- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.1.7 Non-Coding DNA
Non-Coding DNA
- The genome within eukaryotic cells contains many non-coding sections of DNA
- Non-coding DNA does not code for any amino acids
- Non-coding DNA can be found between genes, as non-coding multiple repeats
- This means they contain the same base sequences repeated multiple times
- Non-coding DNA can also be found within genes, as introns
- The coding exons can be separated by one or more introns
- During transcription, eukaryotic cells transcribe the whole gene (all introns and exons) to produce pre-mRNA molecules
- Before the pre-mRNA exits the nucleus the non-coding sections (introns) are removed and the coding sections (exons) are joined together in a process called splicing
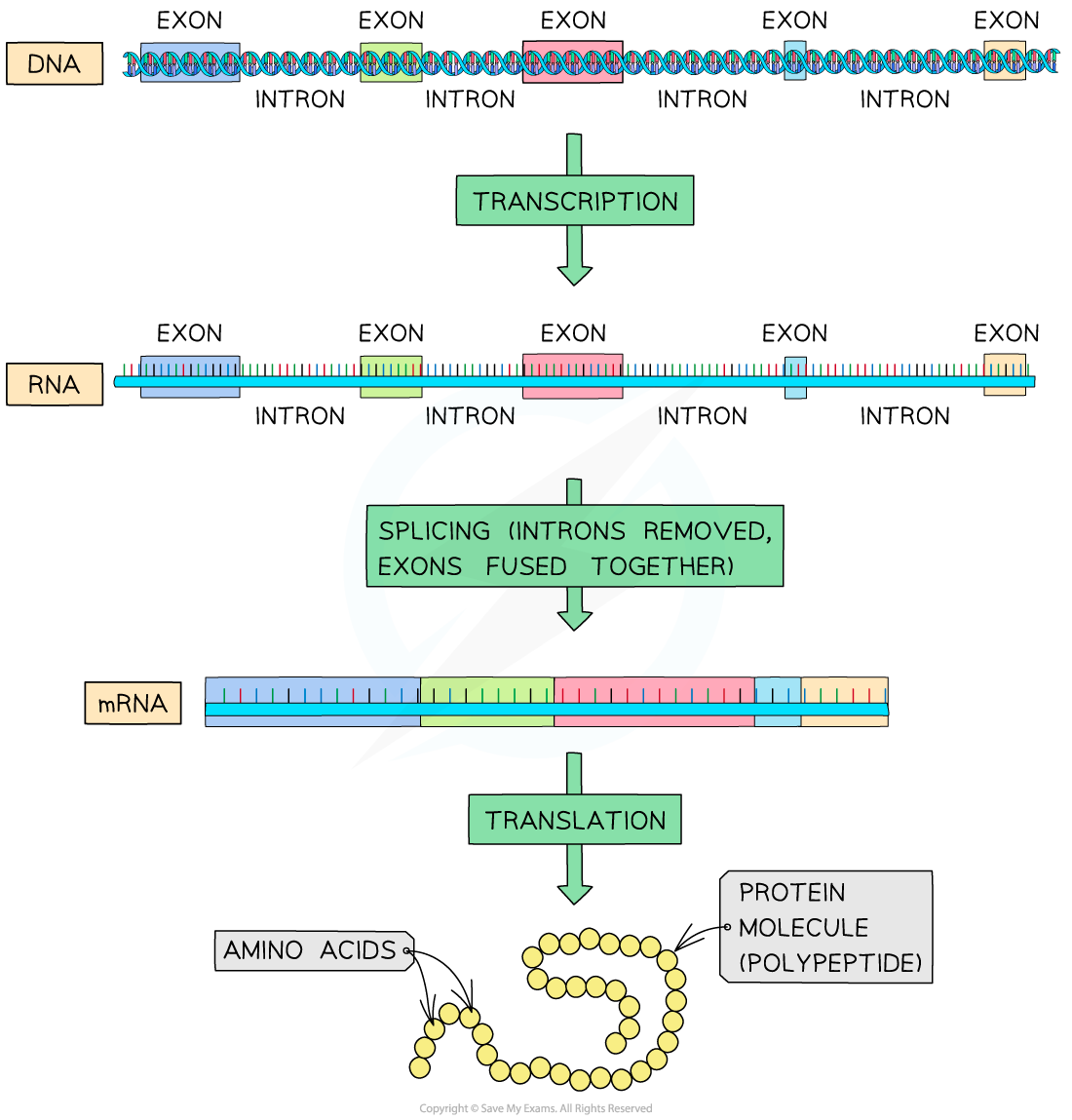
The RNA molecule produced from the transcription of a gene contains introns that must be removed before translation can occur.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








