- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry复习笔记6.3.1 Metal-Aqua Ions
Metal Aqua-Ions
- Transition metal salts that are readily soluble in water are forming metal-aqua complex ions when they dissolve in water
- When we show copper sulfate dissolving in water it is usually written as:
CuSO4 (s) + aq → Cu2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq)
- However, what we really mean by this is that copper(II) ions are forming the hexaaqucopper(II) ion
CuSO4 (s) + aq → [Cu(H2O)6] 2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq)
- The water molecules are ligands attached to the central transition metal cation by dative covalent bonding from the lone pairs on the oxygen molecules
- Iron(II) salts also form the hexaaqua complex ions:
Fe(NO3)2 (s) + aq → [Fe(H2O)6] 2+ (aq) + 2NO3- (aq)
- Two common +3 aqua ions you should know are iron(III) and aluminium:
Fe(NO3)3 (s) + aq → [Fe(H2O)6] 3+ (aq) + 3NO3- (aq)
Al2(SO4)3 (s) + aq → 2[Al(H2O)6] 3+ (aq) + 3SO42- (aq)
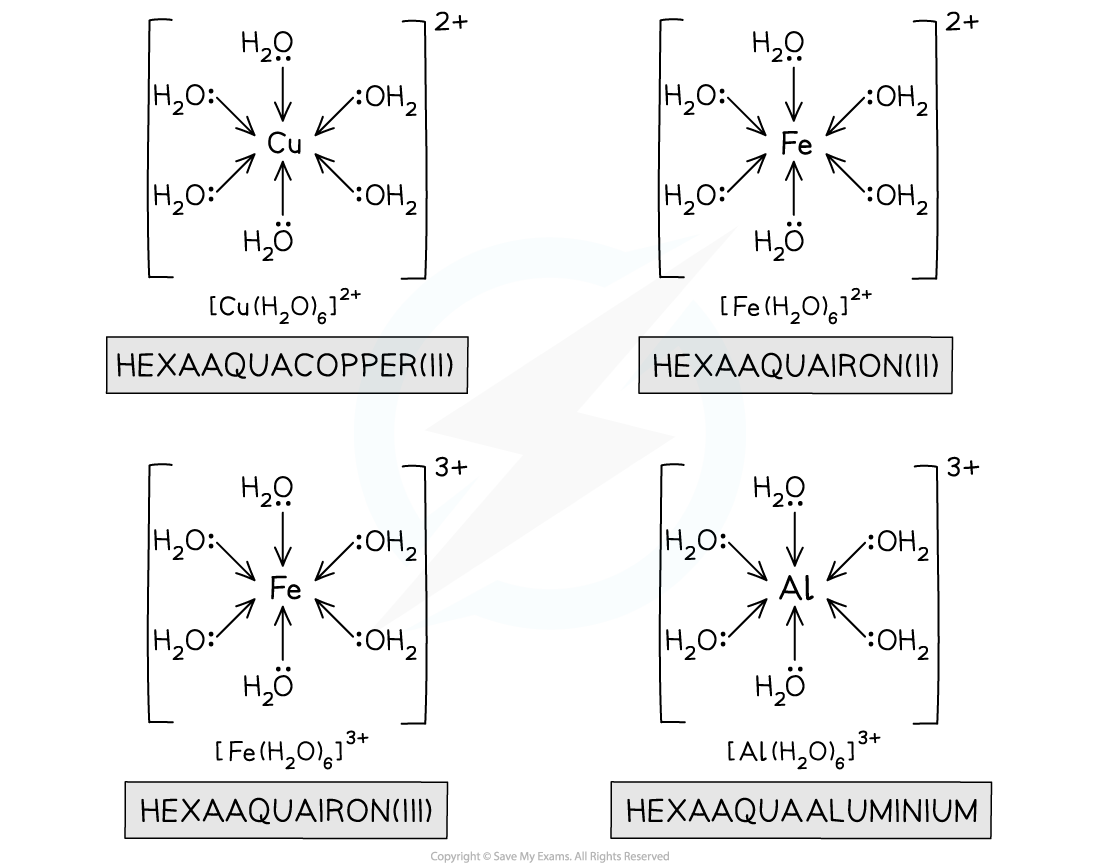
Hexaaqua complex ions of +2 and +3 metal ions
Lewis Acids and Bases
- In the section of acids and bases we saw the Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases
An acid is a substance which can behave as a proton donor
A base is a substance which can behave as a proton acceptor
- Gilbert Lewis is better known in the topic of bonding theory as the chemist whose name is given to electron dot structures of atoms, ions and molecules
- Lewis applied these structures to Brønsted-Lowry theory and realised that acid-base reactions can be interpreted in terms of electron pairs movements rather than in terms of proton transfer
- For example when ammonia reacts with a proton an electron pair moves from ammonia to the proton:
H+ + NH3 → NH4+

The Lewis diagram shows that the base donates an electron pair to forming a dative covalent bond with the proton
- This lead to a new definition of acids and bases
A Lewis acid is a species which can bond by accepting a lone pair of electrons
A Lewis base is a species which can bond by donating a lone pair of electrons
- The bond formed is an example of a co-ordinate or dative covalent bond
- Following these definitions you should be able to see that in a metal-aqua complex ion:
- The metal is a Lewis acid
- The water is a Lewis base
- Although this definition of acids and bases is not required to be learned for the exam, you can see that it is a very useful concept for chemists when explaining movements of electrons pairs in a variety of situations
Acidity in Metal-Aqua Ions
- You might imagine that salts of transition metal ions would be neutral in water
- However, ions of +3 aqua complexes are noticeably acidic compared to the +2 ions
- For example the pKa of [Fe(H2O)6] 3+ (aq) is 2.2 which is significantly more acidic than ethanoic acid which has a pKa of 4.8 (remember the lower the pKa the more acidic the species is)
- The reason for this is that +3 ions are smaller and therefore have a higher charge density than +2 ions
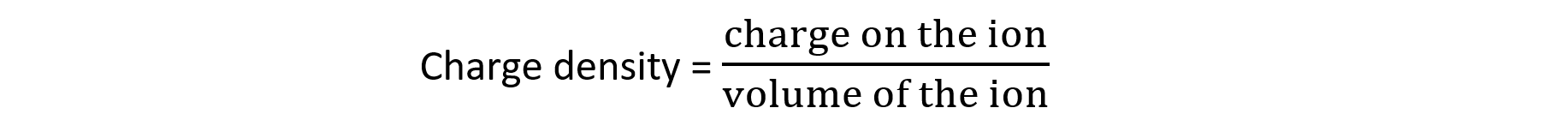
- The higher charge density pulls the water molecules more strongly, which weakens the O-H bond and results in more dissociation, producing a more acidic solution
- We say that the metal ion polarises the water molecules
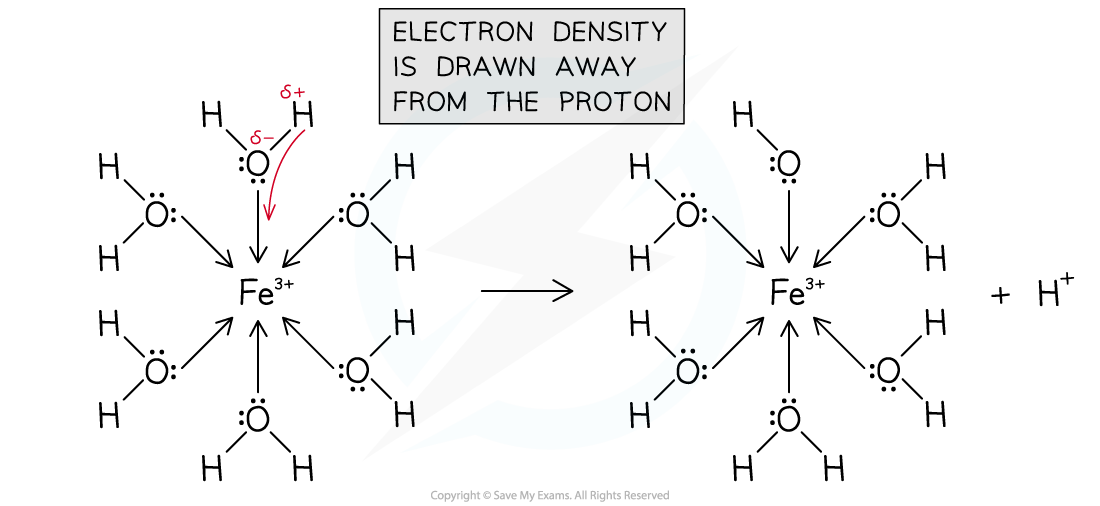
Metal(III) ions have a high charge density and polarise water molecules in the hexaaqua complexes
- This results in hydrogen ions (protons) splitting from the complexes creating acidic solutions
[Fe(H2O)6] 3+ (aq) → [Fe(H2O)5(OH)] 2+ (aq) + H+ (aq)
- Notice that the loss of the proton results in the new pentaaqua complex having a +2 charge
- Another way to think of this is the left over hydroxide ion from splitting a water molecule is negatively charged and cancels one of the charges on the complex ion
- The reaction process can also be shown with the hydroxonium ion as the product:
[Fe(H2O)6] 3+ (aq) + H2O (l) → [Fe(H2O)5(OH)] 2+ (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
- These reactions are sometime called deprotonation reactions and occur in several steps
[Fe(H2O)6] 3+ (aq) → [Fe(H2O)5(OH)] 2+ (aq) + H+ (aq)
[Fe(H2O)5(OH)] 2+ (aq) → [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + (aq) + H+ (aq)
- However, the third deprotonation does not usually occur without the presence of a base
- The base facilitates the removal of the third proton and results in the precipitation of the insoluble hydrated iron(III)hydroxide which appears as a foxy red precipitate:
[Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + (aq) + OH- → Fe(H2O)3(OH)3 (s) + H2O (l)
Exam Tip
The splitting of water molecules can be called a hydrolysis reaction
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









