- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记3.1.6 Gas Exchange vs Water Loss
Compromises between Gas Exchange & Water Loss
- The exchange of gases from the atmosphere is essential for the survival of organisms
- Oxygen is required for respiration
- Carbon dioxide is required for photosynthesis
- Water has a range of vital functions within organisms
- It is a solvent that facilitates the transport of essential nutrients
- Extreme water loss can lead to death
- Scientists have observed in organisms that adaptations that reduce water loss negatively affect gas exchange and vice versa
- As a result, compromises have been made in organisms to ensure that there is a sufficient supply of both water and gases
- Clear examples of this can be seen in terrestrial insects and xerophytic plants
Terrestrial Insects
- Small insects living on the ground are surrounded by air and prone to drying out
- Insects possess a waterproof exoskeleton that prevents water loss
- The waterproof waxy coating of the exoskeleton makes gas exchange by diffusion very difficult
- As a result, insects have evolved a breathing system (the tracheal system)which consists of many tubes that carry oxygen directly to all tissues and cells of the body
- Spiracle are openings in the exoskeleton of insects that are connected to the tracheal system
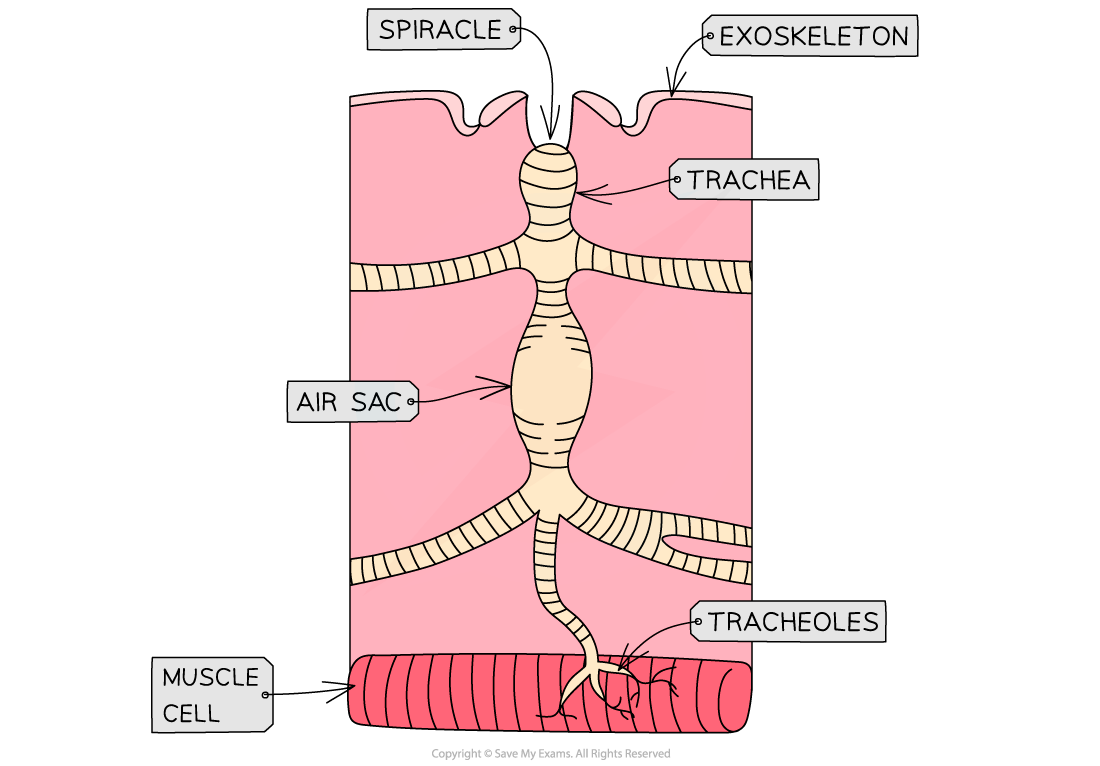
Image showing the structure of the tracheal system of an insect
Xerophytic Plants
- Plants that live in conditions with a plentiful supply of freshwater have leaves with a short diffusion distance through the stomata and a large surface area provided by the air spaces in the spongy mesophyll
- These factors make them vulnerable to water loss
- Plants that live in conditions where freshwater is limited have evolved very effective adaptations to conserve water:
- Very few stomata
- Sunken stomata
- Hairs surrounding stomata
- Needle-shaped or small leaves
- Waxy cuticle
- Plants with these adaptations are described as xerophytic
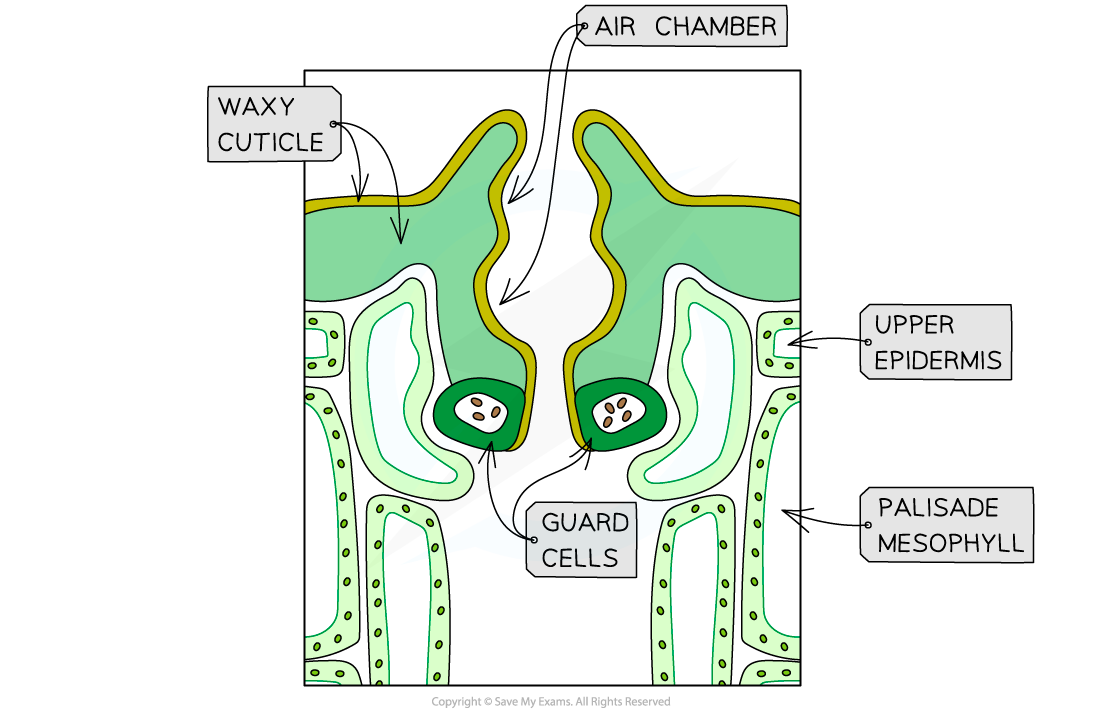 Image showing how sunken stomata protects the escaping water vapour from the external air currents
Image showing how sunken stomata protects the escaping water vapour from the external air currents
Cacti
- Cacti are well-studied xerophytes usually found in the deserts of USA
- They have several characteristics adaptations
- Their leaves have become spines that can no longer photosynthesise
- Photosynthesis occurs in the green stem which possesses chloroplasts
- The stem has a thick cuticle and is very large in diameter which allows it to store water
- There are both shallow and deep penetrating roots which allow it to access all available water
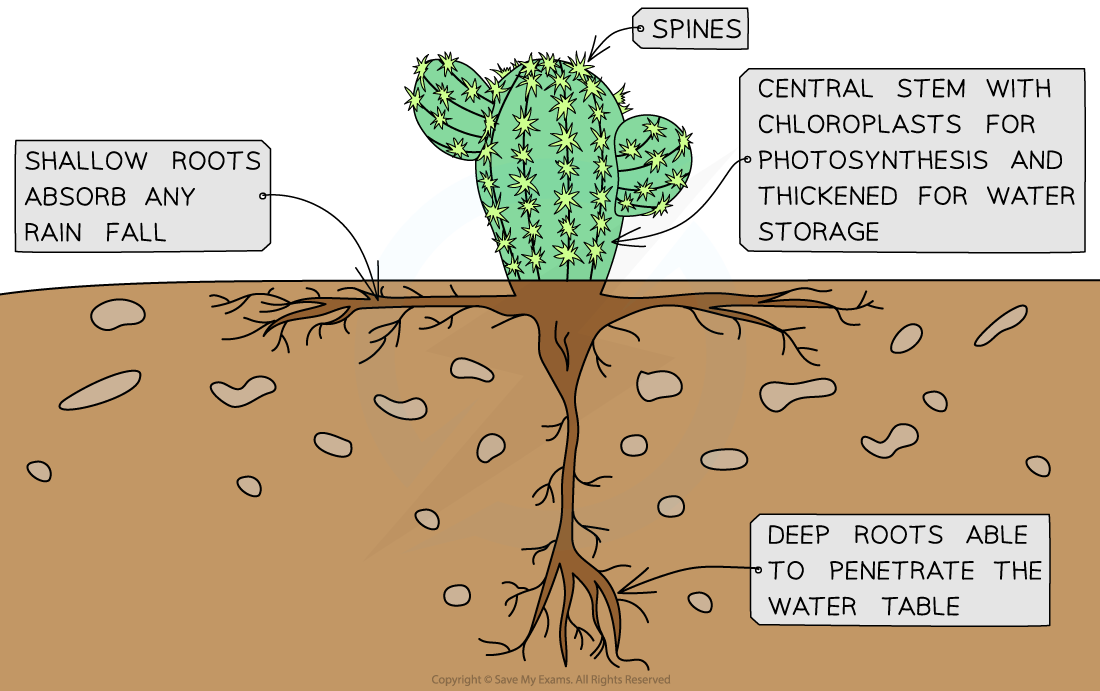 Image showing the adaptations of a Cactus that enables it to survive in dry, hot environments
Image showing the adaptations of a Cactus that enables it to survive in dry, hot environments
Marram Grass
- Sand dunes are another example of a dry environment where plants have evolved to survive
- Marram grass is commonly found on these sand dunes
- Their leaves are well adapted to minimise water loss:
- Leaves can roll up to reduce the exposure of surfaces to the wind
- The rolling of the leaf provides deep grooves which protect the stomata
- The exposed surface has no stomata and a thick cuticle
- The inner surface of the leaf possesses a large number of hairs
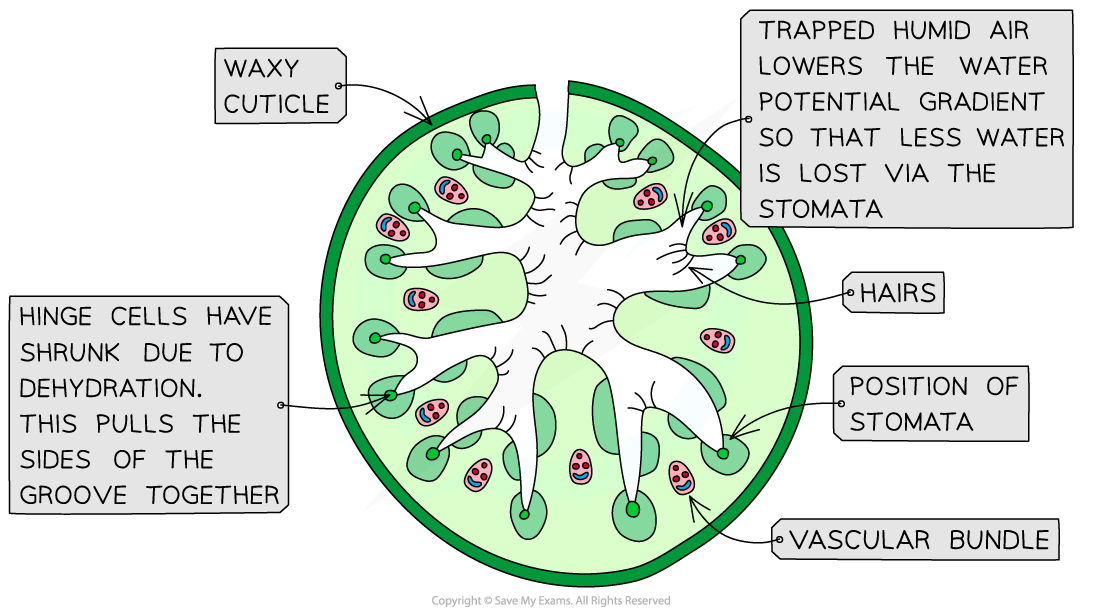
Image showing how the adaptations of the leaf causes water vapour to be trapped and retained near the stomata. This humid air near the stomata means the water potential gradient out of the leaf is reduced, so the rate of evaporation decreases.
Exam Tip
Most plants have a fail-safe mechanism to balance gas exchange with water loss. If the guard cells that open the stomata lose water and become flaccid due to dehydration then the stomata close and no more water can be lost through them.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









