- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记2.5.6 The Role of Helper T cells
The Role of Helper T cells
- Activated T-lymphocytes (those that have receptors specific to an antigen) divide by mitosis to increase in number (similar to the clonal selection and clonal expansion of B-lymphocytes)
- These T-lymphocytes differentiate into two main types of T cell:
- helper T cells
- cytotoxic (killer) T cells
- Helper T cells assist other white blood cells in the immune response
- They release cytokines (hormone-like signals) which stimulate:
- The maturation of B-lymphocytes into antibody-secreting plasma cells
- The production of memory B cells
- The activation of cytotoxic T cells, which destroy virus infected cells and tumour cells
- An increased rate of phagocytosis
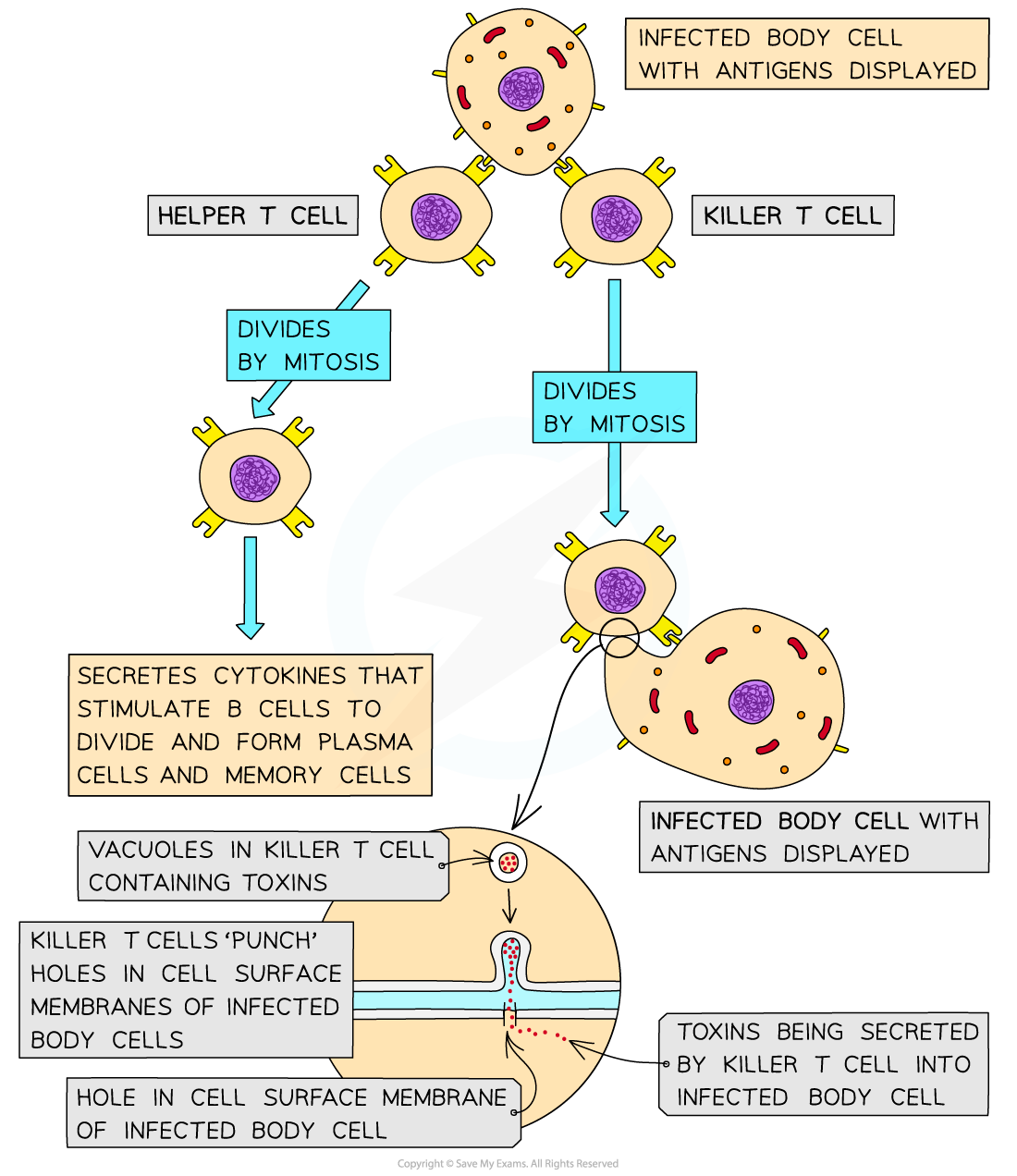
Helper T cells and killer T cells carry out different functions during an immune response
转载自savemyexams

在线登记
最新发布
翰林课程体验,退费流程快速投诉邮箱: yuxi@linstitute.net 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








