- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记1.1.3 Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides: Common Examples
- Sugars can be classified as reducing or non-reducing; this classification is dependent on their ability to donate electrons
- Reducing sugars can donate electrons (the carbonyl group becomes oxidised), the sugars become the reducing agent
- Thus reducing sugars can be detected using Benedict’s test as they reduce the soluble copper sulphate to insoluble brick-red copper oxide
- Examples of reducing sugars include: glucose, fructose and galactose
- Fructose and galactose have the same molecular formula as glucose however they have a different structural formula
- The different arrangement of atoms in these monosaccharides gives them slightly different properties
- Non-reducing sugars cannot donate electrons, therefore they cannot be oxidised
- To be detected non-reducing sugars must first be hydrolysed to break the disaccharide into its two monosaccharides before a Benedict’s test can be carried out
- Example: sucrose
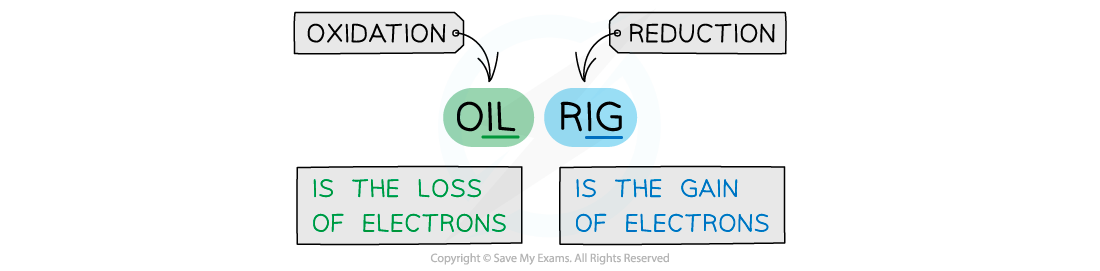
The mnemonic to remember the definitions for oxidation and reduction
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









