- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记3.3.1 Digestion
The Process of Digestion
- Digestion is a process in which relatively large, insoluble biological molecules in food (such as starch, proteins) are hydrolysed into smaller, soluble molecules that can be absorbed across the cell membranes into the bloodstream and delivered to cells in the body
- Enzymes are essential for the process of digestion as they catalyse the hydrolysis
- These small soluble molecules (such as glucose and amino acids) are used either to provide cells with energy (via respiration) or to build other molecules for cell growth, repair and function
- Proteins are hydrolysed into amino acids
- Carbohydrates are hydrolysed into simple sugars
- Lipids are hydrolysed into a mixture of glycerol and fatty acids
Human Digestive System
- The human digestive system includes the following:
- Glands - the salivary glands and glands in the pancreas produce digestive juices
- The stomach and small intestine - the sites of digestion
- The liver - produces bile
- Small intestine - the site of absorption
- Large intestine - site of water reabsorption
Digestive System Table



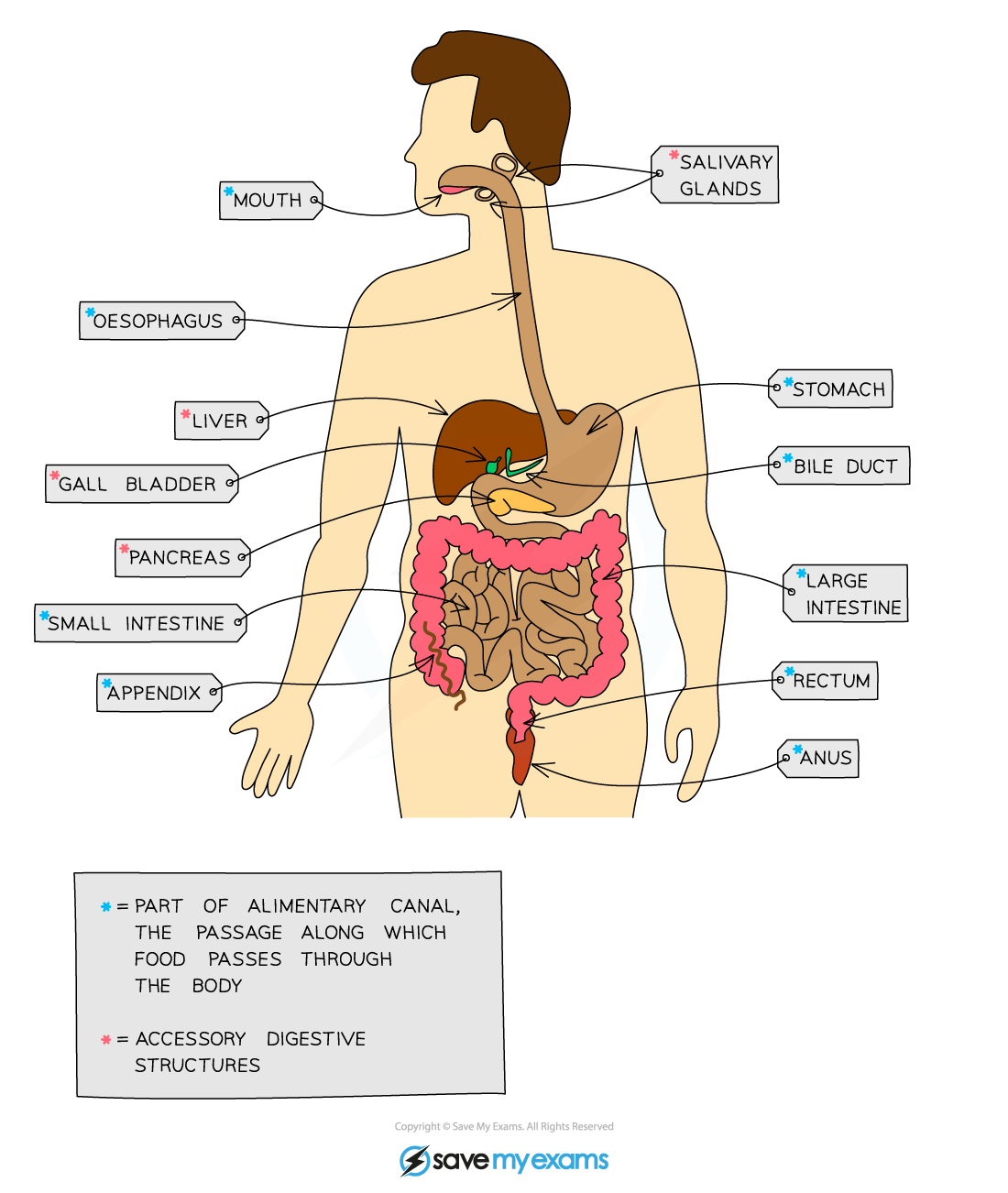
The human digestive system
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








