- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.6.2 Types of Respiration
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.6.2 Types of Respiration
Aerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration requires oxygen
- It is defined as the chemical reaction in cells that uses oxygen to break down nutrient molecules to release energy
- Aerobic respiration is the complete breakdown of glucose to release a relatively large amount of energy for use in cell processes and reactions
- Carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products as well as releasing useful cellular energy
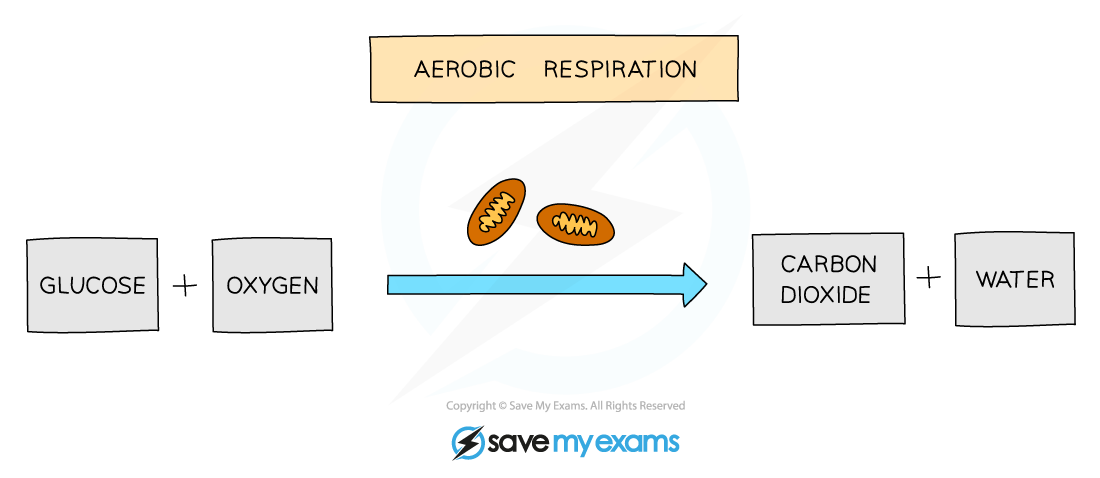 Word equation for aerobic respiration
Word equation for aerobic respiration
- This equation can also be shown as a balanced chemical equation
- One molecule of glucose combines with six molecules of oxygen to produce six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water
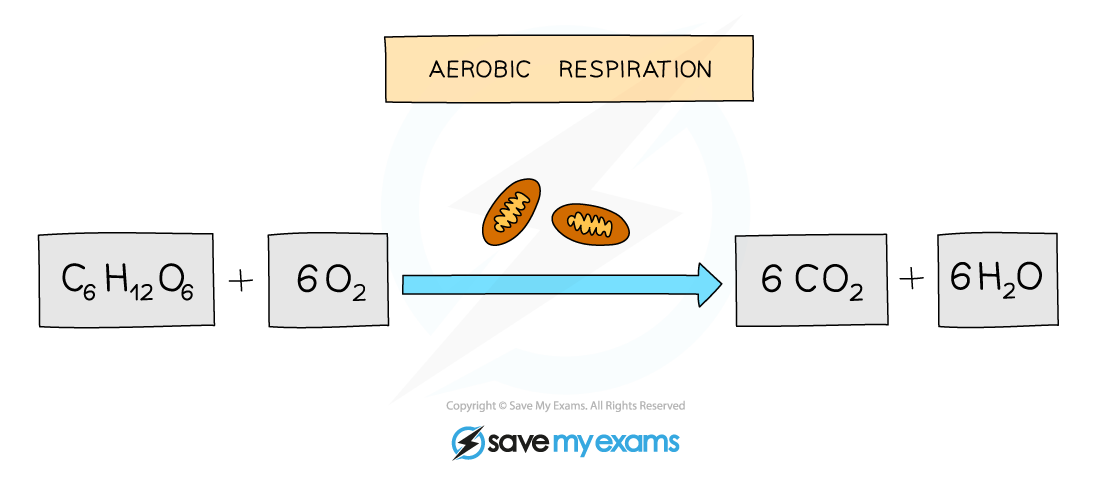 The balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
The balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Exam Tip
There are usually 3 marks given for the aerobic respiration chemical equation in an exam:
- One for getting the correct formula for glucose and oxygen
- One for getting the correct formula for carbon dioxide and water
- One for balancing the equation correctly
So make sure you can do all three to gain maximum marks!
Anaerobic Respiration
- Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen
- It is defined as the chemical reaction in cells that breaks down nutrient molecules to release energy without using oxygen
- It involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose and so releases a relatively small amount of energy for use in cell processes
- Different breakdown products are formed depending on the type of organism that the anaerobic respiration is taking place in
- You need to know the equations for anaerobic respiration in animals and plants (or fungi)
Anaerobic respiration in animals
- Anaerobic respiration mainly takes place in muscle cells during vigorous exercise
- When we exercise at high intensities, our muscles have a higher demand for energy
- Our bodies can only deliver so much oxygen to our muscle cells for aerobic respiration
- When oxygen runs out, glucose is broken down without it, producing lactic acid instead
- Glucose has not been fully broken down meaning there is still energy stored within the bonds of lactic acid molecules
- Anaerobic respiration releases less energy than aerobic respiration
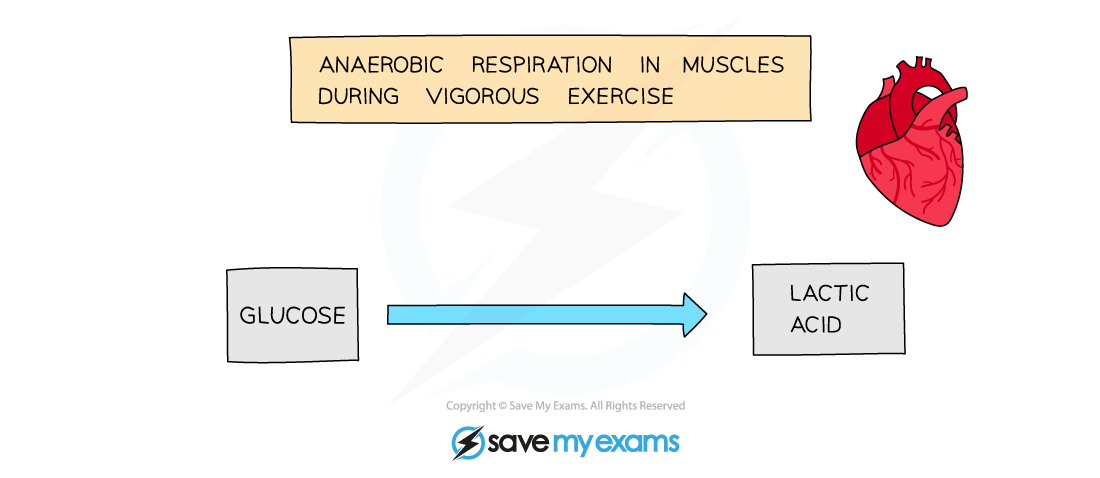 Word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals
- This equation can also be shown as a balanced chemical equation
- One molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of lactic acid
 The balanced chemical equation for anaerobic respiration in animals
The balanced chemical equation for anaerobic respiration in animals
Lactic acid and oxygen debt
- Lactic acid builds up in muscle cells and lowers the pH of the muscle tissue (making the conditions more acidic)
- Acidic conditions can denature the enzymes in cells
- Lactic acid will eventually be broken down using oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products
- The amount of oxygen required to break down the lactic acid that has built up is referred to as the 'oxygen debt'
- The process of breaking down the lactic acid is known as ‘repaying the oxygen debt’
Anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi
- Plants and yeast can respire without oxygen as well, breaking down glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide
- Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation
- Fermentation is economically important in the manufacture of bread (where the carbon dioxide produced helps the dough to rise) and in brewing (where the ethanol produced makes beer)
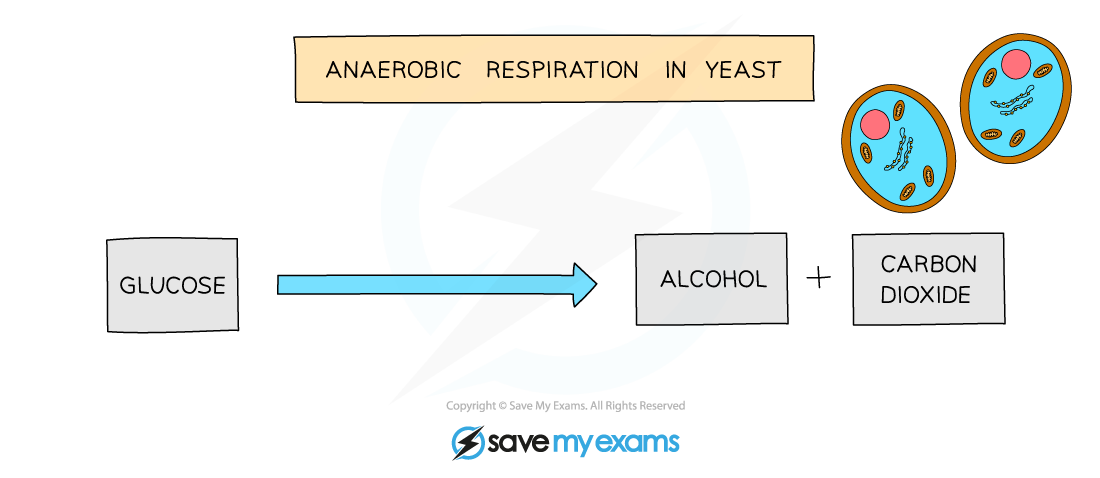 Word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi
- This equation can also be shown as a balanced chemical equation
- One molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of alcohol and two molecules of carbon dioxide
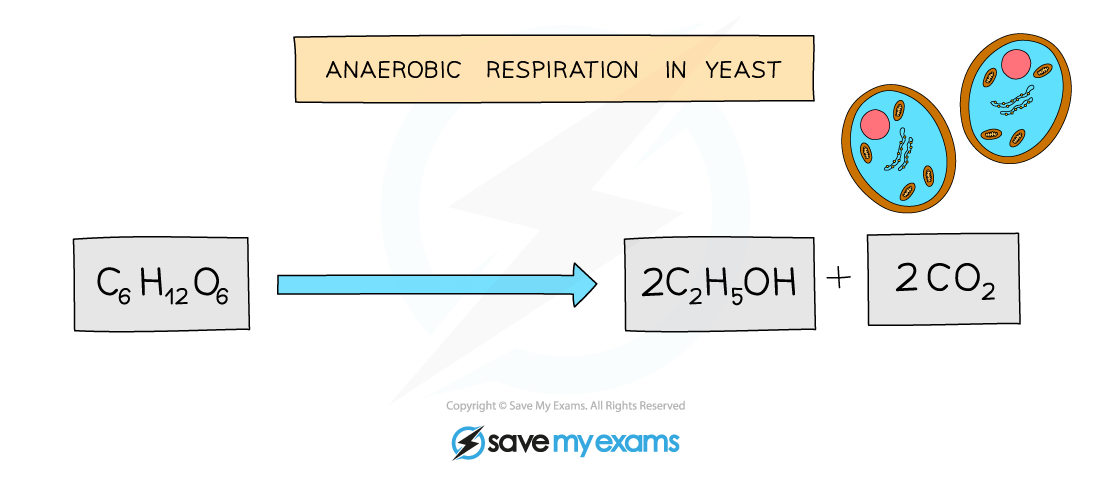 Balanced equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast
Balanced equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast
Comparing Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration
- You need to be able to compare the processes of aerobic and anaerobic respiration with regard to the need for oxygen, the products and the relative amounts of energy transferred
Comparing Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Table 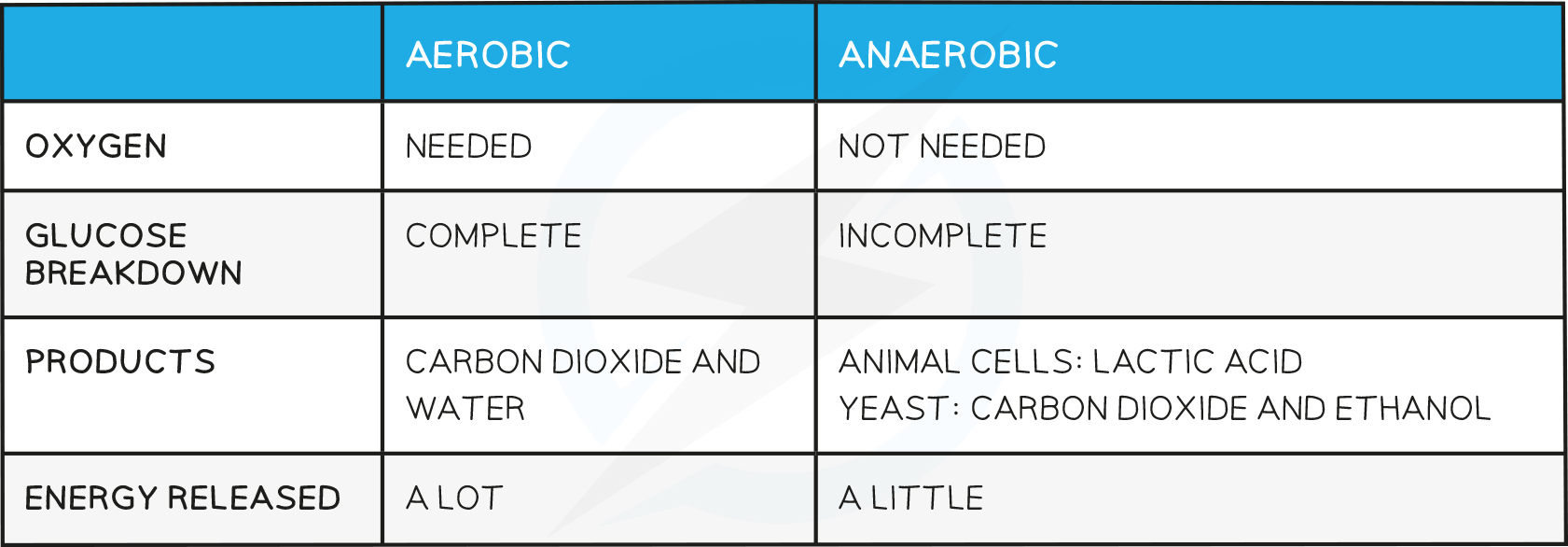

转载自savemyexam

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








