- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
2005 AMC12A 真题及答案详细解析
2005 AMC 12 A 真题
真题及解析
Problem 1
Two is ![]() of
of ![]() and
and ![]() of
of ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 2
The equations ![]() and
and ![]() have the same solution. What is the value of
have the same solution. What is the value of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 3
A rectangle with diagonal length ![]() is twice as long as it is wide. What is the area of the rectangle?
is twice as long as it is wide. What is the area of the rectangle?
![]()
Problem 4
A store normally sells windows at ![]() each. This week the store is offering one free window for each purchase of four. Dave needs seven windows and Doug needs eight windows. How much will they save if they purchase the windows together rather than separately?
each. This week the store is offering one free window for each purchase of four. Dave needs seven windows and Doug needs eight windows. How much will they save if they purchase the windows together rather than separately?
![]()
Problem 5
The average (mean) of 20 numbers is 30, and the average of 30 other numbers is 20. What is the average of all 50 numbers?
![]()
Problem 6
Josh and Mike live 13 miles apart. Yesterday, Josh started to ride his bicycle toward Mike's house. A little later Mike started to ride his bicycle toward Josh's house. When they met, Josh had ridden for twice the length of time as Mike and at four-fifths of Mike's rate. How many miles had Mike ridden when they met?
![]()
Problem 7
Square ![]() is inside the square
is inside the square ![]() so that each side of
so that each side of ![]() can be extended to pass through a vertex of
can be extended to pass through a vertex of ![]() . Square
. Square ![]() has side length
has side length ![]() and
and ![]() . What is the area of the inner square
. What is the area of the inner square ![]() ?
?![[asy] unitsize(4cm); defaultpen(linewidth(.8pt)+fontsize(10pt)); pair D=(0,0), C=(1,0), B=(1,1), A=(0,1); pair F=intersectionpoints(Circle(D,2/sqrt(5)),Circle(A,1))[0]; pair G=foot(A,D,F), H=foot(B,A,G), E=foot(C,B,H); draw(A--B--C--D--cycle); draw(D--F); draw(C--E); draw(B--H); draw(A--G); label("$A$",A,NW); label("$B$",B,NE); label("$C$",C,SE); label("$D$",D,SW); label("$E$",E,NNW); label("$F$",F,ENE); label("$G$",G,SSE); label("$H$",H,WSW);[/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/6/7/b67d246a0ea0a1efc85e8d70586644afa3a3d2ad.png)
![]()
Problem 8
Let ![]() , and
, and ![]() be digits with
be digits with
![]()
What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 9
There are two values of ![]() for which the equation
for which the equation ![]() has only one solution for
has only one solution for ![]() . What is the sum of these values of
. What is the sum of these values of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 10
A wooden cube ![]() units on a side is painted red on all six faces and then cut into
units on a side is painted red on all six faces and then cut into ![]() unit cubes. Exactly one-fourth of the total number of faces of the unit cubes are red. What is
unit cubes. Exactly one-fourth of the total number of faces of the unit cubes are red. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 11
How many three-digit numbers satisfy the property that the middle digit is the average of the first and the last digits?
![]()
Problem 12
A line passes through ![]() and
and ![]() . How many other points with integer coordinates are on the line and strictly between
. How many other points with integer coordinates are on the line and strictly between ![]() and
and ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 13
In the five-sided star shown, the letters ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are replaced by the numbers 3, 5, 6, 7 and 9, although not necessarily in that order. The sums of the numbers at the ends of the line segments
are replaced by the numbers 3, 5, 6, 7 and 9, although not necessarily in that order. The sums of the numbers at the ends of the line segments ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() form an arithmetic sequence, although not necessarily in that order. What is the middle term of the arithmetic sequence?
form an arithmetic sequence, although not necessarily in that order. What is the middle term of the arithmetic sequence?
![[asy] draw((0,0)--(0.5,1.54)--(1,0)--(-0.31,0.95)--(1.31,0.95)--cycle); label("$A$",(0.5,1.54),N); label("$B$",(1,0),SE); label("$C$",(-0.31,0.95),W); label("$D$",(1.31,0.95),E); label("$E$",(0,0),SW); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/7/4/b742a9eaa62d04f46229732736080eeb97f05475.png)
![]()
Problem 14
On a standard die one of the dots is removed at random with each dot equally likely to be chosen. The die is then rolled. What is the probability that the top face has an odd number of dots?
![]()
Problem 15
Let ![]() be a diameter of a circle and
be a diameter of a circle and ![]() be a point on
be a point on ![]() with
with ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be points on the circle such that
be points on the circle such that ![]() and
and ![]() is a second diameter. What is the ratio of the area of
is a second diameter. What is the ratio of the area of ![]() to the area of
to the area of ![]() ?
?
![[asy] unitsize(2.5cm); defaultpen(fontsize(10pt)+linewidth(.8pt)); dotfactor=3; pair O=(0,0), C=(-1/3.0), B=(1,0), A=(-1,0); pair D=dir(aCos(C.x)), E=(-D.x,-D.y); draw(A--B--D--cycle); draw(D--E--C); draw(unitcircle,white); drawline(D,C); dot(O); clip(unitcircle); draw(unitcircle); label("$E$",E,SSE); label("$B$",B,E); label("$A$",A,W); label("$D$",D,NNW); label("$C$",C,SW); draw(rightanglemark(D,C,B,2));[/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/8/0/a805b2766042251797b5817c889a0fb79a637874.png)
![]()
Problem 16
Three circles of radius ![]() are drawn in the first quadrant of the
are drawn in the first quadrant of the ![]() -plane. The first circle is tangent to both axes, the second is tangent to the first circle and the
-plane. The first circle is tangent to both axes, the second is tangent to the first circle and the ![]() -axis, and the third is tangent to the first circle and the
-axis, and the third is tangent to the first circle and the ![]() -axis. A circle of radius
-axis. A circle of radius ![]() is tangent to both axes and to the second and third circles. What is
is tangent to both axes and to the second and third circles. What is ![]() ?
?
![[asy] import graph; unitsize(3mm); defaultpen(linewidth(.8pt)+fontsize(10pt)); dotfactor=3; pair O0=(9,9), O1=(1,1), O2=(3,1), O3=(1,3); pair P0=O0+9*dir(-45), P3=O3+dir(70); pair[] ps={O0,O1,O2,O3}; dot(ps); draw(Circle(O0,9)); draw(Circle(O1,1)); draw(Circle(O2,1)); draw(Circle(O3,1)); draw(O0--P0,linetype("3 3")); draw(O3--P3,linetype("2 2")); draw((0,0)--(18,0)); draw((0,0)--(0,18)); label("$r$",midpoint(O0--P0),NE); label("$s$",(-1.5,4)); draw((-1,4)--midpoint(O3--P3));[/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/9/6/4967d5a2daac64647e471b55c1508bbf1d113eff.png)
![]()
Problem 17
A unit cube is cut twice to form three triangular prisms, two of which are congruent, as shown in Figure 1. The cube is then cut in the same manner along the dashed lines shown in Figure 2. This creates nine pieces. What is the volume of the piece that contains vertex ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 18
Call a number "prime-looking" if it is composite but not divisible by 2, 3, or 5. The three smallest prime-looking numbers are 49, 77, and 91. There are 168 prime numbers less than 1000. How many prime-looking numbers are there less than 1000?
![]()
Problem 19
A faulty car odometer proceeds from digit 3 to digit 5, always skipping the digit 4, regardless of position. If the odometer now reads 002005, how many miles has the car actually traveled?
![]()
Problem 20
For each ![]() in
in ![]() , define
, define

Let ![]() , and
, and ![]() for each integer
for each integer ![]() . For how many values of
. For how many values of ![]() in
in ![]() is
is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 21
How many ordered triples of integers ![]() , with
, with ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , satisfy both
, satisfy both ![]() and
and ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 22
A rectangular box ![]() is inscribed in a sphere of radius
is inscribed in a sphere of radius ![]() . The surface area of
. The surface area of ![]() is 384, and the sum of the lengths of its 12 edges is 112. What is
is 384, and the sum of the lengths of its 12 edges is 112. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 23
Two distinct numbers ![]() and
and ![]() are chosen randomly from the set
are chosen randomly from the set ![]() . What is the probability that
. What is the probability that ![]() is an integer?
is an integer?
![]()
Problem 24
Let ![]() . For how many polynomials
. For how many polynomials ![]() does there exist a polynomial
does there exist a polynomial ![]() of degree 3 such that
of degree 3 such that ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 25
Let ![]() be the set of all points with coordinates
be the set of all points with coordinates ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are each chosen from the set
are each chosen from the set ![]() . How many equilateral triangles have all their vertices in
. How many equilateral triangles have all their vertices in ![]() ?
?
![]()
2005 AMC12 A 真题答案详细解析
 .
.
- Let
 be the width, so the length is
be the width, so the length is  . By the Pythagorean Theorem,
. By the Pythagorean Theorem,  . The area of the rectangle is
. The area of the rectangle is  .
. - For
 windows, the store offers a discount of
windows, the store offers a discount of  (floor function). Dave receives a discount of
(floor function). Dave receives a discount of  and Doug receives a discount of
and Doug receives a discount of  . These amount to
. These amount to  dollars in discounts. Together, they receive a discount of
dollars in discounts. Together, they receive a discount of  , so they save
, so they save  .
. - The sum of the first 20 numbers is
 and the sum of the other 30 numbers is
and the sum of the other 30 numbers is  . Hence the overall average is
. Hence the overall average is  .
. - Let
 be the distances traveled by Josh and Mike, respectively, and let
be the distances traveled by Josh and Mike, respectively, and let  be the time and rate of Mike. Using
be the time and rate of Mike. Using  , we have that
, we have that  and
and  . Then
. Then 
 .
. 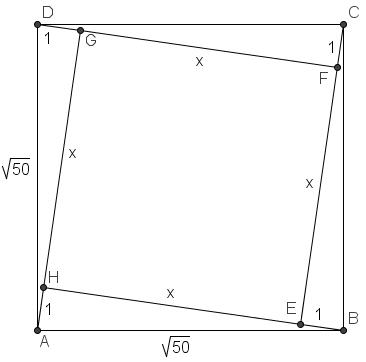 Arguable the hardest part of this question is to visualize the diagram. Since each side of
Arguable the hardest part of this question is to visualize the diagram. Since each side of  can be extended to pass through a vertex of
can be extended to pass through a vertex of  , we realize that
, we realize that  must be tilted in such a fashion. Let a side of
must be tilted in such a fashion. Let a side of  be
be  .
.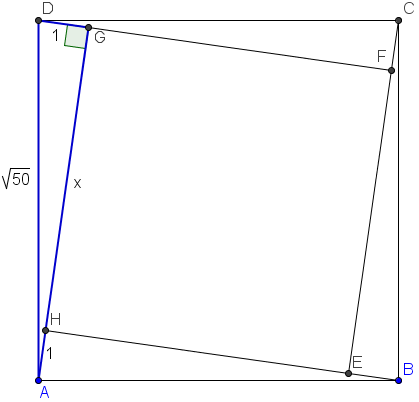 Notice the right triangle (in blue) with legs
Notice the right triangle (in blue) with legs  and hypotenuse
and hypotenuse  . By the Pythagorean Theorem, we have
. By the Pythagorean Theorem, we have  . Thus,
. Thus, ![$[EFGH] = x^2 = 36 mathrm{(C)}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/d/3/2d30f9bca378f43e18618306b3247b27128bf96f.png)
- Clearly the two quantities are both integers, so we check the prime factorization of
 . It is easy to see now that
. It is easy to see now that  works, so the answer is
works, so the answer is  .
. -
Solution 1
A quadratic equation always has two roots, unless it has a double root. That means we can write the quadratic as a square, and the coefficients 4 and 9 suggest this. Completing the square,
 , so
, so  . The sum of these is
. The sum of these is 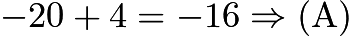 .
.Solution 2
Another method would be to use the quadratic formula, since our
 coefficient is given as 4, the
coefficient is given as 4, the  coefficient is
coefficient is  and the constant term is
and the constant term is  . Hence,
. Hence,  Because we want only a single solution for
Because we want only a single solution for  , the determinant must equal 0. Therefore, we can write
, the determinant must equal 0. Therefore, we can write  which factors to
which factors to  ; using Vieta's formulas we see that the sum of the solutions for
; using Vieta's formulas we see that the sum of the solutions for  is the opposite of the coefficient of
is the opposite of the coefficient of  , or
, or  .
.Solution 3
Using the discriminant, the result must equal
 .
. 



 Therefore,
Therefore,  or
or  , giving a sum of
, giving a sum of  .
. - There are
 sides total on the unit cubes, and
sides total on the unit cubes, and  are painted red.
are painted red.
-
Solution 1
Let the digits be
 so that
so that  . In order for this to be an integer,
. In order for this to be an integer,  and
and  have to have the same parity. There are
have to have the same parity. There are  possibilities for
possibilities for  , and
, and  for
for  .
.  depends on the value of both
depends on the value of both  and
and  and is unique for each
and is unique for each  . Thus our answer is
. Thus our answer is  .
.Solution 2
Thus, the three digits form an arithmetic sequence.
- If the numbers are all the same, then there are
 possible three-digit numbers.
possible three-digit numbers. - If the numbers are different, then we count the number of strictly increasing arithmetic sequences between
 and
and  and multiply by 2 for the decreasing ones:
and multiply by 2 for the decreasing ones:
Common difference Sequences possible Number of sequences 1 
8 2 
6 3 
4 4 
2 This gives us
 . However, the question asks for three-digit numbers, so we have to ignore the four sequences starting with
. However, the question asks for three-digit numbers, so we have to ignore the four sequences starting with  . Thus our answer is
. Thus our answer is  .
. - If the numbers are all the same, then there are
- For convenience’s sake, we can transform
 to the origin and
to the origin and  to
to  (this does not change the problem). The line
(this does not change the problem). The line  has the equation
has the equation  . The coordinates are integers if
. The coordinates are integers if  , so the values of
, so the values of  are
are  , with a total of
, with a total of  coordinates.
coordinates.  (i.e., each number is counted twice). The sum
(i.e., each number is counted twice). The sum  will always be
will always be  , so the arithmetic sequence has a sum of
, so the arithmetic sequence has a sum of  . The middle term must be the average of the five numbers, which is
. The middle term must be the average of the five numbers, which is  .
.
Solution 2
Let the terms in the arithmetic sequence be
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  . We seek the middle term
. We seek the middle term  .
.These five terms are
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  , in some order. The numbers
, in some order. The numbers  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  are equal to 3, 5, 6, 7, and 9, in some order, so
are equal to 3, 5, 6, 7, and 9, in some order, so![[A + B + C + D + E = 3 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 9 = 30.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/0/b/9/0b950e851b01fdef4121776d71bceb64dea71e98.png) Hence, the sum of the five terms is
Hence, the sum of the five terms is![[(A + B) + (B + C) + (C + D) + (D + E) + (E + A) = 2A + 2B + 2C + 2D + 2E = 60.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/6/b/96b4e29fc241c3a8aa1f8d21141905fb3dc1ea96.png) But adding all five numbers, we also get
But adding all five numbers, we also get  , so
, so![[5a + 10d = 60.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/a/d/4ad7963ccb0acc510587c8046427c72115b6e099.png) Dividing both sides by 5, we get
Dividing both sides by 5, we get  , which is the middle term. The answer is (D).
, which is the middle term. The answer is (D).- There are
 dots total. Casework:
dots total. Casework:
- The dot is removed from an even face. There is a
 chance of this happening. Then there are 4 odd faces, giving us a probability of
chance of this happening. Then there are 4 odd faces, giving us a probability of  .
. - The dot is removed from an odd face. There is a
 chance of this happening. Then there are 2 odd faces, giving us a probability of
chance of this happening. Then there are 2 odd faces, giving us a probability of  .
.
Thus the answer is
 .
. - The dot is removed from an even face. There is a
-
Solution 1
Notice that the bases of both triangles are diameters of the circle. Hence the ratio of the areas is just the ratio of the heights of the triangles, or
 (
( is the foot of the perpendicular from
is the foot of the perpendicular from  to
to  ).
).Call the radius
 . Then
. Then  ,
,  . Using the Pythagorean Theorem in
. Using the Pythagorean Theorem in  , we get
, we get  .
.Now we have to find
 . Notice
. Notice  , so we can write the proportion:
, so we can write the proportion:


By the Pythagorean Theorem in
 , we have
, we have  .
.Our answer is
 .
.Solution 2
Let the center of the circle be
 .
.Note that
 .
. is midpoint of
is midpoint of  .
. is midpoint of
is midpoint of  Area of
Area of  Area of
Area of  Area of
Area of  Area of
Area of  .
.Solution 3
Let
 be the radius of the circle. Note that
be the radius of the circle. Note that  so
so  .
.By Power of a Point Theorem,
 , and thus
, and thus 
Then the area of
 is
is  . Similarly, the area of
. Similarly, the area of  is
is  , so the desired ratio is
, so the desired ratio is 
Solution 4
![[asy] unitsize(2.5cm); defaultpen(fontsize(10pt)+linewidth(.8pt)); dotfactor=3; pair O=(0,0), C=(-1/3.0), B=(1,0), A=(-1,0); pair D=dir(aCos(C.x)), e=(-D.x,-D.y); pair H=(e.x,0); draw(A--B--D--cycle); draw(D--e--C); draw(unitcircle,white); drawline(D,C); dot(O); clip(unitcircle); draw(unitcircle); label("$E$",e,SSE); label("$B$",B,NE); label("$A$",A,W); label("$D$",D,NNW); label("$C$",C,SW); label("$H$",H,SE); draw(e--H,dashed); label("O",(0,0),NE); label("1",(C--O),N); label("1",(H--O),N); label("2",(A--C),N); label("2",(H--B),N); label("3",(O--D),NE); label("3",(O--e),NE); label("$2sqrt{2}$",(D--C),W); label("$2sqrt{2}$",(H--e),E); draw(rightanglemark(e,(e.x,0),A,2)); draw(rightanglemark(D,C,B,2));[/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/d/2/dd276b3fa631d279f22b09f353851f773945afe3.png)
Let the center of the circle be
 . Without loss of generality, let the radius of the circle be equal to
. Without loss of generality, let the radius of the circle be equal to  . Thus,
. Thus,  and
and  . As a consequence of
. As a consequence of  ,
,  and
and  . Also, we know that
. Also, we know that  and
and  are both equal to
are both equal to  due to the fact that they are both radii. Thus from the Pythagorean Theorem, we have DC being equal to
due to the fact that they are both radii. Thus from the Pythagorean Theorem, we have DC being equal to  or
or  . Now we know that the area of
. Now we know that the area of ![$[ABD]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/2/e/a2e886f9746495f49e9bb5c7ab9d8e393231e5c9.png) is equal to
is equal to  or
or  . Know we need to find the area of
. Know we need to find the area of ![$[DCE]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/6/5/365f98311a8062205054014e404205f5028cbbf4.png) . By simple inspection
. By simple inspection ![$[COD]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/d/b/4db3affeebe46ef1fb7262b32cb46229bda61c04.png)

![$[HOE]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/e/c/3/ec3e82c0897d27f1e72aac92c7693b7eef19f58a.png) due to angles being equal and CPCTC. Thus
due to angles being equal and CPCTC. Thus  and
and  . Know we know the area of
. Know we know the area of ![$[CHE]=frac{(1+1)(2sqrt{2})}{2}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/7/f/4/7f4cc6c1a0f0dbe3bea0acaafdacd0a67ad13817.png) or
or  . We also know that the area of
. We also know that the area of ![$[OHE]=frac{(1)(2sqrt{2})}{2}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/7/1/271a94f9a12c3c2e91b038039eca8b442057daa8.png) or
or  . Thus the area of
. Thus the area of ![$[COE]=2sqrt{2}-sqrt{2}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/0/d/d0d64c05ee8f73411ec303f3e62795b7954eb767.png) or
or  . We also can calculate the area of
. We also can calculate the area of ![$[DOC]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/4/6/a4652203f508b47f5c17bf26d8f125c58acd5a26.png) to be
to be  or
or  . Thus
. Thus ![$[DCE]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/6/5/365f98311a8062205054014e404205f5028cbbf4.png) is equal to
is equal to ![$[COE]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/6/4/4648746a07833d7ffb1328efc8c982ef917f77d6.png) +
+ ![$[DOC]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/4/6/a4652203f508b47f5c17bf26d8f125c58acd5a26.png) or
or  or
or  . The ratio between
. The ratio between ![$[DCE]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/6/5/365f98311a8062205054014e404205f5028cbbf4.png) and
and ![$[ABD]$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/2/e/a2e886f9746495f49e9bb5c7ab9d8e393231e5c9.png) is equal to
is equal to  or
or 
 .
.Solution 5
We will use the shoelace formula. Our origin is the center of the circle. Denote the ordered pair for
 , and notice how
, and notice how  is a 180 degree rotation of
is a 180 degree rotation of  , using the rotation matrix formula we get
, using the rotation matrix formula we get  . WLOG say that this circle has radius
. WLOG say that this circle has radius  . We can now find points
. We can now find points  ,
,  , and
, and  which are
which are  ,
,  , and
, and  respectively. By shoelace the area of
respectively. By shoelace the area of  is
is  , and the area of
, and the area of  is
is  . Using division we get that the answer is
. Using division we get that the answer is  .
.Solution 6 (Mass Points)
![[asy] /* Geogebra to Asymptote conversion, documentation at artofproblemsolving.com/Wiki go to User:Azjps/geogebra */ import graph; size(7cm); real labelscalefactor = 0.5; /* changes label-to-point distance */ pen dps = linewidth(0.7) + fontsize(10); defaultpen(dps); /* default pen style */ pen dotstyle = black; /* point style */ real xmin = -4.24313994860289, xmax = 6.360350402147026, ymin = -8.17642986522568, ymax = 4.1323989018072735; /* image dimensions */ pen wrwrwr = rgb(0.3803921568627451,0.3803921568627451,0.3803921568627451); /* draw figures */ draw(circle((0.9223776980185863,-1.084225871478444), 3.171161249925393), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw((-0.5623104956355617,1.717909856970905)--(-0.39884850438732933,-3.9670413347199647), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw((-2.2487343499798245,-1.1018908670262892)--(4.0935388680341624,-1.0849377800575102), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw((-0.4813673187299407,-1.0971666418223938)--(2.1729847859273126,-3.904641555130568), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw((-0.5623104956355617,1.717909856970905)--(2.1561002471522333,-3.887757016355488), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw((-2.2487343499798245,-1.1018908670262892)--(-0.5623104956355617,1.717909856970905), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw((-0.5623104956355617,1.717909856970905)--(4.0935388680341624,-1.0849377800575102), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw(circle((-2.858607769046372,-1.1524617347926092), 0.45463011998128017), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw(circle((4.790088296064635,-1.144019465405069), 0.45463011998128006), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw(circle((-0.9168858099122313,-1.6336710898823752), 0.45463011998127983), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw(circle((1.4976032349241348,-1.3128648531558642), 0.4546301199812797), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw(circle((-0.815578577261755,2.334195522261307), 0.4546301199812809), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); draw(circle((2.6119827940793803,-4.5546962979711285), 0.45463011998128033), linewidth(2) + wrwrwr); /* dots and labels */ dot((0.9223776980185863,-1.084225871478444),dotstyle); dot((-0.5623104956355617,1.717909856970905),dotstyle); label("$D$", (-0.49477234053524466,1.8867552447217006), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((-0.39884850438732933,-3.9670413347199647),dotstyle); dot((-2.2487343499798245,-1.1018908670262892),dotstyle); label("A", (-2.183226218043193,-0.9329627307165757), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((4.0935388680341624,-1.0849377800575102),dotstyle); label("B", (4.165360361386693,-0.9160781919414961), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((-0.4813673187299407,-1.0971666418223938),linewidth(4pt) + dotstyle); label("C", (-0.41034964665984724,-0.9667318082667347), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((2.1729847859273126,-3.904641555130568),dotstyle); dot((2.1561002471522333,-3.887757016355488),dotstyle); label("E", (2.2236384022525524,-3.7189116286046926), NE * labelscalefactor); label("2", (-2.9261459241466903,-1.2031153511178476), NE * labelscalefactor,wrwrwr); label("1", (4.722550140964316,-1.186230812342768), NE * labelscalefactor,wrwrwr); label("3", (-0.9844239650125497,-1.6758824368200735), NE * labelscalefactor,wrwrwr); label("4", (1.4300650798238166,-1.355076200093563), NE * labelscalefactor,wrwrwr); label("2", (-0.8831167323620728,2.2919841753236083), NE * labelscalefactor,wrwrwr); label("2", (2.5444446389790625,-4.5969076449088275), NE * labelscalefactor,wrwrwr); clip((xmin,ymin)--(xmin,ymax)--(xmax,ymax)--(xmax,ymin)--cycle); /* end of picture */ [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/2/d/d2d391f1ccbef581393d977447e8cd92d3b98e0d.png)
We set point
 as a mass of 2. This means that point
as a mass of 2. This means that point  has a mass of
has a mass of  since
since  . This implies that point
. This implies that point  has a mass of
has a mass of  and the center of the circle has a mass of
and the center of the circle has a mass of  . After this, we notice that points
. After this, we notice that points  and
and  both must have a mass of
both must have a mass of  since
since  and they are both radii of the circle.
and they are both radii of the circle.To find the ratio of the areas, we do the reciprocal of the multiplication of the mass points of DCE and the multiplication of ABD divided by each other. Which is simply
 which is
which is  (the reciprocal of 3)
(the reciprocal of 3) 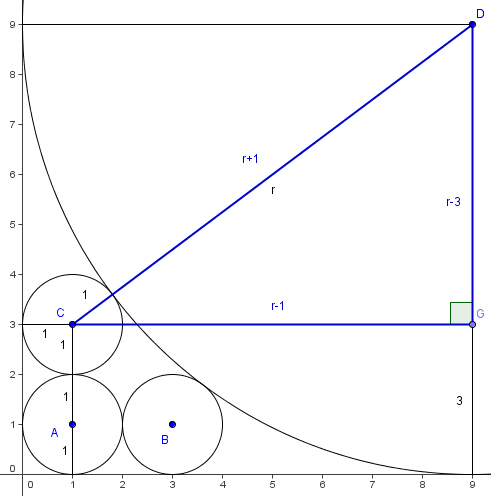 Without loss of generality, let
Without loss of generality, let  . Draw the segment between the center of the third circle and the large circle; this has length
. Draw the segment between the center of the third circle and the large circle; this has length  . We then draw the radius of the large circle that is perpendicular to the x-axis, and draw the perpendicular from this radius to the center of the third circle. This gives us a right triangle with legs
. We then draw the radius of the large circle that is perpendicular to the x-axis, and draw the perpendicular from this radius to the center of the third circle. This gives us a right triangle with legs  and hypotenuse
and hypotenuse  . The Pythagorean Theorem yields:
. The Pythagorean Theorem yields:



Quite obviously
 , so
, so  and
and  .
.- It is a pyramid with height
 and base area
and base area  , so using the formula for the volume of a pyramid,
, so using the formula for the volume of a pyramid,  .
. - The given states that there are
 prime numbers less than
prime numbers less than  , which is a fact we must somehow utilize. Since there seems to be no easy way to directly calculate the number of "prime-looking" numbers, we can apply complementary counting. We can split the numbers from
, which is a fact we must somehow utilize. Since there seems to be no easy way to directly calculate the number of "prime-looking" numbers, we can apply complementary counting. We can split the numbers from  to
to  into several groups:
into several groups: 



 . Hence, the number of prime-looking numbers is
. Hence, the number of prime-looking numbers is  (note that
(note that  are primes).We can calculate
are primes).We can calculate  using the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion: (the values of
using the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion: (the values of  and their intersections can be found quite easily)
and their intersections can be found quite easily)


Substituting, we find that our answer is
 .
. -
Solution 1
We find the number of numbers with a
 and subtract from
and subtract from  . Quick counting tells us that there are
. Quick counting tells us that there are  numbers with a 4 in the hundreds place,
numbers with a 4 in the hundreds place,  numbers with a 4 in the tens place, and
numbers with a 4 in the tens place, and  numbers with a 4 in the units place (counting
numbers with a 4 in the units place (counting  ). Now we apply the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion. There are
). Now we apply the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion. There are  numbers with a 4 in the hundreds and in the tens, and
numbers with a 4 in the hundreds and in the tens, and  for both the other two intersections. The intersection of all three sets is just
for both the other two intersections. The intersection of all three sets is just  . So we get:
. So we get:
Solution 2
Alternatively, consider that counting without the number
 is almost equivalent to counting in base
is almost equivalent to counting in base  ; only, in base
; only, in base  , the number
, the number  is not counted. Since
is not counted. Since  is skipped, the symbol
is skipped, the symbol  represents
represents  miles of travel, and we have traveled
miles of travel, and we have traveled  miles. By basic conversion,
miles. By basic conversion, 
-
Solution 1
For the two functions
 and
and  ,as long as
,as long as  is between
is between  and
and  ,
,  will be in the right domain, so we don't need to worry about the domain of
will be in the right domain, so we don't need to worry about the domain of  .
.Also, every time we change
 , the expression for the final answer in terms of
, the expression for the final answer in terms of  will be in a different form(although they'll all satisfy the final equation), so we get a different starting value of
will be in a different form(although they'll all satisfy the final equation), so we get a different starting value of  . Every time we have two choices for
. Every time we have two choices for  ) and altogether we have to choose
) and altogether we have to choose  times. Thus,
times. Thus,  .
.Note: the values of x that satisfy
![$f^{[n]}(x) = frac {1}{2}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/7/7/b774d366e9a86636a0a3997073f80ee5a0149743.png) are
are  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, .
.Solution 2
We are given that
![$f^{[2005]}(x) = frac {1}{2}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/f/8/cf8eae18d34cdc34dd8eb5c5567f33e726ef8bb4.png) . Thus,
. Thus, ![$f(f^{[2004]}(x))=frac{1}{2}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/6/6/f668ee7c291e18b1df5169984a5e7eafcf5e67a6.png) . Let
. Let ![$f^{[2004]}(x)$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/8/5/285d6d53dec29d3b1f4452b5cf413e8d4c072e0c.png) be equal to
be equal to  . Thus
. Thus  or
or  or
or  . Now we know
. Now we know ![$f^{[2004]}(x)$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/8/5/285d6d53dec29d3b1f4452b5cf413e8d4c072e0c.png) is equal to
is equal to  or
or  . Now we know that
. Now we know that ![$f(f^{[2003]}(x))=frac{1}{4}$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/9/a/29a0962b1a52904e89b2f327367cc00444084fcf.png) or
or  . Now we solve for
. Now we solve for ![$f^{[2003]}(x)$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/f/b/dfbad44ab10772cc79ef6fedb6f2377099af4e68.png) and let
and let ![$f^{[2003]}(x)=z$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/f/e/9fe4a36537e191815c0f7506fe4b2c0f84a22f80.png) . Thus
. Thus  is equal to
is equal to  ,
, ,
, ,and
,and  . As we see,
. As we see, ![$f^{[2005]}(x)$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/7/8/a7847a0f23d0dd2ddbc119cccf0265be6933d1c3.png) has 1 solution,
has 1 solution, ![$f^{[2004]}(x)$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/8/5/285d6d53dec29d3b1f4452b5cf413e8d4c072e0c.png) has 2 solutions, and
has 2 solutions, and ![$f^{[2003]}(x)$](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/f/b/dfbad44ab10772cc79ef6fedb6f2377099af4e68.png) has 4 solutions. Thus for each iteration we double the number of possible solutions. There are 2005 iterations and thus the number of solutions is
has 4 solutions. Thus for each iteration we double the number of possible solutions. There are 2005 iterations and thus the number of solutions is 

 Casework upon
Casework upon  :
:
 : Then
: Then  . Thus we get
. Thus we get  .
. : Then
: Then  . Thus we get
. Thus we get  .
. : Then the exponent of
: Then the exponent of  becomes huge, and since
becomes huge, and since  there is no way we can satisfy the second condition. Hence we have two ordered triples
there is no way we can satisfy the second condition. Hence we have two ordered triples 
- Box P has dimensions
 ,
,  , and
, and  . Its surface area is
. Its surface area is![[2lw+2lh+2wl=384,]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/e/6/be6f4fdd31b4b9eb2042e2256288b5ca1e0d73c5.png) and the sum of all its edges is
and the sum of all its edges is![[l + w + h = dfrac{4l+4w+4h}{4} = dfrac{112}{4} = 28.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/8/6/3/86391c1d6be352d4b06253140f65e260ee99b750.png) The diameter of the sphere is the space diagonal of the prism, which is
The diameter of the sphere is the space diagonal of the prism, which is![[sqrt{l^2 + w^2 +h^2}.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/1/3/31384be5c4dd31ee79fefadd8f754b0e543415a6.png) Notice that
Notice that![[(l + w + h)^2 - (2lw + 2lh + 2wh) = l^2 + w^2 + h^2 = 784 - 384 = 400,]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/0/e/20ea50479e3eb41006e5cba6901f12d434e6abda.png) so the diameter is
so the diameter is![[sqrt{l^2 + w^2 +h^2} = sqrt{400} = 20.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/8/a/b8ab71d91a8a41cd30d5290648d0c972a78086d5.png) The radius is half of the diameter, so
The radius is half of the diameter, so![[r=frac{20}{2} = boxed{textbf{(B)} 10}.]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/8/a/0/8a0ac99e9fe30e6457565990dbbf925afcada5c3.png)
- Let
 , so
, so  . Define
. Define  ,
,  ; then
; then  , so
, so  . Here we can just make a table and count the number of values of
. Here we can just make a table and count the number of values of  per value of
per value of  . The largest possible value of
. The largest possible value of  is 12, and we get
is 12, and we get  .The total number of ways to pick two distinct numbers is
.The total number of ways to pick two distinct numbers is  , so we get a probability of
, so we get a probability of  .
. - We can write the problem as
 .
.Since
 and
and  ,
,  . Thus,
. Thus,  , so
, so  .
.


Hence, we conclude
 ,
,  , and
, and  must each be
must each be  ,
,  , or
, or  . Since a quadratic is uniquely determined by three points, there can be
. Since a quadratic is uniquely determined by three points, there can be  different quadratics
different quadratics  after each of the values of
after each of the values of  ,
,  , and
, and  are chosen.
are chosen.However, we have included
 which are not quadratics: lines. Namely,
which are not quadratics: lines. Namely,




Clearly, we could not have included any other constant functions. For any linear function, we have
 because
because  is y-value of the midpoint of
is y-value of the midpoint of  and
and  . So we have not included any other linear functions. Therefore, the desired answer is
. So we have not included any other linear functions. Therefore, the desired answer is  .
. -
Solution 1 (non-rigorous)
For this solution, we will just find as many solutions as possible, until it becomes intuitive that there are no more size of triangles left.
First, try to make three of its vertices form an equilateral triangle. This we find is possible by taking any vertex, and connecting the three adjacent vertices into a triangle. This triangle will have a side length of
 ; a quick further examination of this cube will show us that this is the only possible side length (red triangle in diagram). Each of these triangles is determined by one vertex of the cube, so in one cube we have 8 equilateral triangles. We have 8 unit cubes, and then the entire cube (green triangle), giving us 9 cubes and
; a quick further examination of this cube will show us that this is the only possible side length (red triangle in diagram). Each of these triangles is determined by one vertex of the cube, so in one cube we have 8 equilateral triangles. We have 8 unit cubes, and then the entire cube (green triangle), giving us 9 cubes and  equilateral triangles.
equilateral triangles.![[asy] import three; unitsize(1cm); size(200); currentprojection=perspective(1/3,-1,1/2); draw((0,0,0)--(2,0,0)--(2,2,0)--(0,2,0)--cycle); draw((0,0,0)--(0,0,2)); draw((0,2,0)--(0,2,2)); draw((2,2,0)--(2,2,2)); draw((2,0,0)--(2,0,2)); draw((0,0,2)--(2,0,2)--(2,2,2)--(0,2,2)--cycle); draw((2,0,0)--(0,2,0)--(0,0,2)--cycle,green); draw((1,0,0)--(0,1,0)--(0,0,1)--cycle,red); label("$x=2$",(1,0,0),S); label("$z=2$",(2,2,1),E); label("$y=2$",(2,1,0),SE); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/d/f/5df79423812cec695f4ed646285125bf0839a518.png)
 vertices.
vertices.
Now, we look for any additional equilateral triangles. Connecting the midpoints of three non-adjacent, non-parallel edges also gives us more equilateral triangles (blue triangle). Notice that picking these three edges leaves two vertices alone (labelled A and B), and that picking any two opposite vertices determine two equilateral triangles. Hence there are
 of these equilateral triangles, for a total of
of these equilateral triangles, for a total of  .
.![[asy] import three; unitsize(1cm); size(200); currentprojection=perspective(1/3,-1,1/2); draw((0,0,0)--(2,0,0)--(2,2,0)--(0,2,0)--cycle); draw((0,0,0)--(0,0,2)); draw((0,2,0)--(0,2,2)); draw((2,2,0)--(2,2,2)); draw((2,0,0)--(2,0,2)); draw((0,0,2)--(2,0,2)--(2,2,2)--(0,2,2)--cycle); draw((1,0,0)--(2,2,1)--(0,1,2)--cycle,blue); label("$x=2$",(1,0,0),S); label("$z=2$",(2,2,1),E); label("$y=2$",(2,1,0),SE); label("$A$",(0,2,0), NW); label("$B$",(2,0,2), NW); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/b/1/fb1ab57797018d7c00bf2d7e5ac2b67c4f698629.png)
Solution 2 (rigorous)
The three-dimensional distance formula shows that the lengths of the equilateral triangle must be
 , which yields the possible edge lengths of
, which yields the possible edge lengths of


 are the only lengths that work, from which we can use the same counting argument as above.
are the only lengths that work, from which we can use the same counting argument as above.
以上解析方式仅供参考
学术活动报名扫码了解!免费领取历年真题!

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1










