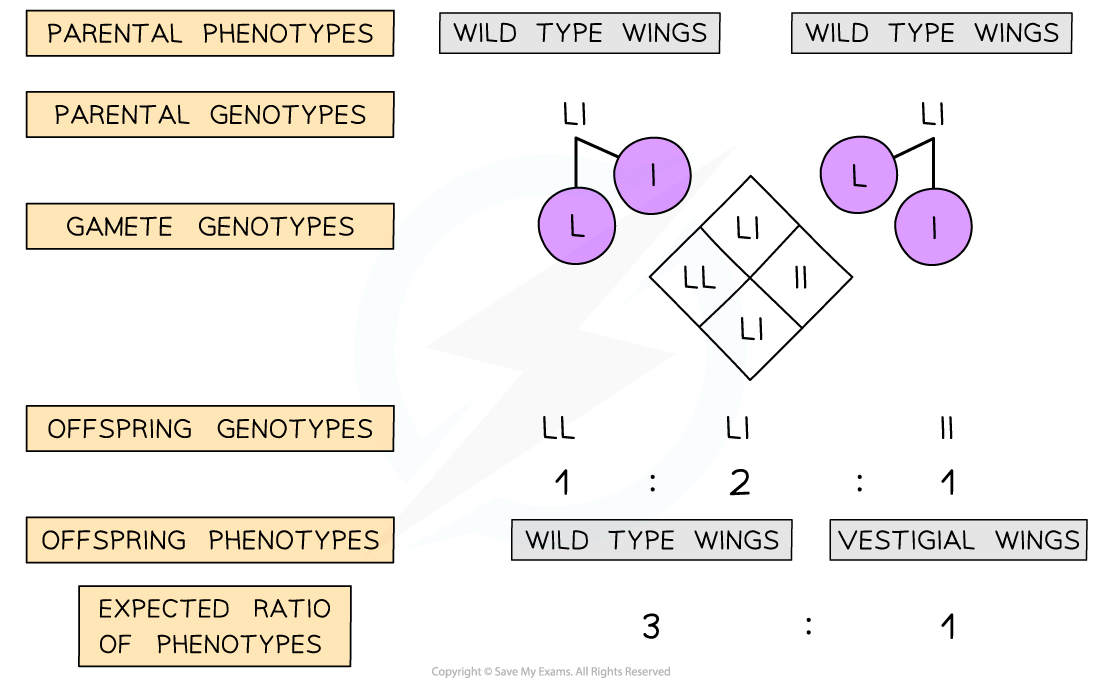
Two parents with the wild type wing length can produce offspring with the vestigial wing length if both of them are heterozygous. Note that the genotype ratio is different from the phenotype ratio for the offspring.
Exam Tip
Remember when dealing with genetic diagrams and questions in the exam, you always know the genotype of the individual displaying the recessive phenotype; they have to be homozygous recessive!
Probability of Inheritance
- Understanding the genetics of an organism or a disease is essential when determining the probability associated with inheritance
- Genetic diagrams produce ratios that suggest the probability of an offspring having or being a particular phenotype
- For example, a common ratio seen in dihybrid crosses is 9:3:3:1
- This ratio results from crossing individuals that are heterozygous for both genes
- The ratio of 9:3:3:1 suggests that there are four possible phenotypes for the offspring
- If there were 16 offspring produced
- 9 would have phenotype W
- 3 would have phenotype X
- 3 would have phenotype Y
- 1 would have phenotype Z
- These ratios can also be converted to percentage probabilities. This is the chance that any offspring produced by those two individuals will have that particular phenotype.
- There is a 56.25% chance that any offspring produced will have phenotype W
- There is an 18.75% chance that any offspring produced will have phenotype X
- There is an 18.75% chance that any offspring produced will have phenotype Y
- There is a 6.25% chance that any offspring produced will have phenotype Z
- Percentage probabilities are often used when dealing with the probability of inheriting genetic diseases
Worked Example
A man (Mike) and a woman (Sarah) want to have their own biological baby. They are concerned as Sarah's father has haemophilia, a blood clotting condition.The allele for a blood clotting factor (F or f) is found on the X chromosome. Females have two copies of the allele whereas men only have one. It is a recessive sex-linked disease. Neither Mike nor Sarah suffer from the condition.Calculate the chance that they will have a baby that suffers from haemophilia. Give your answer as a percentage.
Step 1: Work out Sarah's genotype
As her father was a sufferer he must have the genotype XfY
Her father must have given her his Xf chromosome for her to be the female sex
As she does not suffer from the recessive disease it can be said that she must also have the dominant allele
Her genotype is XFXf
Step 2: Work out Mike's genotype
As Mike does not suffer from the disease he must have the dominant allele on his single X chromosome
His genotype is XFY
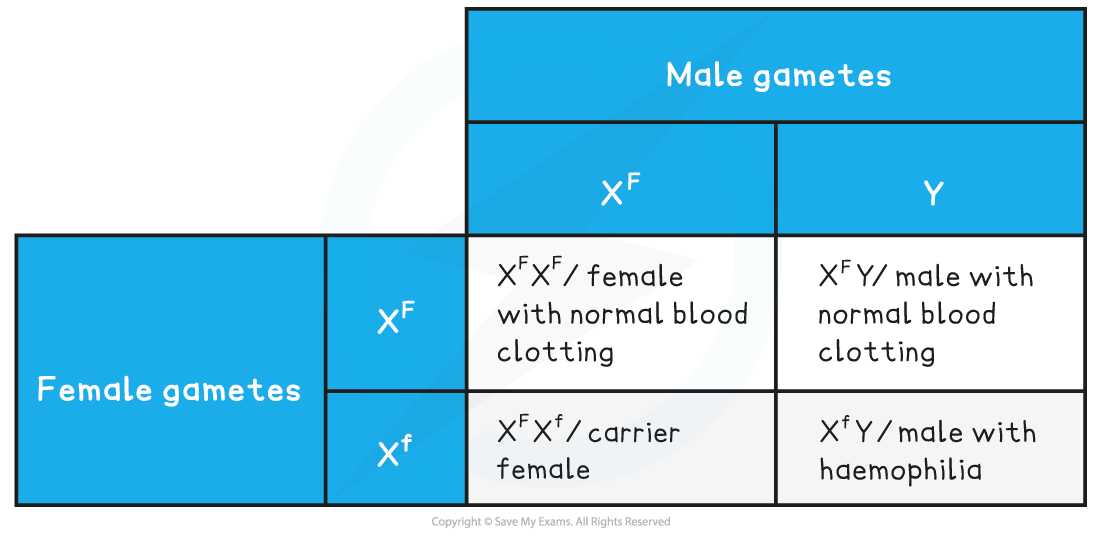
Step 3: Cross the two genotypes using a genetic diagram
Parental phenotypes: carrier female x normal male
Parental genotypes: XFXf XFY
Parental gametes: XF or Xf XF or Y
The predicted ratio of genotypes in offspring -
1 XFXF : 1 XFXf : 1 XFY : 1 XfY
The predicted ratio of phenotypes in offspring -
1 female with normal blood clotting : 1 carrier female : 1 male with normal blood clotting : 1 male with haemophilia
Ratio 1 : 3
Step 4: Use the predicted ratio to obtain the percentage probability
The ratio is 1:3
1 + 3 = 4 so need to find 1 as a percentage of 4
(1 ÷ 4) x 100 = 25
There is a 25% chance or probability that their baby will have haemophilia
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









